Abstract
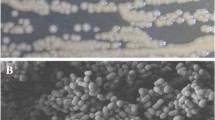
A gram negative bacterium, named JDC-16, which can grow well on the substrate of phthalic acid esters (PAEs) as the sole source of carbon and energy, was isolated from river sludge. Based on the morphology, physiological and biochemical properties and analysis of 16S rRNA gene sequence, it was preliminarily identified belonging to the genus Acinetobacter. The result of substrates utilization range indicates that strain JDC-16 can utilize a variety of phthalates except for diisononyl phthalate (DINP). The degradation tests using diethyl phthalate (DEP) as the model compound show that the optimal pH and temperature for DEP degradation by Acinetobacter sp. JDC-16 is 8.0 and 35 °C, respectively. Meanwhile, degradation kinetics under various initial concentrations of DEP reveals that substrate depletion curves fit well with the modified Gompertz model with high correlation coefficient (R 2>0.99). Furthermore, the substrate induction test indicates that DEP-induction can apparently shorten the lag phase and enhance the degradation rate. This work highlights the potential of this isolate for bioremediation of phthalates-contaminated environments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
LIANG Da-wei, ZHANG Tong, HE Jian-zhong. Phthalates biodegradation in the environment [J]. Applied Microbiology Biotechnology, 2008, 80(2): 183–198.
KAPANEN A, STEPHEN J R, BRUGGEMANN J, KIVIRANTA A, WHITE D C, ITAVAARA M. Diethyl phthalate in compost: Ecotoxicological effects and response of the microbial community [J]. Chemosphere, 2007, 67(11): 2201–2209.
MATSUMOTO M, HIRATA-KOIZUMI M, EMA M. Potential adverse effects of phthalic acid esters on human health: A review of recent studies on reproduction [J]. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology, 2008, 50(1): 37–49.
WANG Jing-long, LIU Ping, QIAN Yi. Microbial degradation of di-n-butyl phthalate [J]. Chemosphere, 1995, 31(9): 4051–4056.
NIAZI J H, PRASAD D T, KAREGOUDAR T B. Initial degradation of dimethylphthalate by esterases from Bacillus species [J]. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 2001, 196(2): 201–205.
ZENG Feng, CUI Kun-yan, XIE Zhi-yong, WU Li-na, LIU Min, SUN Guo-quan, LIN Yu-jun, LUO Dan-ling, ZENG Zun-xiang. Phthalate esters (PAEs): Emerging organic contaminants in agricultural soils in peri-urban areas around Guangzhou, China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2008, 156(2): 425–434.
MARTTINEN S K, KETTUNEN R H, RINTALA J A. Occurrence and removal of organic pollutants in sewages and landfill leachates [J]. Science of Total Environment, 2003, 301(1/2/3): 1–12.
MOHAN SV, SHAILAJA S, KRISHNA MR, REDDY KB, SARMA P N. Bioslurry phase degradation of di-ethyl phthalate (DEP) contaminated soil in periodic discontinuous mode operation: Influence of bioaugmentation and substrate partition [J]. Process Biochemistry, 2006, 41(3): 644–652.
CARTWRIGHT C D, OWEN S A, THOMPSON I P, BURNS R G. Biodegradation of diethyl phthalate in soil by a novel pathway [J]. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 2000, 186(1): 27–34.
CHANG B V, LIAO C S, YUAN S Y. Anaerobic degradation of diethyl phthalate, di-n-butyl phthalate, and di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate from river sediment in Taiwan [J]. Chemosphere, 2005, 58(11): 1601–1607.
HASHIZUME K, NANYA J, TODA C, YASUI T, NAGANO H, KOJIMA N. Phthalate esters detected in various water samples and biodegradation of the phthalates by microbes isolated from river water [J]. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 2002, 25(2): 209–214.
CHANG B V, YANG C M, CHENG C H, YUAN S Y. Biodegradation of phthalate esters by two bacteria strains [J]. Chemosphere, 2004, 55(4): 533–538.
ZENG Feng, CUI Kun-yan, LI Xiang-dong, FU Jia-mo, SHENG Guo-ying. Biodegradation kinetics of phthalate esters by Pseudomonas fluoresences FS1 [J]. Process Biochemistry, 2004, 39(9): 1125–1129.
HERBERT H P, LIANG D W, ZHANG T. Aerobic degradation of diethyl phthalate by Sphingomonas sp [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2007, 98(3): 717–720.
CHAO W L, LIN C M, SHIUNG I I, KUO Y. Degradation of dibutyl-phthalate by soil bacteria [J]. Chemosphere, 2006, 63(8): 1377–1383.
DONG Xiu-zhu, CAI Miao-ying. Manual of common determinative bacteriology [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2001: 188–189. (in Chinese)
YANG Yu, DIAO Meng-xue, SHI Wu-yang, LI Li, DAI Qin-yun, QIU Guan-zhou. Isolation and characterization of organic-sulfur degradation bacterial strain [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2007, 14(3): 324–329.
ZHOU Hong-bo, LIU Xi, FU Bo, QIU Guan-zhou, HUO Qiang, ZENG Wei-min, LIU Jian-she, CHEN Xin-hua. Isolation and characterization of Acidithiobacillus caldus from several typical environments in China [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2007, 14(2): 163–169.
VAMSEE-KRISHNA C, MOHAN Y, PHALE P S. Biodegradation of phthalate isomers by Pseudomonas aeruginosa PP4, Pseudomonas sp PPD and Acinetobacter lwoffii ISP4 [J]. Applied Microbiology Biotechnology, 2006, 72(6): 1263–1269.
WANG Ying, TIAN Ye, HAN Bin, ZHAO Hua-bing, BI Jian-nan, CAI Bao-li. Biodegradation of phenol by free and immobilized Acinetobacter sp. strain PD12 [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2007, 19(2): 222–225. (in Chinese)
ADAV S S, CHEN M Y, LEE D J, REN N Q. Degradation of phenol by Acinetobacter strain isolated from aerobic granules [J]. Chemosphere, 2007, 67(8): 1566–1572.
THANGARAJ K, KAPLEY A, PUROHIT H J. Characterization of diverse Acinetobacter isolates for utilization of multiple aromatic compounds [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2008, 99(7): 2488–2494.
ISHII S, KOKI J, UNNO H, HORI K. Two morphological types of cell appendages on a strongly adhesive bacterium, Acinetobacter sp. strain Tol 5 [J]. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 2004, 70(8): 5026–5029.
LI Jia-xi, GU Ji-Dong, PAN Li. Transformation of dimethyl phthalate, dimethyl isophthalate and dimethyl terephthalate by Rhodococcus rubber Sa and modeling the processes using the modified Gompertz model [J]. International Biodeterioration Biodegradation, 2005, 55(3): 223–232.
FAN Yan-zhen, WANG Ying-ying, QIAN Pei-yuan, GU Ji-Dong. Optimization of phthalic acid batch biodegradation and the use of modified Richards model for modeling degradation [J]. International Biodeterioration Biodegradation, 2004, 53(1): 57–63.
WANG Jing-long, ZHAO Xuan, WU Wei-zhong. Biodegradation of phthalic acid esters (PAEs) in soil bioaugmented with acclimated activated sludge [J]. Process Biochemistry, 2004, 39(12): 1837–1841.
XU Xiang-rong, LI Hua-bin, GU Ji-dong. Metabolism and biochemical pathway of n-butyl benzyl phthalate by Pseudomonas fluorescens B-1 isolated from a mangrove sediment [J]. Ecotoxicology Environmental Safety, 2007, 68(3): 379–385.
WANG Ya-li, YIN Bo, HONG Yi-guo, YAN Yan, GU Ji-dong. Degradation of dimethyl carboxylic phthalate ester by Burkholderia cepacia DA2 isolated from marine sediment of South China Sea [J]. Ecotoxicology, 2008, 17(8): 845–852.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(30770388) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, Rx., Wu, Xl., Wang, Xn. et al. Aerobic biodegradation of diethyl phthalate by Acinetobacter sp. JDC-16 isolated from river sludge. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 17, 959–966 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-010-0584-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-010-0584-3