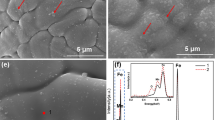
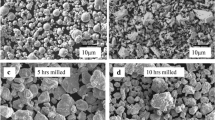
Abstract
Massive vanadium additions as hard phases in powder metallurgy high-speed steels (PM HSS) lead to higher cost and bad machinability. In this study, ultrahigh alloy PM HSS with CPM121 (10W−5Mo−4Cr−10V−9Co, wt.%) as the basic composition, was directly compacted and activation sintered with near-full density (>99.0%) using pre-oxidized and ball-mixed element and carbide powders. Niobium-alloyed steels (w(V)+w(Nb)=10 wt.%) show higher hardness and wear resistance, superior secondary-hardening ability and temper resistance. But excess niobium addition (>5 wt.%) leads to coarsened carbides and deteriorated toughness. EPMA results proved that niobium tends to distribute in MC carbides and forces element W to form M6C and WC carbides. Further, the role of rotary forging on properties of niobium-alloyed steels (S3) was researched. After rotary forging with deformation of 40%, the bending strength and fracture toughness of niobium-alloyed steels could be further improved by 20.74% and 43.86% compared with those of sample S3 without rotary forging, respectively.
摘要
超高钒粉末冶金高速钢通常存在加工困难、生产成本高的问题。研究以超高合金粉末高速钢 CPM121 (10W−5Mo−4Cr−10V−9Co, wt.%)作为基础成分,采用元素和碳化物的预氧化球磨混合粉为原料, 经压制、活化烧结制得致密化(>99.0%)的样品,研究铌的添加(w(V)+w(Nb)=10 wt.%)对 CPM121 粉末 冶金高速钢组织和性能的影响。结果表明:铌强化高速钢表现出较高的硬度及耐磨性、优异的二次硬 化性能和抗回火性。但当铌含量超过5%时则会导致组织中碳化物的粗化和偏聚现象,进而导致材料 的强韧性降低。EPMA 结果表明铌是MC 碳化物的形成元素,促使大量W 在M6C 及WC 碳化物中聚 集。其次,旋锻变形可以大幅度提高材料的强韧性,成分为S3(3%Nb+7%V)的 CPM121 铌高速钢在 40%的变形量下,材料的抗弯强度和冲击韧性相较于未旋锻态分别提高了20.74%和 43.86%。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
FÖLZER A, TORNBERG C. Advances in processing technology for powder-metallurgical tool steels and high speed steels giving excellent cleanliness and homogeneity [J]. Materials Science Forum, 2003, 426–432: 4167–4172. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/msf.426-432.4167.
SOARES E P, VATAVUK J, PANELLI R, PILLIS M F. Evaluation of mechanical properties and microstructure of a high carbon-vanadium tool steel produced by powder metallurgy [J]. Materials Science Forum, 2006, 530–531: 140–144. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/msf.530-531.140.
WANG Rong, ANDRÉN H O, WISELL H, DUNLOP G L. The role of alloy composition in the precipitation behaviour of high speed steels [J]. Acta Metallurgica Et Materialia, 1992, 40: 1727–1738. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0956-7151(92)90116-V.
KREMNEV L S. From high-speed tungsten steel to high-temperature molybdenum steel: A century of high-speed steel [J]. Steel in Translation, 2009, 39(12): 1111–1118. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0967091209120195.
DOBRZAŃSKI L A, KASPRZAK W. The influence of 5% cobalt addition on structure and working properties of the 9-2-2-5, 11-2-2-5 and 11-0-2-5 high-speed steels [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2001, 109(1, 2): 52–64. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(00)00775-5.
XU Liu-jie, WEI Shi-zhong, XING Jian-dong, LI Yan, LONG Rui. Phase structure and fine microstructure of in-situ vanadium carbides in cast high-vanadium high-speed steel [J]. Metals & Materials International, 2006, 12: 371–375. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03027702.
SHTREMEL’ M A, KARABASOVA L V, CHIZHIKOV V I, VODENIKTOV S I. On optimum alloying of high-vanadium, high-speed steel [J]. Metal Science and Heat Treatment, 1999, 41(4): 146–150. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02465798.
WEI Shi-zhong, ZHU Jin-hua, XU Liu-jie, LONG Rui. Effects of carbon on microstructures and properties of high vanadium high-speed steel [J]. Materials & Design, 2006, 27(1): 58–63. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2004.09.027.
VANCURA F, MAŠEK B, AIŠMAN D, JIRKOVÁ H, WAGNER M F X, BÖHME M. Modification of metastable microstructure of CPM15V steel by heat exposure after treatment in semi-solid state [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2014, 586: S159–S164. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.04.064.
WU Li-zhi. Developments and challenges of China high-speed steel industry over last decade [C]// Advanced Steels. 2011: 453–461. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-17665-4_45.
YAN X G, LI D Y. Effects of the sub-zero treatment condition on microstructure, mechanical behavior and wear resistance of W9Mo3Cr4V high speed steel [J]. Wear, 2013, 302(1, 2): 854–862. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2012.12.037.
DO K R, CHOI S H, KWON Y S, PARK D W, CHO K K, AHN I S. Study on the sintering behavior and microstructure development of the powder injection molded T42 high-speed steel [J]. Metals and Materials International, 2011, 17(6): 937–942. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-011-6011-y.
AIŠMAN D, RUBEŠOVÁ K, MIKMEKOVÁ Š. Minithixoforming of high-alloyed CPM REX 121 steel [J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2014, 887–888: 1156–1160. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.887-888.1156.
TAKIGAWA H, MANTO H, KAWAI N, HOMMA K. Properties of high-speed steels produced by powder metallurgy [J]. Powder Metallurgy, 1981, 24(4): 196–202. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1179/pom.1981.24.4.196.
LU L, HOU L G, ZHANG J X, WANG H B, CUI H, HUANG J F, ZHANG Y A, ZHANG J S. Improved the microstructures and properties of M3: 2 high-speed steel by spray forming and niobium alloying [J]. Materials Characterization, 2016, 117: 1–8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2016.04.010.
KIRK F A. Problems in high-speed steel manufacture and use: A challenge for economic powder metallurgy processing [J]. Powder Metallurgy, 1981, 24(2): 70–74. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1179/pom.1981.24.2.70.
XU Liu-jie, XING Jian-dong, WEI Shi-zhong, PENG Tao, ZHANG Yong-zhen, LONG Rui. Artificial neural network prediction of heat-treatment hardness and abrasive wear resistance of high-vanadium high-speed steel (HVHSS) [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2007, 42(8): 2565–2573. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-1278-y.
WIEBNER M, LEISCH M, EMMINGER H, KULMBURG A. Phase transformation study of a high speed steel powder by high temperature X-ray diffraction [J]. Materials Characterization, 2008, 59(7): 937–943. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2007.08.002.
GRINDER O. The HIP way to make cleaner, better steels [J]. Metal Powder Report, 2007, 62(9): 16–22. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0026-0657(07)70190-X.
TAKAHASHI J, KAWAKAMI K, HAMADA J I, KIMURA K. Direct observation of niobium segregation to dislocations in steel [J]. Acta Materialia, 2016, 107: 415–422. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2016.01.070.
WOYDT M, HUANG S, VLEUGELS J, MOHRBACHER H, CANNIZZA E. Potentials of niobium carbide (NbC) as cutting tools and for wear protection [J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2018, 72: 380–387. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2018.01.009.
WANG He-bin, HOU Long-gang, ZHANG Jin-xiang, LU Lin, CUI Hua, ZHANG Ji-shan. The secondary precipitates of niobium-alloyed M3: 2 high speed steel prepared by spray deposition [J]. Materials Characterization, 2015, 106: 245–254. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2015.06.006.
CHEN M Y, GOUNÉ M, VERDIER M, BRÉCHET Y, YANG J R. Interphase precipitation in vanadium-alloyed steels: Strengthening contribution and morphological variability with austenite to ferrite transformation [J]. Acta Materialia, 2014, 64: 78–92. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2013.11.025.
YILMAZ A. Microstructural analysis of a new cast high-speed niobium-alloyed tool steel [J]. Metal Science and Heat Treatment, 2012, 54(7, 8): 349–354. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-012-9511-6.
OKAMOTO R, BORGENSTAM A, ÅGREN J. Interphase precipitation in niobium-microalloyed steels [J]. Acta Materialia, 2010, 58(14): 4783–4790. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2010.05.014.
WOYDT M, MOHRBACHER H. The use of niobium carbide (NbC) as cutting tools and for wear resistant tribosystems [J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2015, 49: 212–218. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2014.07.002.
ZHANG Qian-kun, JIANG Yao, SHEN Wei-jun, ZHANG Hui-bin, HE Yue-hui, LIN Nan, LIU C T, HUANG Han, HUANG Xiao-lin. Direct fabrication of high-performance high speed steel products enhanced by LaB6 [J]. Materials & Design, 2016, 112: 469–478. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.09.044.
TORRES Y, CASELLAS D, ANGLADA M, LLANES L. Fracture toughness evaluation of hardmetals: Influence of testing procedure [J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2001, 19(1): 27–34. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0263-4368(00)00044-5.
RAGHAVAN V. C−Fe−V (carbon-iron-vanadium) [J]. Journal of Phase Equilibria, 1993, 14(5): 622–623. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02669147.
PAN Fu-sheng, WANG Wei-qing, TANG Ai-tao, WU Li-zhi, LIU Ting-ting, CHENG Ren-ju. Phase transformation refinement of coarse primary carbides in M2 high speed steel [J]. Progress in Natural Science: Materials International, 2011, 21(2): 180–186. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0071(12)60053-7.
GODEC M, BATIČ B Š, MANDRINO D, NAGODE A, LESKOVŠEK V, ŠKAPIN S D, JENKO M. Characterization of the carbides and the martensite phase in powder-metallurgy high-speed steel [J]. Materials Characterization, 2010, 61(4): 452–458. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2010.02.003.
HUANG Shui-gen, VLEUGELS J, LI Lin, van der BIEST O. Experimental investigation and thermodynamic assessment of the V-W-C system [J]. ChemInform, 2005, 36(33): 68–74. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/chin.200533015.
KUBLII V Z, VELIKANOVA T Y. Ordering in the carbide W2C and phase equilibria in the tungsten-carbon system in the region of its existence [J]. Powder Metallurgy and Metal Ceramics, 2004, 43(11, 12): 630–644. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-005-0032-3.
LEE H M, ALLEN S M, GRUJICIC M. Coarsening resistance of M_2C carbides in secondary hardening steels: Part II. Alloy design aided by a thermochemical database [J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1991, 22(12): 2869–2876. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02650248.
AKASH A, MAYO M J. Pore growth during initial-stage sintering [J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1999, 82(11): 2948–2952. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1999.tb02186.x.
KANG S J L, JUNG Y I. Sintering kinetics at final stage sintering: Model calculation and map construction [J]. Acta Materialia, 2004, 52(15): 4573–4578. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2004.06.015.
KARAGÖZ S, FISCHMEISTER H F. Niobium-alloyed high speed steel by powder metallurgy [J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1988, 19(6): 1395–1401. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02674013.
PAVLíČKOVÁ M, VOJTĚCH D, NOVÁK P, GEMPERLOVÁ J, GEMPERLE A, ZÁRUBOVÁ N, LEJČEK P, JURČI P, STOLAŘ P. Thermal treatment of PM-tool steel alloyed with niobium [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003, 356(1, 2): 200–207. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(03)00120-5.
ZAPATA W C, DA COSTA C E, TORRALBA J M. Wear and thermal behaviour of M2 high-speed steel reinforced with NbC composite [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1998, 33(12): 3219–3225. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004324729342.
ZHOU C, MOON J R, PEACOCK S. Rotary forging of sintered iron based composites [J]. Powder Metallurgy, 1991, 34(1): 33–38. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1179/pom.1991.34.1.33.
ZHOU Bin, SHEN Yu, CHEN Jun, CUI Zhen-shan. Breakdown behavior of eutectic carbide in high speed steel during hot compression [J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, International, 2011, 18(1): 41–48. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(11)60009-5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The overarching research goals and the direct fabrication technology (DFT) were developed by HE Yue-hui, ZHANG Qian-kun, XIAO Yi-feng, WU Liang, QIAN Jin-wen, and LIN Nan. LI Su-wang, SHEN Wei-jun and CHEN Ze-min analyzed the measured data, and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. ZHANG Qian-kun and LI Su-wang edited the draft of manuscript. All authors replied to reviewers’ comments and revised the final version.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of interest
ZHANG Qian-kun, LI Su-wang, XIAO Yi-feng, WU Liang, QIAN Jin-wen, CHEN Ze-min, SHEN Wei-jun, LIN Nan and HE Yue-hui declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Foundation item: Projects(51771237, 51704257) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2019JJ60019) supported by the Joint Fund of Hunan Province, China; Project(17QDZ25) supported by the School Level Fund of Xiangtan University, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Qk., Li, Sw., Xiao, Yf. et al. Effects of niobium addition on microstructure and properties of CPM121 powder metallurgy high-speed steel. J. Cent. South Univ. 28, 1206–1218 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4690-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4690-1
Key words
- CPM121
- niobium-alloying
- microstructure
- mechanical properties
- temper resistance
- wear resistance
- rotary forging
- powder metallurgy