Abstract
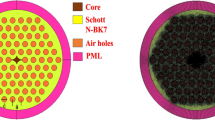
In order to compensate the dispersion accumulated in a single mode fiber (SMF) for higher communication capacity, a simplified dispersion-compensation microstructure fiber (DC-MSF) with seven cores is proposed in this paper. The fiber’s cladding is made of pure silica without air holes, and its outer cores are composed of six germanium up-doped cylinders, which has the advantage of simple structure. The finite element method (FEM) and beam propagation method (BPM) are used to study the properties of the fiber, and the relationship between the structural parameters of the fiber and the dispersion, as well as the phase matching wavelength, is obtained. By optimizing the structural parameters of the fiber, the dispersion of the fiber can reach −5 291.47 ps·nm−1·km−1 at 1 550 nm, and the coupling loss to the conventional single-mode fiber is only 0.137 dB. Compared with the conventional dispersion-compensation fiber, the fiber has lots of advantages, such as single mode transmission, easy to fabricate and low coupling loss with traditional SMF, etc.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ISLAM M I, AHMED K, SEN S, et al. Proposed square lattice photonic crystal fiber for extremely high nonlinearity, birefringence and ultra-high negative dispersion compensation[J]. Journal of optical communications, 2019, 40(4): 401–410.
UPADHYAY A, SINGH S, PRAJAPATI Y K, et al. Numerical analysis of large negative dispersion and highly birefringent photonic crystal fiber[J]. Optik-international journal for light and electron optics, 2020, 218: 164997.
ABDELAAL S M H, YOUNIS B M, OBAYYA S S A, et al. Highly negative dispersion dual-core liquid crystal photonic crystal fiber[J]. Optical fiber technology, 2020, 60: 102330.
LIU Z L, ZHANG C L, QU Y W. An all-solid dispersion-compensating photonic crystal fiber based on mode coupling mechanism in dual-concentric core[J]. International journal of optics, 2020, 2020: 4718054.
HOWLADER A H, ISLAM M S, RAZZAK S M A. Proposal for dispersion compensating square-lattice photonic crystal fiber[J]. Optoelectronics letters, 2021, 17(3): 160–164.
GÉRÔME F, AUGUSTE J L, BLONDY J M. Design of dispersion-compensating fibers based on a dual-concentric-core photonic crystal fiber[J]. Optics letters, 2004, 29(23): 2725–2727.
YANG S, ZHANG Y, PENG X, et al. Theoretical study and experimental fabrication of high negative dispersion photonic crystal fiber with large area mode field[J]. Optics express, 2006, 14(7): 3015–3023.
YUAN J, SANG X, YU C, et al. Large negative dispersion in dual-concentric-core photonic crystal fiber with hybrid cladding structure based on complete leaky mode coupling[J]. Optics communications, 2011, 284(24): 5847–5852.
HSU J M, ZHENG W H, LEE C L, et al. Theoretical investigation of a dispersion compensating photonic crystal fiber with ultra-high dispersion coefficient and extremely low confinement loss[J]. Photonics and nanostructures-fundamentals and applications, 2015, 16: 1–8.
WANG W, QU Y, ZHANG C, et al. Novel design of broadband dispersion compensating photonic crystal fiber with all solid structure and low index difference[J]. Optik-international journal for light and electron optics, 2017: S0030402617313736.
PANDEY S K, MAURYA J B, PRAJAPATI Y K. PCF design with extremely high nonlinearity and extremely negative dispersion[EB/OL]. (2021-08-22) [2023-04-26]. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs3.rs-426030/v1.
HOWLADER A H, ISLAM M S, RAZZAK S M A. Proposal for dispersion compensating square-lattice photonic crystal fiber[J]. Optoelectronics letters, 2021, 17(3): 160–164.
LIANG H, SHI W. Numerical studying of broadband tunable dispersion compensation based on photonic crystal fiber[J]. Optical engineering, 2022, 61(7): 076109.
SHAO W, LIANG H, MA F, et al. Coaxial dual-core dispersion compensation photonic crystal fiber with wavelength-tunable ultrahigh negative dispersion[J]. Journal of the optical society of America B, 2023.
FENG Y, FENG C, XU H, et al. Design and numerical analysis of large negative dispersion and ultra-high nonlinearity CS2 filled LCPCF[J]. Optical and quantum electronics, 2023.
ZHANG Y N. Optimization of highly nonlinear dispersion-flattened photonic crystal fiber for supercontinuum generation[J]. Chinese physics B, 2013, 22(001): 298–302.
SEIFOURI M, DEKAMIN M, OLYAEE S. A new circular chalcogenide/silica hybrid microstructured optical fiber with high negative dispersion for the purpose of dispersion compensation[J]. Optik-international journal for light and electron optics, 2015, 126(21): 3093–3098.
TSUCHIDA Y, SAITOH K, KOSHIBA M. Design of single-moded holey fibers with large-mode-area and low bending losses: the significance of the ring-core region[J]. Optics express, 2007, 15(4): 1794–1803.
BOURLIAGUET B, PARÉ C, MOND F, et al. Microstructured fiber splicing[J]. Optics express, 2003, 11(25): 3412–3417.
YANG M, XU H, LIN T, et al. A broadband polarization filter based on liquid crystal core and gold-coated microstructure fiber[J]. Optical and quantum electronics, 2021, 53: 572.
LI F, HE M, ZHANG X, et al. Ultra-high birefringence and nonlinearity photonic crystal fiber with a nanoscale core shaped by an air slot and silicon strips[J]. Optical fiber technology, 2020, 54: 102082.
STEEL M J, WHITE T P, STERKE M D, et al. Symmetry and degeneracy in microstructured optical fibers[J]. Optics letters, 2001, 26(8): 488–490.
ERONYAN M A, DEVETYAROV D R, REUTSKIY A A, et al. MCVD method for manufacturing polarization-maintaining and radiation resistant optical fiber with germanosilicate elliptical core[J]. Materials letters, 2021, 10: 301.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
This work has been supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (No.F2021203002), the Science and Technology Project of Hebei Education Department (No.ZD2021409), the Research Projects of Talent Project Training Funds of Hebei Province (No.C20221067), the Talent Project of Tangshan City (No.A202110009), and the Science and Technology Project of Tangshan City (No.22130216G).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Wang, C., Yang, H. et al. A simplified dispersion-compensation microstructure fiber with seven cores. Optoelectron. Lett. 20, 216–221 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11801-024-3131-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11801-024-3131-4