Abstract
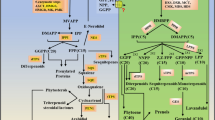
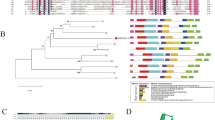
As one of the most important phytohormones, the abscisic acid (ABA) is often used to breed stress-tolerant crop lines with both higher yields and active ingredient contents. In higher plants, the 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase (NCED) has been found to be a regulatory enzyme involved in ABA biosynthesis. In research, the novel gene SmNCED3 was isolated from S. miltiorrhiza. The open reading frame of SmNCED3 was 1725-bp, and it was encoding 574 amino acids with a calculated molecular mass of 63,822 kDa, which was verified by the expression of SmNCED3 in E. coli. The deduced SmNCED3 amino acid sequence had high sequence homology with NCED sequences from other plants and contained a putative chloroplast transit targeting signal peptide at its N terminus. Phylogenetic analysis demonstrated that SmNCED3 had a closer affinity to NCED3 in Arabidopsis thaliana (AtNCED3). The 1732-bp 5′ flanking sequence of SmNCED3 was also cloned. It contained several phytohormone response elements, biotic or abiotic stress-related elements, and plant development-related elements. Real-time PCR revealed that SmNCED3 was highly expressed in leaves, and was strongly induced by exogenous ABA. A subcellular localization experiment indicated that SmNCED3 was located in chloroplast stroma, chloroplast membranes, and thylakoid membranes. The overexpression of SmNCED3 promoted ABA accumulation. These results indicated that SmNCED3 might be a rate-limiting gene regulating ABA biosynthesis, and improving abiotic stresses tolerance and active ingredient contents in plants.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aswath CR, Kim SH, Mo SY, Kim DH (2005) Transgenic plants of creeping bent grass harboring the stress inducible gene, 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase, are highly tolerant to drought and NaCl stress. Plant Growth Regul 47:129–139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-005-3380-6
Bettaieb I, Hamrouni-Sellami I, Bourgou S, Limam F, Marzouk B (2011) Drought effects on polyphenol composition and antioxidant activities in aerial parts of Salvia officinalis L. Acta Physiol Plant 33:1103–1111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-010-0638-z
Du X, Zhang C, Guo W, Jin W, Liang Z, Yan X, Guo Z, Liu Y, Yang D (2015) Nitric oxide plays a central role in water stress-induced tanshinone production in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots. Molecules 20(5):7574–7585. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20057574
Hao G, Jiang X, Feng L, Tao R, Li Y, Huang L (2016) Cloning, molecular characterization and functional analysis of a putative R2R3-MYB transcription factor of the phenolic acid biosynthetic pathway in S. miltiorrhiza Bge. f. alba. Plant Cell Tiss Org 124:151–168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-015-0883-3
Hu B, Jin J, Guo A, Zhang H, Luo J, Gao G (2015) GSDS 2.0: an upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 31:1296–1297. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu817
Ikegami K, Okamoto M, Seo M, Koshiba T (2008) Activation of abscisic acid biosynthesis in the leaves of Arabidopsis thaliana in response to water deficit. J Plant Res 122:235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-008-0201-9
Iuchi S, Kobayashi M, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2000) A stress-inducible gene for 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase involved in abscisic acid biosynthesis under water stress in drought-tolerant cowpea. Plant Physiol 123:553–562. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.123.2.553
Iuchi S, Kobayashi M, Taji T, Naramoto M, Seki M, Kato T, Tabata S, Kakubari Y, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2001) Regulation of drought tolerance by gene manipulation of 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase, a key enzyme in abscisic acid biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J 27:325–333. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.2001.01096.x
Jia Y, Bai Z, Pei T, Ding K, Liang Z, Gong Y (2017) The protein kinase SmSnRK2.6 positively regulates phenolic acid biosynthesis in Salvia miltiorrhiza by interacting with SmAREB1. Front Plant Sci 8:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01384
Kai G, Xu H, Zhou C, Liao P, Xiao J, Luo X, You L, Zhang L (2011) Metabolic engineering tanshinone biosynthetic pathway in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root cultures. Metab Eng 13:319–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2011.02.003
Li C, Srivastava M, Nong Q, Yang L, Li Y (2013) Molecular cloning and characterization of SoNCED, a novel gene encoding 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase from sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.). Genes Genom 35:101–109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-013-0065-9
Liu D, Guo L, Huang L, Jin H, Wu L, Zeng Y, Yang Y (2011a) Effects of soil water content on seedlings growth and active ingredients of Salvia miltiorrhiza. Chin J Chin Mater Med 36:321–325 (ISSN 1001-5302)
Liu H, Wang X, Wang D, Zou Z, Liang Z (2011b) Effect of drought stress on growth and accumulation of active constituents in Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge. Ind Crop Prod 33:84–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2010.09.006
Ma P, Liu J, Zhang C, Liang Z (2013) Regulation of water-soluble phenolic acid biosynthesis in Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge. Appl Biochem Biotech 170:1253–1262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0265-4
Moyano E, Fornalé S, Palazón J, Cusidó RM, Bagni N, Piñol MT (2002) Alkaloid production in Duboisia hybrid hairy root cultures overexpressing the pmt gene. Phytochemistry 59:697–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0031-9422(02)00044-4
Nambara E, Marion-Poll A (2005) Abscisic acid biosynthesis and catabolism. Annu Rev Plant Biol 56:165–185. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.56.032604.144046
Nelson BK, Cai X, Nebenfuehr A (2007) A multicolored set of in vivo organelle markers for co-localization studies in Arabidopsis and other plants. Plant J 51:1126–1136. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03212.x
Qin X, Zeevaart JAD (1999) The 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid cleavage reaction is the key regulatory step of abscisic acid biosynthesis in water-stressed bean. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:15354–15361. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.26.15354
Qin X, Zeevaart JAD (2002) Overexpression of a 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase gene in Nicotiana plumbaginifolia increases abscisic acid and phaseic acid levels and enhances drought tolerance. Plant Physiol 128:544–551. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.128.2.544
Roychoudhury A, Paul S, Basu S (2013) Cross-talk between abscisic acid-dependent and abscisic acid-independent pathways during abiotic stress. Plant Cell Rep 32:985–1006. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-013-1414-5
Shao Y, Wei J, Wu F, Zhang H, Yang D, Liang Z (2016) DsTRD: Danshen transcriptional resource database. Plos One 11:e0149747
Shen L, Ren J, Jin W, Wang R, Ni C, Tong M, Liang Z, Yang D (2016) Role of NO signal in ABA-induced phenolic acids accumulation in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy. Chin J Biotech 32(2):222–230. https://doi.org/10.13345/j.cjb.150271
Tan B, Schwartz SH, Zeevaart JAD, McCarty DR (1997) Genetic control of abscisic acid biosynthesis in maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:12235–12240. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.94.22.12235
Tan B, Joseph LM, Deng W, Liu L, Li Q, Cline K, McCarty DR (2003) Molecular characterization of the Arabidopsis 9-cis epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase gene family. Plant J 35:44–56. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01786.x
Tian X, Ji J, Wang G, Jin C, Guan C, Wu D, Li Z (2015) Cloning and expression analysis of 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase gene 1 involved in fruit maturation and abiotic stress response in Lycium chinense. J Plant Growth Regul 34:465–474. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-015-9481-1
Tuteja N (2007) Abscisic acid and abiotic stress signaling. Plant Signal Behav 2:135–138. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.2.3.4156
Vishwakarma K, Upadhyay N, Kumar N, Yadav G, Singh J, Mishra R, Kumar V, Verma R, Upadhyay RG, Pandey M (2017) Abscisic acid signaling and abiotic stress tolerance in plants: a review on current knowledge and future prospects. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00161
Vosoughi N, Gomarian M, Pirbalouti A, Khaghani S, Malekpoor F (2018) Essential oil composition and total phenolic, flavonoid contents, and antioxidant activity of sage (Salvia officinalis L.) extract under chitosan application and irrigation frequencies. Ind Crop Prod 117:366–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.03.021
Wang Z, Cui L, Chen C, Liu X, Yan Y, Wang Z (2012) Downregulation of cinnamoyl CoA reductase affects lignin and phenolic acids biosynthesis in Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge. Plant Mol Biol Rep 30:1229–1236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-012-0444-4
Wang H, Wu Y, Yang X, Guo X, Cao X (2017) SmLEA2, a gene for late embryogenesis abundant protein isolated from Salvia miltiorrhiza, confers tolerance to drought and salt stress in Escherichia coli and S. miltiorrhiza. Protoplasma 254:685–696. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-016-0981-z
Wei T, Deng K, Gao Y, Liu Y, Yang M, Zhang L, Zhang X, Wang C, Song W, Chen C (2016a) Arabidopsis DREB1B in transgenic Salvia miltiorrhiza increased tolerance to drought stress without stunting growth. Plant Physiol Biochem 104:17–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.03.003
Wei T, Deng K, Liu D, Gao Y, Liu Y, Yang M, Zhang L, Zheng X, Wang C, Song W (2016b) Ectopic expression of DREB transcription factor, AtDREB1A, confers tolerance to drought in transgenic Salvia miltiorrhiza. Plant Cell Physiol 57:1593–1609. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcw084
Wei T, Deng K, Zhang Q, Gao Y, Liu Y, Yang M, Zhang L, Zheng X, Wang C, Liu Z (2017) Modulating AtDREB1C expression improves drought tolerance in Salvia miltiorrhiza. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00052
Xian L, Sun P, Hu S, Wu J, Liu J (2014) Molecular cloning and characterization of CrNCED1, a gene encoding 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase in Citrus reshni, with functions in tolerance to multiple abiotic stresses. Planta 239:61–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-013-1963-4
Xiao Y, Zhang L, Gao S, Saechao S, Di P, Chen J, Chen W (2011) The c4h, tat, hppr and hppd genes prompted engineering of rosmarinic acid biosynthetic pathway in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root cultures. Plos One. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0029713
Xu H, Song J, Luo H, Zhang Y, Li Q, Zhu Y, Xu J, Li Y, Song C, Wang B (2016) Analysis of the genome sequence of the medicinal plant Salvia miltiorrhiza. Mol Plant 9:949–952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2016.03.010
Yang D, Sheng D, Duan Q, Liang X, Liang Z, Liu Y (2012) PEG and ABA trigger the burst of reactive oxygen species to increase tanshinone production in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots. J Plant Growth Regul 31:579–587. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-012-9268-6
Zhang Y, Yang J, Lu S, Cai J, Guo Z (2008) Overexpressing SgNCED1 in tobacco increases ABA level, antioxidant enzyme activities, and stress tolerance. J Plant Growth Regul 27:151–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-008-9041-z
Zhang Y, Yan Y, Wang Z (2010) The Arabidopsis PAP1 transcription factor plays an important role in the enrichment of phenolic acids in Salvia miltiorrhiza. J Agric Food Chem 58:12168–12175. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf103203e
Zhang H, Yang B, Liu W, Li H, Wang L, Wang B, Deng M, Liang W, Deyholos MK, Jiang Y (2014a) Identification and characterization of CBL and CIPK gene families in canola (Brassica napus L.). BMC Plant Biol 14:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-14-8
Zhang S, Song G, Li Y, Gao J, Liu J, Fan Q, Huang C, Sui X, Chu X, Guo D (2014b) Cloning of 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase gene (TaNCED1) from wheat and its heterologous expression in tobacco. Biol Plant 58:89–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-013-0373-6
Zhang S, Li H, Liang X, Yan Y, Xia P, Jia Y, Liang Z (2015) Enhanced production of phenolic acids in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root cultures by combing the RNAi-mediated silencing of chalcone synthase gene with salicylic acid treatment. Biochem Eng J 103:185–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2015.07.019
Zhao G, Shi Q, Han Y, Li S, Wang C (2014) The physiological and biochemical responses of a medicinal plant (Salvia miltiorrhiza L.) to stress caused by various concentrations of NaCl. Plos One. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0089624
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant nos. 81403033, 81673536 and 81373908) and partly supported by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Key Project (Grant No. LZ16H280001). We also thank Prof. Weibo Jin (Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, China) for his assistance in this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The paper has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by H. Peng.
Yanyan Jia and Jingling Liu are co-first authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, Y., Liu, J., Bai, Z. et al. Cloning and functional characterization of the SmNCED3 in Salvia miltiorrhiza. Acta Physiol Plant 40, 133 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-018-2704-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-018-2704-x