Abstract
Purpose of Review
The role of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) inhibitors, notably angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEi) or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), in the COVID-19 pandemic has not been fully evaluated. With an increasing number of COVID-19 cases worldwide, it is imperative to better understand the impact of RAAS inhibitors in hypertensive COVID patients. PubMed, Embase and the pre-print database Medrxiv were searched, and studies with data on patients on ACEi/ARB with COVID-19 were included. Random effects models were used to estimate the pooled mean difference with 95% confidence interval using Open Meta[Analyst] software.
Recent Findings
A total of 28,872 patients were included in this meta-analysis. The use of any RAAS inhibition for any conditions showed a trend to lower risk of death/critical events (OR 0.671, CI 0.435 to 1.034, p = 0.071). Within the hypertensive cohort, however, there was a significant lower association with deaths (OR 0.664, CI 0.458 to 0.964, p = 0.031) or the combination of death/critical outcomes (OR 0.670, CI 0.495 to 0.908, p = 0.010). There was no significant association of critical/death outcomes within ACEi vs non-ACEi (OR 1.008, CI 0.822 to 1.235, p = 0.941) and ARB vs non-ARB (OR 0.946, CI 0.735 to 1.218, p = 0.668).
Summary
This is the largest meta-analysis including critical events and mortality data on patients prescribed ACEi/ARB and found evidence of beneficial effects of chronic ACEi/ARB use especially in hypertensive cohort with COVID-19. As such, we would strongly encourage patients to continue with RAAS inhibitor pharmacotherapy during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), emerging from Wuhan, China, in December 2019 has quickly evolved into a global pandemic. It is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) [1] and affects all the organs of the body and especially the lungs. As of 20th May 2020, WHO reported 4,789,205 cases of COVID-19 worldwide and 318,789 deaths [2].
In such an unprecedented pandemic, the role of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) inhibitors, notably angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEi) or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), in COVID-19 has been questioned. The particular concern emerged given the significant role of ACE2 as a receptor for SARS-COV-2, which enables entry into host cells [3]. Considering the substantial expression of ACE2 receptors in the respiratory and cardiovascular system, it is not a surprise that SARS-COV-2 causes not only respiratory, but also extensive cardiac injury [4]. The chronic use of RAAS inhibitors has been speculated to increase the levels of ACE2 and potentially exaggerate the severity of COVID-19 with early reports supporting this [3].
RAAS inhibitors, although primarily used for hypertension, are indicated in other cardiovascular patients including those with prior myocardial infarction, heart failure, cerebrovascular disease or chronic kidney disease [5]. The patients with cardiovascular diseases are at particular risk of COVID-19 infections [6, 7]. Hence, with an increasing number of COVID-19 cases worldwide and the likelihood of a ‘second wave’ of infection, it is imperative to better understand the impact RAAS inhibitor use in COVID-19 patients. We, thus, conducted an up-to-date systematic review and meta-analysis of RAAS blockers in patients with COVID-19.
Methods
Search Strategy
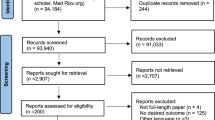
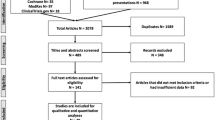
The systematic review was conducted and reported in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. PubMed and Embase and pre-print database Medrxiv were searched from inception to 17 May 2020 using key terms such as ‘Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme inhibitors’, ‘Angiotensin Receptor Blockers’, ‘coronavirus disease 2019’, and ‘SARS-COV-2’. The full search strategy is included in (Supplementary Figure 1). Studies published in languages other than English were excluded. A snowballing method was used to the references of retrieved papers to expand the search.
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
All studies identified in our search were screened using the titles and the abstracts. Duplicate studies and multiple reports from same studies were removed. Any article identified as having a potential of fulfilling our inclusion criteria underwent full-text evaluation. Any study design, except for narrative reviews or opinion-based publications, with ACEi/ARB data on adult (≥ 18 years) patients with COVID-19 was included, and relevant information such as type of study, characteristics of patients, mortality and data relating to clinical severity of COVID-19 infection was extracted.
The proportion of COVID-19 patients on ACEi/ARB and their mortality and clinical severity data was compared to non-ACEi/ARB patients. We only included deaths and ‘critical’ events in our analysis defined as ITU admission and invasive and non-invasive ventilation. Data for severe outcomes [8] including high-flow oxygen use but in a non-ITU [1] setting were excluded. Where studies included more than one outcome of ‘critical’ events, e.g. ITU admission and ECMO use, we only considered the lowest qualifying criterion to avoid double-counting of patients.
Statistical Analysis
The data was analysed using random effects in Open Meta[Analyst] software version 10.12 (developed by the Centre for Evidence Synthesis, Brown University, School of Public Health, RI, USA) [9]. Statistical heterogeneity was evaluated by calculating I2 statistics. The statistical significance was defined as p < 0.05.
Publication Bias
Funnel plots were used to assess publication bias using Review Manager (RevMan) software (Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014).
Study Quality
The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS), a nine-point scale to assess the quality of cohort and case control/case-series, was used to evaluate the included studies.
Results
Our search yielded 1031 studies from the database (PubMed and Embase) searches (Supplementary Figure 2). After de-duplication, we rejected 666 trials after title-abstract screening. A total of forty trials underwent full-text evaluation. Trials including clinically suspected COVID-19 patients but without a positive test [10] or no original data were excluded. A total of twenty studies were thus included in meta-analysis (Table 1). Following submission of our article, one study [6] was retracted [11], and therefore we excluded this from our analysis.
Most studies were retrospective, observational [3, 12,13,14,15], multi-centre studies mainly conducted in China [3, 12, 16,17,18]. There were no randomised controlled studies. Many studies included mortality data for a subgroup, commonly hypertensive patients in their analysis. One study used cardiovascular patients and the other studies included hypertensive patients with diabetes. All included trials scored six or higher than 6 (moderate to high) in the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) (Supplementary Table 1).
A total of 27.9% (8041/28872) of the patients with COVID-19 were on ACEi/ARBs (Table 1). Among hypertensive COVID-19 patients, 32.3% (3140/9706) were on ACEi/ARB.
Most studies categorised clinical outcomes for patients as ‘critical’ or ‘severe’ [3, 12, 16, 17] assessed using Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention report [19]. The patients with at least ‘critical’ clinical outcome or need for intensive care or who died were included in this analysis. In a pooled analysis of 16,099 patients in sixteen studies, there was a trend towards a reduction in the odds of death/critical outcomes in those on ACEi/ARB as compared to those not on ACEi/ARB (pooled OR 0.671, CI 0.435 to 1.034, p = 0.071) as shown in Fig. 1. Importantly among hypertensive patients in eleven studies (subgroup H), there was a significantly lower risk of death/critical outcomes (OR 0.670, CI 0.495 to 0.908, p = 0.010) (Fig. 1) confirming the safe chronic use of ACEi/ARB and an association with better outcomes. Sensitivity analysis of death/critical events for both groups together (hypertensive and non-hypertensive patients) rendered the overall results significant when each of four studies [7, 14, 20, 21•] was removed individually (Supplementary Figures 4–7). However, no significant changes were seen in the overall population when any of the other studies was excluded. Meta-regression, in addition to subgroup analyses, was done to estimate the effect of hypertension as a covariate which was not significant (p = 0.205).
Subgroup analysis of death/critical events in ACEi/ARB vs non-ACEi/ARB. Subgroup analysis of death/critical events (OR 0.671, CI 0.435 to 1.034, p = 0.071) in sixteen studies with 5996 patients on ACEi/ARB vs 10,103 non-ACEi/ARB patients. Total effect for subgroup H with 11 studies (OR 0.670, CI 0.495 to 0.908, p = 0.010). Subgroups H and T refer to reference population; H is hypertension, T for sample population with mixed comorbidities. I^2 refers to I2 as a measure of heterogeneity
A total of twelve studies reported death in patients taking ACEi/ARB vs non-ACEi/ARB. The meta-analysis demonstrated no increased risk of death in patients taking ACEi/ARB (pooled OR 0.857, CI 0.634 to 1.160, p = 0.318) as shown in Fig. 2. Among the hypertensive cohort (subgroup H), there was a statistically significant reduction in the odds of death/critical events in patients taking ACEi/ARB (OR 0.664, CI 0.458 to 0.964, p = 0.031).
Subgroup analysis of death in ACEi/ARB vs non-ACEi/ARB. Subgroup analysis of death in twelve studies (OR 0.857, CI 0.634 to 1.160, p = 0.318) in ACEi/ARB vs non-ACEi/ARB. Subgroup H with nine studies (OR 0.664, CI 0.458 to 0.964, p = 0.031).Subgroups H and T refer to reference population; H is hypertension; T for sample population with mixed comorbidities. I^2 refers to I2 as a measure of heterogeneity
Additionally, in a pooled analysis of nine studies that reported discrete data for ACEi, there was no association of critical/death outcomes in patients on ACEi as compared with those not on ACEi (OR 1.008, CI 0.822 to 1.235, p = 0.941) as shown in Fig. 3. With regard to patients on ARB, similarly, there was no difference (pooled OR 0.946, CI 0.735 to 1.218, p = 0.668) in critical/death compared to those non-ARB (Fig. 4), although for both ACEi and ARB, we might have been underpowered to detect a smaller effect.
Subgroup analysis of death/critical events in ACEi vs non-ACEi. Subgroup analysis of death/critical events in eight studies (OR 1.008, CI 0.822 to 1.235, p = 0.941) in ACEi vs non-ACEi. Subgroups H and T refer to reference population; H is hypertension, T for sample population with mixed comorbidities. I^2 refers to I2 as a measure of heterogeneity
Subgroup analysis of death/critical events in ARB vs non-ARB. Subgroup analysis of death/critical events in eight studies (OR 0.946, CI 0.735 to 1.218, p = 0.668) in ARB vs non-ARB. Subgroups H and T refers to reference population; H is hypertension, T for sample population with mixed comorbidities. I^2 refers to I2 as a measure of heterogeneity
Discussion
The role of RAAS blockers in COVID-19 remains to be fully elucidated, and this has led to significant discussions in the medical communities regarding the safety of these drugs. Whilst multiple national societies supported the continuous use of RAAS inhibitors, we have seen many patients unilaterally stopping them due to concerns after reading the initial reports [22,23,24]. The emerging outbreak means that there is a need for robust clinical data on these antihypertensives in COVID-19 patients [23].
Our meta-analysis, the largest and most detailed undertaken to date, showed a third of hypertensive and a quarter of overall COVID-19 patients were prescribed an ACEi/ARB, likely due to the increasing risk of infection in patients with comorbidities such as cardiovascular diseases, hypertension and diabetes [8]. Although cardiovascular diseases in combination with COVID-19 portend increased risk of severity and mortality [8, 12], the use of ACEi/ARB is not the likely culprit. The use of ACEi/ARB did not show any association with severity of disease or even death among patients admitted with COVID-19.
On the contrary, this meta-analysis showed that death/critical events may even decrease with the use of ACEi/ARB across pathologies, although the analysis failed statistical significance (p = 0.071). This effect however was magnified and was significant among the hypertensive cohorts. Hypertensive patients with COVID-19 who were on ACEi/ARB were 0.67 times less likely to have a fatal/critical outcome than those not on ACEi/ARB (p = 0.01). ACEi/ARB was also associated with a significantly lower risk of death (p = 0.03) in hypertensive patients. Our results are comparable to another meta-analysis comprising of nine studies and 3936 hypertensive patients. This study demonstrated a lower mortality association of ACEi/ARB treatment in hypertensive COVID-19 patients compared to non-ACEi/ARB (OR 0.57, 95% CI 0.38–0.84, p 0.004) [25••]. The benefits of RAAS inhibitors were comparable in both ACEi and ARB. Whilst we did not see a significantly lower risk of death/critical outcomes in patients taking ACE vs non-ACEi and in ARB vs non-ARB, as only a few studies included these data, our analysis might have been underpowered.
Nevertheless, our study in addition to reassuring patients taking RAAS inhibitors begs an important question on whether ACEi/ARB therapy has an obscure beneficial role in patients admitted with COVID-19. Animal studies previously have shown a downregulated expression of ACE2 following SARS infection which results in increased activation of RAAS [13, 26]. This leads to a sequelae of events [13], notably acute lung injury and consequently, adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) [27]. Thus, the use of ACEi/ARB and deactivation of RAAS might be beneficial in preventing this sequence of events [13].
In addition to the benefits of ACEi/ARB in cardiovascular patients [28, 29], our study clearly demonstrates the beneficial effects of ACEi/ARB especially in hypertensive cohort with COVID-19. Whilst the meta-analysis does not modify the existing clinical practice, it provides essential information on the use of RAAS blockers in COVID-19 patients and supports the recommendations of the national medical societies to continue treatment with these drugs [22,23,24]. Withholding ACEi/ARB could lead to compromising cardiopulmonary reserve in patients who are already at increased risk of COVID-19 [30, 31] which is an important issue for future research and warrants a clinical trial.
Limitations
Due to the emerging infection, there is insufficient data to compare these analyses to a control population. In order to undertake a comprehensive evaluation of all data on the usage of ACEi/ARB in COVID-19, the search strategy was inclusive. Pre-print data were included which could potentially introduce bias, but at this time of increasing COVID-19 disease, it was pertinent to review all relevant and essential data.
Furthermore, heterogeneity in the meta-analysis is likely due to the varied sample population or different definitions for severity of the disease. For instance, some studies only analysed hypertensive or cardiovascular patients or those of at least ‘moderate’ severity, whilst some are based on hospital inpatients which is likely to be of at least moderate in disease severity. Several steps were taken to decrease heterogeneity; a standard definition of ‘critical’, published by CDCC [19] was used and subgroup analysis of hypertensive patients was done. Additionally, those studies including clinically suspected/confirmed COVID-19 were excluded to keep a comparable group of patients.
Future Directions
Although our study sheds light on the association between RAAS blockers and mortality in COVID-19, it begs another question as to whether ACEi/ARB lowers the mortality in these patients. There are no clinical data currently on the effect of ACEi/ARB in COVID-19. In order to establish a viable association, future randomised controlled studies are required.
Conclusion
In conclusion, whilst our meta-analysis demonstrated no association between the use of ACEi/ARB and the severity and mortality among patients admitted with COVID-19, it found evidence of beneficial effects in the hypertensive cohort. As such, we would strongly recommend patients to continue with RAAS inhibitor pharmacotherapy during the COVID-19 pandemic. Further randomised clinical trials are warranted to confirm these findings.
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Huang Z, Cao J, Yao Y, Jin X, Luo Z, Xue Y, et al. The effect of RAS blockers on the clinical characteristics of COVID-19 patients with hypertension. Ann Transl Med. 2020;8:430.
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) Situation report-121 highlights. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/20200520-covid-19-sitrep-121.pdf?sfvrsn=c4be2ec6_4. Accessed 9 Aug 2020
Feng Y, Ling Y, Bai T, et al. COVID-19 with different severity: a multi-center study of clinical features. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.202002-0445OC.
Wang Y, Roever L, Tse G, Liu T. 2019-novel coronavirus-related acute cardiac injury cannot be ignored. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2020;22:14.
Kow CS, Zaidi STR, Hasan SS. Cardiovascular disease and use of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors in COVID-19. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2020;20:217–221.
Mehra MR, Desai SS, Kuy S, Henry TD, Patel AN. Cardiovascular disease, drug therapy, and mortality in Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:e102.
Guo T, Fan Y, Chen M, Wu X, Zhang L, He T, et al. Cardiovascular implications of fatal outcomes of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). JAMA Cardiol. 2020;5:811. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1017.
Li J, Wang X, Chen J, Zhang H, Deng A. Association of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors with severity or risk of death in patients with hypertension hospitalized for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection in Wuhan, China. JAMA Cardiol. 2020;5:825. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1624.
Wallace BC, Dahabreh IJ, Trikalinos TA, Lau J, Trow P, Schmid CH. Closing the gap between methodologists and end-users: R as a computational back-end. J Stat Softw. 2012;49:1–15.
Zeng Z, Sha T, Zhang Y, Wu F, Hu H, Li H, et al. Hypertension in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a single-center retrospective observational study short title: hypertension in COVID-19 pneumonia patients. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.04.06.20054825.
Mehra MR, Desai SS, Kuy S, Henry TD, Patel AN. Retraction: cardiovascular disease, drug therapy, and mortality in Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:2582. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2007621.NEJMc2021225.
Peng YD, Meng K, Guan HQ, Leng L, Zhu RR, Wang BY, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of 112 cardiovascular disease patients infected by 2019-nCoV. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2020;48:E004.
Zhang P, Zhu L, Cai J, et al. Association of inpatient use of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers with mortality among patients with hypertension hospitalized with COVID-19. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317134.
Mehta N, Kalra A, Nowacki AS, Anjewierden S, Han Z, Bhat P, et al. Association of use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers with testing positive for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). JAMA Cardiol. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1855.
de Abajo FJ, Rodríguez-Martín S, Lerma V, et al. Use of renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system inhibitors and risk of COVID-19 requiring admission to hospital: a case-population study. Lancet. 2020;6736:1–10.
Meng J, Xiao G, Zhang J, He X, Ou M, Bi J, et al. Renin-angiotensin system inhibitors improve the clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients with hypertension. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020;9:757–60.
Yang G, Tan Z, Zhou L, et al. Effects of ARBs and ACE is on virus infection, inflammatory status and clinical outcomes in COVID-19 patients with hypertension: a single center retrospective study. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15143.
Yan H, Valdes AM, Vijay A, et al. Role of drugs affecting the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system on susceptibility and severity of COVID-19: a large case-control study from Zheijang Province, China. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.04.24.20077875.
Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA - J Am Med Assoc. 2020;323:1239–42.
Richardson S, Hirsch JS, Narasimhan M, Crawford JM, McGinn T, Davidson KW, et al. Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York city area. JAMA. 2020;323:2052. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.6775.
• Dauchet L, Lambert M, Gauthier V, et al. ACE inhibitors, AT1 receptor blockers and COVID-19: clinical epidemiology evidences for a continuation of treatments. The ACER-COVID study. medRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.04.28.20078071. A recent study that suggested the risk and increased severity of COVID-19 infection was not associated with consumption of ACEi and ARB.
Position statement of the ESC council on hypertension on ACE-inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers. https://www.escardio.org/Councils/Council-on-Hypertension-(CHT)/News/position-statement-of-the-esc-council-on-hypertension-on-ace-inhibitors-and-ang. Accessed 25 May 2020.
HFSA/ACC/AHA statement addresses concerns re: using RAAS antagonists in COVID-19 - American College of Cardiology. https://www.acc.org/latest-in-cardiology/articles/2020/03/17/08/59/hfsa-acc-aha-statement-addresses-concerns-re-using-raas-antagonists-in-covid-19. Accessed 3 May 2020.
ESH LETTER COVID-19 | European Society of Hypertension. https://www.eshonline.org/spotlights/esh-letter-covid-19-2/. Accessed 25 May 2020.
•• Guo X, Zhu Y, Hong Y RESEARCH LETTER Decreased mortality of COVID-19 with renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors therapy in patients with hypertension: a meta-analysis. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15572. A recent meta-analysis demonstrating decreased mortality of covid-19 with Renin Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitors Therapy in hypertensive patients.
Liu L, Qiu HB, Yang Y, Wang L, Ding HM, Li HP. Losartan, an antagonist of AT1 receptor for angiotensin II, attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rat. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2009;481:131–6.
Reynolds HR, Adhikari S, Pulgarin C, et al. Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system inhibitors and risk of Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:2441–2448.
Dahlöf B, Hansson L, Lindholm LH, Scherstén B, Wester PO, Ekbom T, et al. Stop-hypertension 2: a prospective intervention trial of “newer” versus “older” treatment alternatives in old patients with hypertension. Blood Press. 1993;2:136–41.
Swedberg K, Held P, Kjekshus J, Rasmussen K, Rydén L, Wedel H. Effects of the early administration of enalapril on mortality in patients with acute myocardial infarction: results of the cooperative new Scandinavian Enalapril Survival Study II (Consensus II). N Engl J Med. 1992;327:678–84.
Pflugfelder PW, Baird G, Tonkon MJ, DiBianco R, Pitt B, The Quinapril Heart Failure Trial Investigators. Clinical consequences of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor withdrawl in chronic heart failure: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study of quinapril. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1993;22:1557–63.
Lee SM, Takemoto S, Wallace AW. Association between withholding angiotensin receptor blockers in the early postoperative period and 30-day mortality: a cohort study of the Veterans Affairs Healthcare system. Anesthesiology. 2015;123:288–306.
Availability of Data and Material
All data are available from the corresponding author on request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RB planned and designed the study, executed systematic review and meta-analysis and wrote first draft. MW executed systematic review and meta-analysis and amended significantly the manuscript. VV conceived, planned and designed the study, supervised the systematic review and meta-analysis and amended significantly the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Ranu Baral, Madeline White and Vassilios Vassiliou declare no conflicts of interest relevant to this manuscript.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Ethics Approval
Meta-analysis of published data, so no ethics approval was required.
Consent to Participate
N/A, meta-analysis
Consent for Publication
N/A, meta-analysis
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Evidence-Based Medicine, Clinical Trials and Their Interpretations
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 889 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Baral, R., White, M. & Vassiliou, V.S. Effect of Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitors in Patients with COVID-19: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of 28,872 Patients. Curr Atheroscler Rep 22, 61 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11883-020-00880-6
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11883-020-00880-6