Abstract
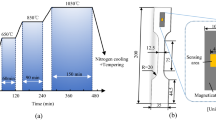
The hardness and abrasive wear resistance were measured after High-Vanadium High-Speed Steel (HVHSS) were quenched at 900 °C–1100 °C, and then tempered at 250 °C–600 °C. Via one-hidden-layer and two-hidden-layer Back-Propagation (BP) neural networks, the non-linear relationships of hardness (H) and abrasive wear resistance (ε) vs. quenching temperature and tempering temperature (T1, T2) were established, respectively, on the base of the experimental data. The results show that the well-trained two-hidden-layer networks have rather smaller training errors and much better generalization performance compared with well-trained one-hidden-layer neural networks, and can precisely predict hardness and abrasive wear resistance according to quenching and tempering temperatures. The prediction values have sufficiently mined the basic domain knowledge of heat treatment process of HVHSS. Therefore, a new way of predicting hardness and wear resistance according to heat treatment technique was provided by the authors.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim CK, Park JI, Lee S, Kim YC, Kim NJ, Yang JS (2005) Metall Mater Trans 36A:87
Kim SW, Lee UJ, Woo KD, Kim DK (2003) Mater Sci Technol 19:1727
Hwang KC, Lee S, Lee DHC (1998) Mater Sci Eng A254:282
Li CS, Liu XH, Wang GD, Yang G (2002) Mater Sci Technol 18:1581
Wei S, Zhu J, Xu L (2005) Trans Mater Heat Treat 26:44
Wei SZ, Long R (2001) Cement 8:31
Sano Y, Hattori T, Haga M (1992) ISIJ Int 32:1194
Park JW, Lee HC, Lee S (1999) Metall Mater Trans 30:399
Liu H, Liu Y, Yu S (2000) Tribol 20(6):401
White H (1990) Neural Netw 3:535
Altinkok N, Koker R (2005) J Mater Sci 40:1767
Reddy NS, Prasada Rao AK, Chakraborty M, Murty BS (2005) Mater Sci Eng A391:131
Su J, Dong Q, Liu P, Li H, Kang B (2003) J Wuhan Univ Technol-Mat Sci Edit 18:50
Sahoo GB, Ray C, Wade HF (2005) Ecol Model 183:29–46
Mackay, David JC (1992) Neural Comput 4:415
Gençay R, Min Q (2001) IEEE Trans Neural Netw 12:726
Liu P, Lei J, Jing X, Tian B (2005) Trans Mater Heat Treat 26:86
Su J, Dong Q, Liu P, Li H, Kang B (2003) Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 13:1419
Guo J, Yang Z, in “Analysis and Design of Neural Network Based on Matlab6.5”(Publishing House of Electronics Industry, Beijing, 2003) pp 313
Wei S, Zhu J, Long R (2004) Hot Work Technol 12:31
Tong J, Zhang W (1994) Chinese J Mech Eng 30:103
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by Key Scientific and Technological Breakthrough Project of Henan Province, China (No.0322020300).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liujie, X., Jiandong, X., Shizhong, W. et al. Artificial neural network prediction of heat-treatment hardness and abrasive wear resistance of High-Vanadium High-Speed Steel (HVHSS). J Mater Sci 42, 2565–2573 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-1278-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-1278-y