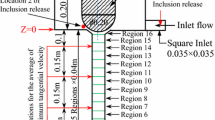
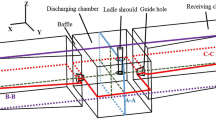
Abstract
To explore the effect of intermittent induction heating mode on inclusions in the tundish, a three-dimensional coupled electromagnetic field, flow field and inclusion field were developed. Numerical results show that medium frequency medium heating and medium frequency medium pause mode and head-to-tail long heating mode are beneficial to the removal of inclusions in the channel. At the same time, these two induction heating modes can not only help the macroscopic transmission and collision growth of inclusions but also help the removal of inclusions, which are two very good induction heating modes. The overall order of magnitude of the turbulent collision source term during induction heating is one order of magnitude higher than that of the turbulent collision source term without induction heating, and the difference within the channel is nearly two orders of magnitude, suggesting that the reasonable heating mode and heating time can help maximize the collision growth and removal of inclusions in the channel.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.X. Dou, B.W. Zhang, Q. Yue, and H. Xiao, Metalurgija 59, 125 (2020).
Q. Zhang, G. Xu, and K. Iwai, ISIJ Int. 62, 56 (2022).
X. Qing, C. Hong, X.P. Wang, H. He, H.Y. Tang, and J.Q. Zhang, Steel Res. Int. 93, 2100839 (2022).
X.Q. Chen, P. Wang, H. Xiao, B. Yi, H.Y. Tang, and J.Q. Zhang, J. Mater. Res. Technol. 24, 1410 (2023).
H.Y. Tang, K.M. Wang, S.L. Xiao, J.W. Liu, and J.Q. Zhang, Metals 11, 1075 (2021).
Q. Yue, C.B. Zhang, and X.H. Pei, Ironmak. Steelmak. 44, 227 https://doi.org/10.1080/03019233.2016.1209919 (2017).
L.F. Zhang, S.Q. Wang, Q.P. Dong, J.W. Gao, and L.N.W. Damoah, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 45, 2153 (2014).
S. Taniguchi and J.K.J.M. Brimacombe, Magnetohydrodynamics 32, 134 (1996).
K. Takahashi and S. Taniguchi, ISIJ Int. 43, 820 (2003).
Y. Sahai, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 47, 2095 (2016).
D. Mazumdar, Steel Res. Int. 90, 201800279 (2019).
S. Joo and R.I.L. Guthrie, Metall. Trans. B 24, 755 (1993).
K. Chattopadhyay, M. Isac, and R.I.L. Guithrie, ISIJ Int. 50, 331 (2010).
O.J. Ilegbusi and J. Szekely, ISIJ Int. 29, 1031 (1989).
Q. Wang, F.S. Qi, B.K. Li, and F. Tsukihashi, ISIJ Int. 54, 2796 (2014).
F. Xing, S.G. Zheng, Z.Q. Liu, and M.Y. Zhu, Metals. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9050561 (2019).
F. Xing, S.G. Zheng, and M.Y. Zhu, Steel Res. Int. https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.201700542 (2018).
H.Y. Tang, L.Z. Guo, G.H. Wu, H. Xiao, H.Y. Yao, and J.Q. Zhang, Metals. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8060374 (2018).
H. Lei, B. Yang, Q. Bi, Y.Y. Xiao, S.F. Chen, and C.Y. Ding, ISIJ Int. 59, 1811 (2019).
W.X. Dou, Z.X. Yang, Z.M. Wang, and Q. Yue, Metals 11, 1536 https://doi.org/10.3390/met11101536 (2021).
B. Yi, G.F. Zhang, Q. Jiang, P.P. Zhang, Z.H. Feng, and N. Tian, Materials. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16155254 (2023).
B. Yang, K. Liu, H. Lei, and P. Han, High Temp. Mater. Process. 41, 460 (2022).
D. Mazumdar and R.I.L. Guthrie, ISIJ Int. 39, 524 (1999).
H. Ling, L. Zhang, and H. Li, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 47, 2991 (2016).
B. Yang, H. Lei, Q. Bi, J.M. Jiang, H.W. Zhang, Y. Zhao, and J.A. Zhou, Steel Res. Int. 89, 1800173 (2018).
Acknowledgement
Thanks to the University of Science Technology of Liaoning United Fund (HGSKL-USTLN(2022)07) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, B., Lei, H. & Gou, D. Numerical Simulation of Inclusion Collision Growth and Removal in a Tundish with Intermittent Induction Heating. JOM (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-024-06589-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-024-06589-0