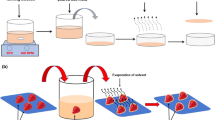
Abstract
Complex emulsions are potential colloidal dispersions in formulating edible films, but these emulsions often have a low stability while their formulation is very complicated. This study, therefore, focuses on formulating water-in-oil-in-water (W/O/W) emulsions stabilized by the mixtures of biopolymers (including pectin and cellulose extracted from the coffee pulps) using the ultrasound technology. Classical techniques including a rheology analyzer, texture analyzer, and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) were applied to evaluate the stability of double emulsions and physicochemical properties of edible films. Obtained results revealed that W/O/W emulsions could be formulated from the biopolymer solutions using the ultrasound technology. These double emulsions showed a high stability, and the phase separation did not occur during 1 week of the storage at the ambient temperature. Edible films based on W/O/W emulsions have a high mechanical resistance (tensile strength of 1.3–1.8 MPa and Young’s modulus of 40–50 MPa), a high melting point (120–140 °C), a low water vapor permeability (3–16 g.mm.m−2.h−1.KPa−1), and a high antioxidant capacity (2.5–4.4 kg film/mol DPPH).




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Alghooneh, A., Mohammad Amini, A., Behrouzian, F., & Razavi, S. M. A. (2017). Characterisation of cellulose from coffee silverskin. International Journal of Food Properties, 20(11), 2830–2843. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2016.1253097
Arham, R., Mulyati, M. T., Metusalach, M., & Salengke, S. (2016). Physical and mechanical properties of agar based edible film with glycerol plasticizer. International Food Research Journal, 23(4), 1669–1675.
Artiga-Artigas, M., Molet-Rodríguez, A., Salvia-Trujillo, L., & Martín-Belloso, O. (2019). Formation of Double (W 1 /O/W 2) Emulsions as carriers of hydrophilic and lipophilic active compounds. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 12(3), 422–435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-018-2221-3
Bátori, V., Jabbari, M., Åkesson, D., Lennartsson, P. R., Taherzadeh, M. J., & Zamani, A. (2017). Production of pectin-cellulose biofilms: A new approach for citrus waste recycling. International Journal of Polymer Science, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9732329
Cataldo, V. A., Cavallaro, G., Lazzara, G., Milioto, S., & Parisi, F. (2017). Coffee grounds as filler for pectin: Green composites with competitive performances dependent on the UV irradiation. Carbohydrate Polymers, 170, 198–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.04.092
Chaichi, M., Hashemi, M., Badii, F., & Mohammadi, A. (2017). Preparation and characterization of a novel bionanocomposite edible film based on pectin and crystalline nanocellulose. Carbohydrate Polymers, 157, 167–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.09.062
Collazo-Bigliardi, S., Ortega-Toro, R., & Chiralt Boix, A. (2018). Isolation and characterisation of microcrystalline cellulose and cellulose nanocrystals from coffee husk and comparative study with rice husk. Carbohydrate Polymers, 191, 205–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.03.022
Dao, D. N., Le, P. H., Do, D. X., Dang, T. M. Q., Nguyen, S. K., & Nguyen, V. (2022). Pectin and cellulose extracted from coffee pulps and their potential in formulating biopolymer films. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-02339-x
de Vargas, V. H., Marczak, L. D. F., Flôres, S. H., & Mercali, G. D. (2022). Advanced technologies applied to enhance properties and structure of films and coatings: A review. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 15(6), 1224–1247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-022-02768-6
Esquivel, P., & Jiménez, V. M. (2012). Functional properties of coffee and coffee by-products. Food Research International, 46(2), 488–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2011.05.028
Farahnaky, A., Saberi, B., & Majzoobi, M. (2013). Effect of glycerol on physical and mechanical properties of wheat starch edible films. Journal of Texture Studies, 44(3), 176–186. https://doi.org/10.1111/jtxs.12007
Gökkaya Erdem, B., Dıblan, S., & Kaya, S. (2021). A comprehensive study on sorption, water barrier, and physicochemical properties of some protein- and carbohydrate-based edible films. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 14(11), 2161–2179. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-021-02712-0
Huynh Mai, C., Thanh Diep, T., Le, T. T. T., & Nguyen, V. (2020). Advances in colloidal dispersions: A review. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology, 41(4), 479–494. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2019.1591970
Jiménez, A., Fabra, M. J., Talens, P., & Chiralt, A. (2012). Edible and biodegradable starch films: A review. Food and Bioprocess Technology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-012-0835-4
Jolayemi, O. S., Stranges, N., Flamminii, F., Casiraghi, E., & Alamprese, C. (2021). Influence of free and encapsulated olive leaf phenolic extract on the storage stability of single and double emulsion salad dressings. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 14(1), 93–105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-020-02574-y
Khadem, B., & Sheibat-Othman, N. (2019). Theoretical and experimental investigations of double emulsion preparation by ultrasonication. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 58(19), 8220–8230. research-article. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.9b00556
Kodal Coşkun, B., Çalikoǧlu, E., Karagöz Emiroǧlu, Z., & Candoǧan, K. (2014). Antioxidant active packaging with soy edible films and oregano or thyme essential oils for oxidative stability of ground beef patties. Journal of Food Quality, 37(3), 203–212. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfq.12089
Leong, T. S. H., Zhou, M., Zhou, D., Ashokkumar, M., & Martin, G. J. O. (2018). The formation of double emulsions in skim milk using minimal food-grade emulsifiers – A comparison between ultrasonic and high pressure homogenisation efficiencies. Journal of Food Engineering, 219, 81–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2017.09.018
Liu, F., Jiang, Y., Du, B., Chai, Z., Jiao, T., Zhang, C., et al. (2013). Design and characterization of controlled-release edible packaging films prepared with synergistic whey-protein polysaccharide complexes. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 61(24), 5824–5833. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf4009923
Mendes, J. F., Norcino, L. B., Manrich, A., Pinheiro, A. C. M., Oliveira, J. E., & Mattoso, L. H. C. (2020). Characterization of pectin films integrated with cocoa butter by continuous casting: Physical, thermal and barrier properties. Journal of Polymers and the Environment, 28(11), 2905–2917. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-020-01829-1
Murillo-Martínez, M. M., Pedroza-Islas, R., Lobato-Calleros, C., Martínez-Ferez, A., & Vernon-Carter, E. J. (2011). Designing W1/O/W2 double emulsions stabilized by protein-polysaccharide complexes for producing edible films: Rheological, mechanical and water vapour properties. Food Hydrocolloids, 25(4), 577–585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2010.06.015
Murthy, P. S., Manjunatha, M. R., Sulochannama, G., & Naidu, M. M. (2012). Extraction, characterization and bioactivity of coffee anthocyanins. European Journal of Biological Sciences, 4(1), 13–19. https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.ejbs.2012.4.1.6149
Murthy, P. S., & Madhava Naidu, M. (2012). Sustainable management of coffee industry by-products and value addition - A review. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 66, 45–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2012.06.005
Mussatto, S. I., Machado, E. M. S., Martins, S., & Teixeira, J. A. (2011). Production, composition, and application of coffee and its industrial residues. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 4(5), 661–672. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-011-0565-z
Ng, H. M., Sin, L. T., Tee, T. T., Bee, S. T., Hui, D., Low, C. Y., & Rahmat, A. R. (2015). Extraction of cellulose nanocrystals from plant sources for application as reinforcing agent in polymers. Composites Part B: Engineering, 75, 176–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2015.01.008
Otoni, C. G., Avena-Bustillos, R. J., Azeredo, H. M. C., Lorevice, M. V., Moura, M. R., Mattoso, L. H. C., & McHugh, T. H. (2017). Recent advances on edible films based on fruits and vegetables—A review. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 16(5), 1151–1169. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12281
Pastor, C., Sánchez-González, L., Chiralt, A., Cháfer, M., & González-Martínez, C. (2013). Physical and antioxidant properties of chitosan and methylcellulose based films containing resveratrol. Food Hydrocolloids, 30(1), 272–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2012.05.026
Phan, T. D., Debeaufort, F., Luu, D., & Voilley, A. (2005). Functional properties of edible agar-based and starch-based films for food quality preservation. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 53(4), 973–981. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf040309s
Phan The, D., Debeaufort, F., Voilley, A., & Luu, D. (2009a). Biopolymer interactions affect the functional properties of edible films based on agar, cassava starch and arabinoxylan blends. Journal of Food Engineering, 90(4), 548–558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2008.07.023
Phan The, D., Debeaufort, F., Voilley, A., & Luu, D. (2009b). Influence of hydrocolloid nature on the structure and functional properties of emulsified edible films. Food Hydrocolloids, 23(3), 691–699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2008.05.006
Reichembach, L. H., & de Oliveira Petkowicz, C. L. (2020). Extraction and characterization of a pectin from coffee (Coffea arabica L.) pulp with gelling properties. Carbohydrate Polymers, 245(June), 116473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116473
Ribeiro, A. M., Estevinho, B. N., & Rocha, F. (2020). Edible films prepared with different biopolymers, containing polyphenols extracted from elderberry (Sambucus Nigra L.), to protect food products and to improve food functionality. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 13(10), 1742–1754. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-020-02516-8
Ribeiro, A. M., Estevinho, B. N., & Rocha, F. (2021,). Preparation and incorporation of functional ingredients in edible films and coatings. Food and Bioprocess Technology. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-020-02528-4
Rojas-Bravo, M., Rojas-Zenteno, E. G., Hernández-Carranza, P., Ávila-Sosa, R., Aguilar-Sánchez, R., Ruiz-López, I. I., & Ochoa-Velasco, C. E. (2019). A potential application of mango (Mangifera indica L. cv Manila) peel powder to increase the total phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity of edible films and coatings. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 12(9), 1584–1592. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-019-02317-8
Talón, E., Trifkovic, K. T., Nedovic, V. A., Bugarski, B. M., Vargas, M., Chiralt, A., & González-Martínez, C. (2017). Antioxidant edible films based on chitosan and starch containing polyphenols from thyme extracts. Carbohydrate Polymers, 157, 1153–1161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.10.080
Tang, Y., Yang, S., Zhang, N., & Zhang, J. (2014). Preparation and characterization of nanocrystalline cellulose via low-intensity ultrasonic-assisted sulfuric acid hydrolysis. Cellulose, 21(1), 335–346. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0158-2
Teng, F., He, M., Xu, J., Chen, F., Wu, C., Wang, Z., & Li, Y. (2020). Effect of ultrasonication on the stability and storage of a soy protein isolate-phosphatidylcholine nanoemulsions. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-70462-8
Thanh Diep, T., Phan Dao, T., Vu, H. T., Quoc Phan, B., Ngoc Dao, D., & Huu Bui, T. (2018). Double emulsion oil-in water-in oil (O/W/O) stabilized by sodium caseinate and k-carrageenan. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2018.1462198
Ulloa Rojas, J. B., Verreth, J. A. J., Amato, S., & Huisman, E. A. (2003). Biological treatments affect the chemical composition of coffee pulp. Bioresource Technology, 89(3), 267–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(03)00070-1
Valdespino-León, M., Calderón-Domínguez, G., De La Paz Salgado-Cruz, M., Rentería-Ortega, M., Farrera-Rebollo, R. R., & Morales-Sánchez, E. (2020). Biodegradable electrosprayed pectin films: An alternative to valorize coffee mucilage. Waste and Biomass Valorization, (0123456789). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-020-01194-z
Vartiainen, J., Vähä-Nissi, M., & Harlin, A. (2014). Biopolymer films and coatings in packaging applications—A review of recent developments. Materials Sciences and Applications, 05(10), 708–718. https://doi.org/10.4236/msa.2014.510072
Xu, J., Li, X., Xu, Y., Wang, A., Xu, Z., Wu, X., et al. (2021). Dihydromyricetin-loaded pickering emulsions stabilized by dialdehyde cellulose nanocrystals for preparation of antioxidant gelatin–based edible films. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 14(9), 1648–1661. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-021-02664-5
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Phan The Dong (Saigon University, Vietnam) for his support relating to SEM measurement and discussion. Ms. Pham Thanh Lam (Nong Lam University) was acknowledged for her support relating to DSC measurements.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the International Found Science (Grant: I-3-F-6281, recipient: Viet Nguyen).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Phuong Hong Le: investigation, methodology, data curation, writing—original draft. Duy Ngoc Dao: investigation, methodology, resources, data curation. Ha Thu Thi Huynh: investigation, data curation. Phuong Thanh Nguyen: investigation, data curation. Viet Nguyen: supervision, conceptualization, writing—review editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Le, P.H., Dao, D.N., Huynh, H.T.T. et al. Formulation of Edible Films Based on W/O/W Emulsions Stabilized by Coffee Byproducts. Food Bioprocess Technol 16, 2531–2540 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-023-03088-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-023-03088-z