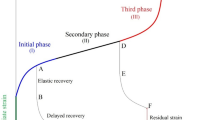
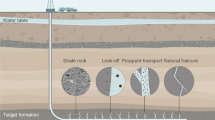
Abstract
Hydraulic fracturing, as a key technology of deep energy exploitation, accelerates the rapid development of the modern petroleum industry. To study the mechanisms of hydraulic fracture propagation and rock failure mode of the vertical well hydraulic fracturing, the true triaxial hydraulic fracturing test and numerical simulation are carried out, and the influence of the principal stress difference, water injection displacement, perforation angle and natural fracture on fracture propagation is analyzed. The results show that the fracture propagation mode of limestone is mainly divided into two types: the single vertical fracture and the transverse-longitudinal crossed complex fracture. Under high displacement, the fracturing pressure is larger, and the secondary fracture is more likely to occur, while variable displacement loading is more likely to induce fracture network. Meanwhile, the amplitude of acoustic emission (AE) waveform of limestone during fracturing is between 0.01 and 0.02 mV, and the main frequency is maintained in the range of 230–300 kHz. When perforation angle θ=45°, it is easy to produce the T-type fracture that connects with the natural fracture, while X-type cracks are generated when 0=30°. The results can be used as a reference for further study on the mechanism of limestone hydraulic fracturing.
摘要
水力压裂作为深部能源开发的关键技术, 促进了现代石油工业的快速发展。为研究垂直井水力 压裂裂缝扩展机制和岩石破坏模式, 开展了真三轴水力压裂试验和数值模拟研究, 分析了主应力差、 注水排量、射孔角度和天然裂缝对水力裂缝扩展的影响。结果表明, 灰岩裂缝扩展模式主要分为两类: 单一垂直裂缝和纵横向交叉复杂裂缝。高排量下岩体的破裂压力更大, 且易诱发二次压裂; 而变排量 加载更容易诱发形成裂缝网络。同时, 灰岩在压裂过程中的声发射波形幅值在0.01~0.02 mV 范围内, 主频保持在230~300 kHz 范围内。当射孔角度θ=45°时, 易产生与天然裂缝交汇的“T”型水力裂缝, 而当θ=30°时, 易产生X 型裂缝。研究结果可为进一步研究灰岩水力压裂机理提供参考。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
HU Wen-rui, WEI Yi, BAO Jing-wei. Development of the theory and technology for low permeability reservoirs in China [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development (English version), 2018, 45(4): 685–697. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1876-3804(18)30072-7.
VANDENHOEK P J, VANDENBERG J T M, SHLYAPOBERSKY J. Theoretical and experimental investigation of rock dilatancy near the tip of a propagating hydraulic fracture [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Science & Geomechanics Abstracts, 1993, 30(7): 1261–1264. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(93)90105-M.
ZHANG De-cheng, RANJITH P G, PERERA M S A. The brittleness indices used in rock mechanics and their application in shale hydraulic fracturing: A review [J]. Journal of Petroleum Science & Engineering, 2016, 143: 158–170. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2016.02.011.
PAN Dong-dong, LI Shu-cai, XU Zhen-hao, LI Li-ping, LU Wei, LIN Peng, HUANG Xin, SUN Shang-qu, GAO Cheng-lu. Model tests and numerical analysis for water inrush caused by karst caves filled with confined water in tunnels [J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2018, 40(5): 828–836. DOI: https://doi.org/10.11779/CJGE201805007.
LIU Hong-lei, YANG Tian-hong, CHEN Shi-kuo, YU Qing-lei, WANG Pei-tao. The mechanism of hydraulic fracturing and the engineering meaning of water outburst during rockmass failure [J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2010, 27(3): 356–362.
NAOI M, CHEN You-qing, NISHIHARA K, YAMAMOTO K, YANO S, WATANABE S. Monitoring hydraulically-induced fractures in the laboratory using acoustic emissions and the fluorescent method [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2018, 104: 53–63. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2018.02.015.
WU Chen, GONG Feng-qiang, LUO Yong. A new quantitative method to identify the crack damage stress of rock using AE detection parameters [J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and Environment, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-020-01932-6.
LI Zhi, JIA Chang-gui, YANG Chun-he, ZENG Yi-jin, GUO Yin-tong, HENG Shuai, WANG Lei, HOU Zhen-kun. Propagation of hydraulic fissures and bedding planes in hydraulic fracturing of shale [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2015, 34(1): 12–20. DOI: https://doi.org/10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2015.01.002. (in Chinese)
WANG Han-yi. Hydraulic fracture propagation in naturally fractured reservoirs: Complex fracture or fracture networks [J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2019, 68: 102911. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2019.102911.
ZHAO Yu, HE Peng-fei, ZHANG Yong-fa, WANG Chao-lin. A new criterion for a toughness-dominated hydraulic fracture crossing a natural frictional interface [J]. Rock Mechanics & Rock Engineering, 2018. 52(8): 2617–2229. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1683-y.
GUO Tian-kui, ZHANG Shi-cheng, QU Zhan-qing, ZHOU Tong, XIAO Yong-shun, GAO Jun. Experimental study of hydraulic fracturing for shale by stimulated reservoir volume [J]. Fuel, 2014, 128: 373–380. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2014.03.029.
MA Geng, ZHANG Fan, LIU Xiao, FENG Dan, ZHANG Peng-wei. Experimental study of impact of crustal stress on fracturing pressure and hydraulic fracture [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2016, 37(S2): 216–222. DOI: https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2016.S2.026.
WU Jing-jing, ZHANG Shao-he, SUN Ping-he, CAO Han, CHEN Jiang-zhan. Experimental study on acoustic emission characteristics in coal seam pulse hydraulic fracturing [J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2017, 48(7): 1866–1874. DOI: https://doi.org/10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2017.07.025. (in Chinese)
FAN Yong, ZHAO Yan-lin, ZHU Zhe-ming, ZHOU Chang-lin, ZHANG Xian-shang. Theoretical study of break down pressures and fracture initiation angles based on model containing wellbore and perforations [J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2019, 50(3): 669–678. DOI: https://doi.org/10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2019.03.021. (in Chinese)
RUEDA C J A, MEJIA S E C, ROEHL D, PEREIRA L C. Hydro-mechanical modeling of hydraulic fracture propagation and its interactions with frictional natural fractures [J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2019, 111: 290–300. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2019.03.020.
LIN Hai, DENG Jin-gen, LIU Wei, XIE Tao, XU Jie, LIU Hai-long. Numerical simulation of hydraulic fracture propagation in weakly consolidated sandstone reservoirs [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2018, 25(12): 2944–2952. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3964-8.
PAKZAD R, WANG S Y, SLOAN S W. Numerical simulation of hydraulic fracturing in low-/high-permeability, quasi-brittle and heterogeneous rocks [J]. Rock Mechanics & Rock Engineering, 2018, 51(4): 1153–1171. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-017-1386-9.
TANG Chen-an, THAM L G, LEE P K K, YANG Tian-hong. Coupled analysis of flow, stress and damage (FSD) in rock failure [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics & Mining Sciences, 2002, 39(4): 477–489. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1365-1609(02)00023-0.
LI Zhi-chao, LI Lian-chong, LI Ming, ZHANG Liao-yuan, TANG Chun-an. A numerical investigation on the effects of rock brittleness on the hydraulic fractures in the shale reservoir [J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science & Engineering, 2017, 50: 22–32. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2017.09.013.
SHI Gen-hua. Discontinuous deformation analysis: A new numerical model for the statics and dynamics of deformable block structures [J]. Engineering Computations, 1992, 9(2): 157–168. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1108/eb023855.
VAHAB M, KHALILI N. Numerical investigation of the flow regimes through hydraulic fractures using the X-FEM technique [J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2016, 169: 146–162. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2016.11.017.
FARZIN H, ALI M. A new three dimensional approach to numerically model hydraulic fracturing process [J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2014, 124: 451–467. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2013.12.006.
GAO Cheng-lu, ZHOU Zong-qing, LI Zhuo-hui, LI Li-ping, CHENG Shuai. Peridynamics simulation of surrounding rock damage characteristics during tunnel excavation [J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2020, 97. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2020.103289.
ZHOU Zong-qing, RANJITH P G, YANG Wei-min, SHI Shao-shuai, WEI Che-che, LI Zhuo-hui. A new set of scaling relationships for DEM-CFD simulations of fluid-solid coupling problems in saturated and cohesiveless granular soils [J]. Computational Particle Mechanics, 2019, 6(4): 657–669. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40571-019-00246-z.
WANG Tao, HU Wan-rui, ELSWORTH D, ZHOU Wei, ZHOU Wei-bo, ZHAO Xian-yu. The effect of natural fractures on hydraulic fracturing propagation in coal seams [J]. Journal of Petroleum Science & Engineering, 2017, 150: 180–190. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2016.12.009.
YOON J S, ZANG A, STEPHANSSON O, HOFMANN H, ZIMMERMANN G. Discrete element modelling of hydraulic fracture propagation and dynamic interaction with natural fractures in hard rock [J]. Procedia Engineering, 2017, 191: 1023–1031. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2017.05.275.
Itasca Consulting Group Inc. PFC2D-particle flow code in two dimensions [M]. Ver. 4.0 User’s Manual. ICG, Minneapolis.
GUO Tian-kui, QU Zhan-qing, GONG Di-guang, LEI Xin, LIU Ming. Numerical simulation of directional propagation of hydraulic fracture guided by vertical multi-radial boreholes [J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2016, 35: 175–188. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2016.08.056.
CHENG Yu-gang, LU Yi-yu, GE Zhao-long, CHENG Liang, ZHENG Jing-wei, ZHANG Wen-feng. Experimental study on crack propagation control and mechanism analysis of directional hydraulic fracturing [J]. Fuel, 2018, 218: 316–324. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.01.034.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The overarching research goals were developed by YANG Wei-min, ZHOU Zong-qing. LI Lian-chong, DING Ruo-song, GENG Yang and ZHAI Ming-yang carried out true triaxial hydraulic fracturing test. YANG Wei-min, DING Ruo-song and ZHAI Ming-yang analyzed the test results. GENG Yang and WU Zhong-hu established a numerical model. ZHOU Zong-qing and GENG Yang analyzed the calculated results. The initial draft of the manuscript was written by ZHOU Zong-qing and GENG Yang. All authors replied to reviewers’ comments and revised the final version.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of interest
YANG Wei-min, GENG Yang, ZHOU Zong-qing, LI Lian-chong, DING Ruo-song, WU Zhong-hu, and ZHAI Ming-yang declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Foundation item: Projects(51879148, 51709159, 51911530214) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2019GSF111030) supported by Shandong Provincial Key R&D Program of China; Project(KT201804) supported by the Project of Special Fund for Science and Technology of Water Resources Department of Guizhou Province, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Wm., Geng, Y., Zhou, Zq. et al. True triaxial hydraulic fracturing test and numerical simulation of limestone. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 27, 3025–3039 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4526-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4526-4
Key words
- true triaxial
- hydraulic fracturing
- acoustic emission
- particle flow code (PFC)
- perforation angle
- natural fracture