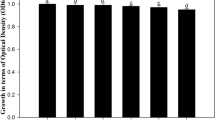
Abstract
Serendipita indica is a root endophytic fungus and can symbiose with many plant species. Effector proteins secreted by fungi show many functions during symbiosis or infection. To investigate the role of the protein PIIN 05330 secreted by S. indica, the gene PIIN_05330 was cloned and its transgenic Arabidopsis lines were constructed. The transgenic lines were evaluated for their drought tolerance. The results showed that these transgenic Arabidopsis lines were sensitive to drought stress during the germination stage. Compared with Arabidopsis wild type (WT) and the empty vector (VT) lines seedlings, the transgenic lines had higher total root surface area, root diameters, total root volumes, relative root elongation rates, total root length, and root tip numbers. In addition, the transgenic lines showed higher aboveground biomass and chlorophyll levels. Compared with WT and VT lines, activities of SOD, POD and CAT increased in the transgenic Arabidopsis lines under drought condition, especially their CAT activities. Under drought stress, levels of AsA and GSH in the transgenic lines were higher than those in control WT and VT, and concentrations of H2O2 and MDA were significantly lower than those in control WT and VT. Under drought stress, proline concentrations increased, and total concentrations of soluble sugars and proteins significantly increased in transgenic lines, compared with control WT and VT, indicating that the transgenic lines had a higher ability to reduce plant damage and protect plant cell membrane system. All these results suggest that the effector protein PIIN_05330 improved drought tolerance of the transgenic Arabidopsis lines.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05016-3
Bajji M, Lutts S, Kinet JM (2001) Water deficit effects on solute contribution to osmotic adjustment as a function of leaf ageing in three durum wheat (Triticum durum Desf.) cultivars performing differently in arid conditions. Plant Sci 160(4):669–681. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-9452(00)00443-x
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00018060
Baxter L, Tripathy S, Ishaque N, Boot N, Cabral A, Kemen E, Thines M, Ah-Fong A, Anderson R, Badejoko W, Bittner-Eddy P, Boore JL, Chibucos MC, Coates M, Dehal P, Delehaunty K, Dong S, Downton P, Dumas B, Fabro G, Fronick C, Fuerstenberg SI, Fulton L, Gaulin E, Govers F, Hughes L, Humphray S, Jiang RHY, Judelson H, Kamoun S, Kyung K, Meijer H, Minx P, Morris P, Nelson J, Phuntumart V, Qutob D, Rehmany A, Rougon-Cardoso A, Ryden P, Torto-Alalibo T, Studholme D, Wang Y, Win J, Wood J, Clifton SW, Rogers J, Van den Ackerveken G, Jones JDG, McDowell JM, Beynon J, Tyler BM (2010) Signatures of adaptation to obligate biotrophy in the Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis genome. Science 330(6010):1549–1551. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1195203
Beyer WF Jr, Fridovich I (1987) Assaying for superoxide dismutase activity: some large consequences of minor changes in conditions. Anal Biochem 161(2):559–566. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(87)90489-1
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1976.9999
Cao YJ, Wei Q, Liao Y, Song HL, Li X, Xiang CB, Kuai BK (2009) Ectopic overexpression of AtHDG11 in tall fescue resulted in enhanced tolerance to drought and salt stress. Plant Cell Rep 28(4):579–588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-008-0659-x
Challabathula D, Analin B, Mohanan A, Bakka K (2022) Differential modulation of photosynthesis, ROS and antioxidant enzyme activities in stress-sensitive and -tolerant rice cultivars during salinity and drought upon restriction of COX and AOX pathways of mitochondrial oxidative electron transport. J Plant Physiol 268:153583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2021.153583
Cheng HQ, Zou YN, Wu QS, Kuča K (2021) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi alleviate drought stress in trifoliate orange by regulating H+-ATPase activity and gene expression. Front Plant Sci 12:659694. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.659694
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16(6):735–743. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.1998.00343.x
Cui J, Jiang N, Zhou X, Hou X, Yang G, Meng J, Luan Y (2018) Tomato MYB49 enhances resistance to Phytophthora infestans and tolerance to water deficit and salt stress. Planta 248(6):1487–1503. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-018-2987-6
Dalio RJD, Maximo HJ, Oliveira TS, Dias RO, Breton MC, Felizatti H, Machado M (2018) Phytophthora parasitica effector PpRxLR2 suppresses Nicotiana benthamiana immunity. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 31(4):481–493. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-07-17-0158-FI
de Freitas PM, Veneault-Fourrey C, Vion P, Guinet F, Morin E, Barry KW, Lipzen A, Singan V, Pfister S, Na H, Kennedy M, Egli S, Grigoriev I, Martin F, Kohler A, Peter M (2018) Secretome analysis from the ectomycorrhizal ascomycete Cenococcum geophilum. Front Microbiol 9:141. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00141
Dhindsa SR, Plumb-Dhindsa P, Thorpe TA (1981) Leaf senescence: correlated with increased levels of membrane permeability and lipid peroxidation, and decreased levels of superoxide dismutase and catalase. J Exp Bot 32(1):93–101. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/32.1.93
Dong S, Ma Y, Li S, Dong N, Liu L (2018) Effect of drought stress and re-watering on ascorbate-glutathionecycle of soybean. J Northeast Agric Univ 49(1):10–18. https://doi.org/10.19720/j.cnki.issn.1005-9369.2018.01.002
Dreywood R (1946) Qualitative test for carbohydrate material. Ind Eng Chem Anal Ed 18(8):499. https://doi.org/10.1021/i560156a015
Du Y, Chen X, Guo Y, Zhang X, Zhang H, Li F, Huang G, Meng Y, Shan W (2021) Phytophthora infestans RXLR effector PITG20303 targets a potato MKK1 protein to suppress plant immunity. New Phytol 229(1):501–515. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.16861
Espino S, Schenk HJ (2011) Mind the bubbles: achieving stable measurements of maximum hydraulic conductivity through woody plant samples. J Exp Bot 62(3):1119–1132. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq338
Fernando A, Selvaraj M, Ishitani M, Nakashima K, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2021) How utilizing the genes involved in drought tolerance could tackle the climate change-related food crisis. Mol Plant 14(10):1601–1603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2021.08.002
Fiorilli V, Belmondo S, Khouja HR, Abbà S, Faccio A, Daghino S, Lanfranco L (2016) RiPEIP1, a gene from the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Rhizophagus irregularis, is preferentially expressed in planta and may be involved in root colonization. Mycorrhiza 26(6):609–621. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-016-0697-0
Foyer CH, Noctor G (2005) Redox homeostasis and antioxidant signaling: a metabolic interface between stress perception and physiological responses. Plant Cell 17(7):1866–1875. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.105.033589
Ghabooli M, Khatabi B, Ahmadi FS, Sepehri M, Mirzaei M, Amirkhani A, Jorrín-Novo JV, Salekdeh GH (2013) Proteomics study reveals the molecular mechanisms underlying water stress tolerance induced by Piriformospora indica in barley. J Proteomics 94:289–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2013.09.01
Gomez E, Irvine DS, Aitken RJ (1998) Evaluation of a spectrophotometric assay for the measurement of malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxyalkenals in human spermatozoa: relationships with semen quality and sperm function. Int J Androl 21(2):81–94. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2605.1998.00106.x
Green A (2016) Severe drought in Zimbabwe triggers food crisis. Lancet 387(10022):931–932. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00633-4
Gujjar RS, Roytrakul S, Chuekong W, Supaibulwatana K (2021) A synthetic cytokinin influences the accumulation of leaf soluble sugars and sugar transporters, and enhances the drought adaptability in rice. 3 Biotech 11(8):369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02908-3
Halo BA, Al-Yahyai RA, Al-Sadi AM (2020) An endophytic Talaromyces omanensis enhances reproductive, physiological and anatomical characteristics of drought-stressed tomato. J Plant Physiol 249:153163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2020.153163
Hoffman MT, Carrick PJ, Gillson L, West AG (2009) Drought, climate change and vegetation resposne in the succulent karoo, South Africa. South African J Sci 105:54–60
Huang YM, Zou YN, Wu QS (2017) Alleviation of drought stress by mycorrhizas is related to increased root H2O2 efflux in trifoliate orange. Sci Rep 7:42335. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep42335
Huang D, Ma M, Wang Q, Zhang M, Jing G, Li C, Ma F (2020) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi enhanced drought resistance in apple by regulating genes in the MAPK pathway. Plant Physiol Biochem 149:245–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.02.020
Jiang RH, Tripathy S, Govers F, Tyler BM (2008) RXLR effector reservoir in two Phytophthora species is dominated by a single rapidly evolving superfamily with more than 700 members. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(12):4874–4879. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0709303105
Kaur H, Manna M, Thakur T, Gautam V, Salvi P (2021) Imperative role of sugar signaling and transport during drought stress responses in plants. Physiol Plant 171(4):833–848. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.13364
Kenneth JL, Thomas DS (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 25(4):402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Kim YS, Kim IS, Bae MJ, Choe YH, Kim YH, Park HM, Kang HG, Yoon HS (2013) Homologous expression of cytosolic dehydroascorbate reductase increases grain yield and biomass under paddy field conditions in transgenic rice (Oryza sativa L. japonica). Planta 237(6):1613–1625. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-013-1862-8
Kloppholz S, Kuhn H, Requena N (2011) A secreted fungal effector of Glomus intraradices promotes symbiotic biotrophy. Curr Biol 21(14):1204–1209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2011.06.044
Krasensky J, Jonak C (2012) Drought, salt, and temperature stress-induced metabolic rearrangements and regulatory networks. J Exp Bot 63(4):1593–1608. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/err460
Kuromori T, Seo M, Shinozaki K (2018) ABA transport and plant water stress responses. Trends Plant Sci 23(6):513–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2018.04.001
Kuzhuppillymyal-Prabhakarankutty L, Tamez-Guerra P, Gomez-Flores R, Rodriguez-Padilla MC, Ek-Ramos MJ (2020) Endophytic Beauveria bassiana promotes drought tolerance and early flowering in corn. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 36(3):47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-020-02823-4
Li Z, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Peng Y, Merewitz E, Ma X, Huang L, Yan Y (2016) The alterations of endogenous polyamines and phytohormones induced by exogenous application of spermidine regulate antioxidant metabolism, metallothionein and relevant genes conferring drought tolerance in white clover. Environm Experiment Bot 124:22–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2015.12.004
Li X, He X, Hou L, Ren Y, Wang S, Su F (2018) Dark septate endophytes isolated from a xerophyte plant promote the growth of Ammopiptanthus mongolicus under drought condition. Sci Rep 8(1):7896. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-26183-0
Li X, He XL, Zhou Y, Hou YT, Zuo YL (2019) Effects of dark septate endophytes on the performance of Hedysarum scoparium under water deficit stress. Front Plant Sci 10:903. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00903
Liang X, Zhang L, Natarajan SK, Becker DF (2013) Proline mechanisms of stress survival. Antioxid Redox Signal 19(9):998–1011. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2012.5074
Liu J, Zhang X, Sun Y, Lin W (2010) Antioxidative capacity and enzyme activity in Haematococcus pluvialis cells exposed to superoxide free radicals. Chin J Oceanol Limnol 28(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-010-9244-6
Liu Z, Li Y, Ma L, Wei H, Zhang J, He X, Tian C (2015) Coordinated regulation of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and soybean MAPK pathway genes improved mycorrhizal soybean drought tolerance. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 28(4):408–419. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-09-14-0251-R
Liu X, Li L, Li M, Su L, Lian S, Zhang B, Li X, Ge K, Li L (2018) AhGLK1 affects chlorophyll biosynthesis and photosynthesis in peanut leaves during recovery from drought. Sci Rep 8(1):2250. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-20542-7
Liu L, Xu L, Jia Q, Pan R, Oelmüller R, Zhang W, Wu C (2019) Arms race: diverse effector proteins with conserved motifs. Plant Signal Behav 14(2):1557008. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592324.2018.1557008
Liu B, Jing D, Liu F, Ma H, Liu X, Peng L (2021a) Serendipita indica alleviates drought stress responses in walnut (Juglans regia L.) seedlings by stimulating osmotic adjustment and antioxidant defense system. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105(23):8951–8968. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11653-9
Liu M, Hu J, Zhang A, Dai Y, Chen W, He Y, Zhang H, Zheng X, Zhang Z (2021b) Auxilin-like protein MoSwa2 promotes effector secretion and virulence as a clathrin uncoating factor in the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. New Phytol 230(2):720–736. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.17181
Mahajan S, Tuteja N (2005) Cold, salinity and drought stresses: an overview. Arch Biochem Biophys 444(2):139–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2005.10.018
Majidi MIHA, Y-AlQubury H (2016) Determination of vitamin C (ascorbic acid) contents in various fruit and vegetable by UV-spectrophotometry and titration methods. J Chem Pharmac Sci 9(4):2972–2974
Nejati-Yazdinejad M (2007) Indirect determination of ascorbic acid (vitamin C) by spectrophotometric method. Internat J Food Sci Technol 42:1402–1407. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2006.01353.x
Oztur M, Unal BT, García-Caparrós P, Khursheed A, Gul A, Hasanuzzaman M (2021) Osmoregulation and its actions during the drought stress in plants. Physiol Plant 172(2):1321–1335. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.13297
Paradiso A, Berardino R, de Pinto MC, Sanità di Toppi L, Storelli MM, Tommasi F, De Gara L (2008) Increase in ascorbate-glutathione metabolism as local and precocious systemic responses induced by cadmium in durum wheat plants. Plant Cell Physiol 49(3):362–374. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcn013
Plett JM, Martin F (2012) Poplar root exudates contain compounds that induce the expression of MiSSP7 in Laccaria bicolor. Plant Signal Behav 7(1):12–15. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.7.1.18357
Plett JM, Daguerre Y, Wittulsky S, Vayssieres A, Deveau A, Melton SJ, Kohler A, Morrell-Falvey JL, Brun A, Veneault-Fourrey C, Martin F (2014) Effector MiSSP7 of the mutualistic fungus Laccaria bicolor stabilizes the Populus JAZ6 protein and represses jasmonic acid (JA) responsive genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111(22):8299–8304. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1322671111
Prasad Singh P, Srivastava D, Jaiswar A, Adholeya A (2019) Effector proteins of Rhizophagus proliferus: conserved protein domains may play a role in host-specific interaction with different plant species. Braz J Microbiol 50:593–601. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42770-019-00099-x
Prema Sundara Valli P, Muthukumar T (2018) Dark septate root endophytic fungus Nectria haematococca improves tomato growth under water limiting conditions. Indian J Microbiol 58(4):489–495. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-018-0749-6
Priya M, Dhanker OP, Siddique KHM, HanumanthaRao B, Nair RM, Pandey S, Singh S, Varshney RK, Prasad PVV, Nayyar H (2019) Drought and heat stress-related proteins: an update about their functional relevance in imparting stress tolerance in agricultural crops. Theor Appl Genet 132:1607–1638. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-019-03331-2
Sami F, Yusuf M, Faizan M, Faraz A, Hayat S (2016) Role of sugars under abiotic stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 109:54–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.09.005
Sebastiana M, da Silva AB, Matos AR, Alcântara A, Silvestre S, Malhó R (2018) Ectomycorrhizal inoculation with Pisolithus tinctorius reduces stress induced by drought in cork oak. Mycorrhiza 28(3):247–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-018-0823-2
Sebastiana M, Duarte B, Monteiro F, Malhó R, Caçador I, Matos AR (2019) The leaf lipid composition of ectomycorrhizal oak plants shows a drought-tolerance signature. Plant Physiol Biochem 144:157–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2019.09.032
Sharma P, Jha AB, Dubey RS, Pessarakli M (2012) Reactive oxygen species, oxidative damage, and antioxidative defense mechanism in plants under stressful conditions. J Bot 2012:217037. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/217037
Shukla S, Husak G, Turner W, Davenport F, Funk C, Harrison L, Krell N (2021) A slow rainy season onset is a reliable harbinger of drought in most food insecure regions in Sub-Saharan Africa. PLoS One 16(1):e0242883. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0242883
Sun C, Johnson JM, Cai D, Sherameti I, Oelmüller R, Lou B (2010) Piriformospora indica confers drought tolerance in Chinese cabbage leaves by stimulating antioxidant enzymes, the expression of drought-related genes and the plastid-localized CAS protein. J Plant Physiol 167(12):1009–1017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2010.02.013
Sun J, Yan XW, Le MW, Rao YL, Yan TX, Ye YY, Zhou HY (2019) Physiological response mechanism of drought dtress in different drought-tolerance genotypes of sesame during flowering period. Scientia Agricultura Sinica 52(7):1215–1226. https://doi.org/10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2019.07.009
Tiwari P, Indoliya Y, Chauhan AS, Pande V, Chakrabarty D (2020) Over-expression of rice R1-type MYB transcription factor confers different abiotic stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 206:111361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111361
Trenberth KE, Dai A, van der Schrier G, Jones PD, Barichivich J, Briffa KR, Sheffield J (2014) Global warming and changes in drought. Nat Clim Change 4:17–22. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate2067
Ushimaru T, Nakagawa T, Fujioka Y, Daicho K, Naito M, Yamauchi Y, Nonaka H, Amako K, Yamawaki K, Murata N (2006) Transgenic Arabidopsis plants expressing the rice dehydroascorbate reductase gene are resistant to salt stress. J Plant Physiol 163(11):1179–1184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2005.10.002
Voß S, Betz R, Heidt S, Corradi N, Requena N (2018) RiCRN1, a crinkler effector from the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Rhizophagus irregularis, functions in arbuscule development. Front Microbiol 9:2068. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.02068
Wang J, Zhang H, Gao J, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Tang M (2021) Effects of ectomycorrhizal fungi (Suillus variegatus) on the growth, hydraulic function, and non-structural carbohydrates of Pinus tabulaeformis under drought stress. BMC Plant Biol 21(1):171. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-021-02945-3
Wu QS, Lou YG, Li Y (2015) Plant growth and tissue sucrose metabolism in the system of trifoliate orange and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Sci Hortic 181:189–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2014.11.006
Zandi P, Schnug E (2022) Reactive oxygen species, antioxidant responses and implications from a microbial modulation perspective. Biology (Basel) 11(2):155. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020155
Zhang W, Wang J, Xu L, Wang A, Huang L, Du H, Qiu L, Oelmüller R (2018) Drought stress responses in maize are diminished by Piriformospora indica. Plant Signal Behav 13(1):e1414121. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592324.2017.1414121
Zou YN, Wu QS, Kuča K (2021) Unravelling the role of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in mitigating the oxidative burst of plants under drought stress. Plant Biol (Stuttg) 23(S1):50–57. https://doi.org/10.1111/plb.13161
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the College of Horticulture and Gardening, Yangtze University for the equipment support. The authors are grateful to Dr. Abazar Ghorbani for many excellent advises on the revision of this manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31870378) and Fujian University Key Laboratory for Plant–Microbe Interaction, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (PMI2018KF2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Chu Wu: designed the experiments, analysed the data, and revised the manuscript. Jianmiao Chen: gathered and analyzed data, and wrote the manuscript. Yuanming Ye: performed the experiments and wrote the manuscript. Jinwang Qu: participated in the experiments. All authors have read and approved to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All the studies in this manuscript follow ethical standards.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Ye, Y., Qu, J. et al. PIIN_05330 transgenic Arabidopsis plants enhanced drought-stress tolerance. Biologia 78, 937–950 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-022-01268-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-022-01268-4