Abstract
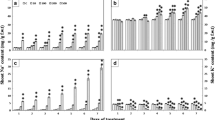
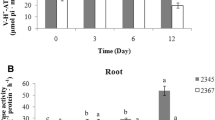
Nitraria tangutorum Bobr. is a typical halophyte with superior tolerance to salinity. However, little is known about its physiological adaptation mechanisms to the salt environment. In the present study, N. tangutorum seedlings were treated with different concentrations of NaCl (100, 200, 300 and 400 mmol L−1) combined with five levels of Ca2+ (0, 5, 10, 15 and 20 mmol L−1) to investigate the effects of salt stress and exogenous Ca2+ on Na+ compartmentalization and ion pump activities of tonoplast and plasma membrane (PM) in leaves. Na+ and Ca2+ treatments increased the fresh weight and dry weight of N. tangutorum seedlings. The absorption of Na+ in roots, stems and leaves was substantially increased with the increases of NaCl concentration, and Na+ was mainly accumulated in leaves. Exogenous Ca2+ reduced Na+ accumulation in roots but promoted Na+ accumulation in leaves. The absorption and transportation of Ca2+ in N. tangutorum seedlings were inhibited under NaCl treatments. Exogenous Ca2+ promoted Ca2+ accumulation in the plant. Na+ contents in apoplast and symplast of leaves were also significantly increased, and symplast was the main part of Na+ intracellular compartmentalization. The tonoplast H+-ATPase and H+-PPase activities were significantly promoted under salt stress (NaCl concentrations ≤300 mmol L−1). PM H+-ATPase activities gradually increased under salt stress (NaCl concentrations ≤200 mmol L−1) followed by decreases with NaCl concentration increasing. The tonoplast H+-ATPase, H+-PPase and PM H+-ATPase activities increased first with the increasing exogenous Ca2+ concentration, reached the maximums at 15 mmol L−1 Ca2+, and then decreased. The tonoplast and PM Ca2+-ATPase activities showed increasing trends with the increases of NaCl and Ca2+ concentration. These results suggested that certain concentrations of exogenous Ca2+ effectively enhanced ion pump activities of tonoplast and PM as well as promoted the intracellular Na+ compartmentalization to improve the salt tolerance of N. tangutorum.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amor NB, Megdiche W, Jiménez A, Sevilla F, Abdelly C (2010) The effect of calcium on the antioxidant systems in the halophyte Cakile maritima under salt stress. Acta Physiol Plant 32:453–461
Anil VS, Rajkumar P, Kumar P, Mathew MK (2008) A plant Ca2+ pump, ACA2, relieves salt hypersensitivity in yeast. Modulation of cytosolic calcium signature and activation of adaptive Na+ homeostasis. J Biol Chem 283:3497–3506
Baltscheffsky M, Schultz A, Baltscheffsky H (1999) H+-proton-pumping inorganic pyrophosphatase: a tightly membrane-bound family. FEBS Lett 452:121–127
Binzel ML, Hess FD, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM (1988) Intracellular compartmentation of ions in salt adapted tobacco cells. Plant Physiol 86:607–614
Blumwald E, Aharon GS, Apse MP (2000) Sodium transport in plant cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1465:140–151
Bourgeais-Chaillou P, Guerrier G (1992) Salt-responses in Lycopersicon esculentum calli and whole plants. J Plant Physiol 140:494–501
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM, Pardo JM (1998) Plants use calcium to resolve salt stress. Trends Plant Sci 3:411–412
Bush DS (1995) Calcium regulation in plant cells and its role in signaling. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 46:95–122
Cai XY, Chen XD, Li CZ, Liu C (2013) Effects of exogenous Ca2+ on the seed germination of Koelreuteria paniculata in limestone area of Southwest China under drought stress. Chin J Appl Ecol 24:1341–1346
Carafoli E (1991) Calcium pump of the plasma membrane. Physiol Rev 71:129–153
Dietz KJ, Tavakoli N, Kluge C, Mimura T, Sharma SS, Harris GC, Chardonnens AN, Golldack D (2001) Significance of the V-type ATPase for the adaptation to stressful growth conditions and its regulation on the molecular and biochemical level. J Exp Bot 52:1969–1980
Duby G, Boutry M (2009) The plant plasma membrane proton pump ATPase: a highly regulated P-type ATPase with multiple physiological roles. Pflügers Arch 457:645–655
Fukuda A, Nakamura A, Tagiri A, Tanaka H, Miyao A, Hirochika H, Tanaka Y (2004) Function, intracellular localization and the importance in salt tolerance of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter from rice. Plant Cell Physiol 45:146–159
Gaxiola RA, Palmgren MG, Schumacher K (2007) Plant proton pumps. FEBS Lett 581:2204–2214
Geisler M, Frangne N, Gomès E, Martinoia E, Palmgren MG (2000) The ACA4 gene of Arabidopsis encodes a vacuolar membrane calcium pump that improves salt tolerance in yeast. Plant Physiol 124:1814–1827
Hasegawa PM, Bressan RA, Zhu JK, Bohnert HJ (2000) Plant cellular and molecular responses to high salinity. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 51:463–499
Janicka-Russak M (2011) Plant plasma membrane H+-ATPase in adaptation of plants to abiotic stresses. In: Shanker A (ed) Abiotic stress response in plants-physiological, biochemical and genetic perspectives. InTech, Rijeka, pp 197–218
Janicka-Russak M, Kłobus G (2007) Modification of plasma membrane and vacuolar H+-ATPases in response to NaCl and ABA. J Plant Physiol 164:295–302
Janicka-Russak M, Kabała K, Wdowikowska A, Kłobus G (2013) Modification of plasma membrane proton pumps in cucumber roots as an adaptation mechanism to salt stress. J Plant Physiol 170:915–922
Jensen TP, Buckby LE, Empson RM (2004) Expression of plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase family members and associated synaptic proteins in acute and cultured organotypic hippocampal slices from rat. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 152:129–136
Kabała K, Kłobus G (2001) Characterization of the tonoplast proton pumps in Cucumis sativus L. root cells. Acta Physiol Plant 23:55–63
Kabała K, Janicka-Russak M, Kłobus G (2010) Different responses of tonoplast proton pumps in cucumber roots to cadmium and copper. J Plant Physiol 167:1328–1335
Kiegle E, Moore CA, Haseloff J, Tester MA, Knight MR (2001) Cell-type-specific calcium responses to drought, salt and cold in the Arabidopsis root. Plant J 23:267–278
Kłobus G, Janicka-Russak M (2004) Modulation by cytosolic components of proton pump activities in plasma membrane and tonoplast from Cucumis sativus roots during salt stress. Physiol Plant 121:84–92
Long JM, Widders IE (1990) Quantification of apoplastic potassium content by elution analysis of leaf lamina tissue from Pea (Pisum sativum L. cv Argenteum). Plant Physiol 94:1040–1047
Lynch J, Polito VS, Läuchli A (1989) Salinity stress increases cytoplasmic Ca activity in maize root protoplasts. Plant Physiol 90:1271–1274
Mao G, Xu X, Chen Q, Yue Z, Zhu L (2013) Flue gas desulfurization gypsum by-products alters cytosolic Ca2+ distributionand Ca2+-ATPase activity in leaf cells of oil sunflower in alkaline soil. J Plant Interact. doi:10.1080/17429145.2013.791378
Matinzadeh Z, Breckle SW, Mirmassoumi M, Akhani H (2013) Ionic relationships in some halophytic Iranian Chenopodiaceae and their rhizospheres. Plant Soil 372:523–539
Matsushita N, Matoh T (1991) Characterization of Na+ exclusion mechanisms of salt-tolerant reed plants in comparison with salt-sensitive rice plants. Physiol Plant 83:170–176
Morth JP, Pedersen BP, Buch-Pedersen MJ, Andersen JP, Vilsen B, Palmgren MG, Nissen P (2011) A structural overview of the plasma membrane Na+, K+-ATPase and H+-ATPase ion pumps. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 12:60–70
Munns R, James RA, Läuchli A (2006) Approaches to increasing the salt tolerance of wheat and other cereals. J Exp Bot 57:1025–1043
Niu X, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM, Pardo JM (1995) Ion homeostasis in NaCl stress environments. Plant Physiol 109:735–742
Pérez-Alfocea F, Balibrea ME, Santa Cruz A, Estañ MT (1996) Agronomical and physiological characterization of salinity tolerance in a commercial tomato hybrid. Plant Soil 180:251–257
Pfeiffer W, Hager A (1993) A Ca2+-ATPase and a Mg2+/H+-antiporter are present on tonoplast membranes from roots of Zea mays L. Planta 191:377–385
Pitann B, Schubert S, Mühling KH (2009) Decline in leaf growth under salt stress is due to an inhibition of H+-pumping activity and increase in apoplastic pH of maize leaves. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 172:535–543
Popova OV, Golldack D (2007) In the halotolerant Lobularia maritima (Brassicaceae) salt adaptation correlates with activation of the vacuolar H+-ATPase and the vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter. J Plant Physiol 164:1278–1288
Quintero JM, Fournier JM, Benlloch M, Rodríguez-Navarro A (2008) Na+ accumulation in root symplast of sunflower plants exposed to moderate salinity is transpiration-dependent. J Plant Physiol 165:1248–1254
Sahu BB, Shaw BP (2009) Salt-inducible isoform of plasma membrane H+ ATPase gene in rice remains constitutively expressed in natural halophyte, Suaeda maritima. J Plant Physiol 166:1077–1089
Serrano R, Mulet JM, Rios G, Marquez JA, De Larrinoa IF, Leube MP, Mendizabal I, Pascual-Ahuir A, Proft M, Ros R, Montesinos C (1999) A glimpse of the mechanisms of ion homeostasis during salt stress. J Exp Bot 50:1023–1036
Shone MGT, Flood Afrc AV (1985) Measurement of free space and sorption of large molecules by cereal roots. Plant Cell Environ 8:309–315
Strehler EE, Zacharias DA (2001) Role of alternative splicing in generating isoform diversity among plasma membrane calcium pumps. Physiol Rev 81:21–50
Tattini M, Traversi ML (2009) On the mechanism of salt tolerance in olive (Olea europaea L.) under low- or high-Ca2+ supply. Environ Exp Bot 65:72–81
Wakeel A, Hanstein S, Pitann B, Schubert S (2010) Hydrolytic and pumping activity of H+-ATPase from leaves of sugar beet (Beata vulgaris L.) as affected by salt stress. J Plant Physiol 167:725–731
Wang B, Lüttge U, Ratajczak R (2001) Effects of salt treatment and osmotic stress on V-ATPase and V-PPase in leaves of the halophyte Suaeda salsa. J Exp Bot 52:2355–2365
Yan YQ, Liu XL, Wang K, Fan JP, Shi XC (2010) Effect of complex saline-alkali stress on physiological parameters of Nitratia tangutorum. Chin J Plant Ecol 34:1213–1219
Yan Y, Yuan X, Liu W, Xuan Y, Zhang Y (2014) Effect of salt stress and exogenous Ca2+ on ion absorption and transportation of Nitraria. J Northeast Forest Univ 45:71–78
Yang Y, Zhang F, Zhao M, An L, Zhang L, Chen N (2007) Properties of plasma membrane H+-ATPase in salt-treated Populus euphratica callus. Plant Cell Rep 26:229–235
Yang Y, Shi R, Wei X, Fan Q, An L (2010a) Effect of salinity on antioxidant enzymes in calli of the halophyte Nitraria tangutorum Bobr. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 102:387–395
Yang Y, Wei X, Shi R, Fan Q, An L (2010b) Salinity-induced physiological modification in the callus from halophyte Nitraria tangutorum Bobr. J Plant Growth Regul 29:465–476
Yang Y, Yang F, Li X, Shi R, Lu J (2013) Signal regulation of proline metabolism in callus of the halophyte Nitraria tangutorum Bobr. grown under salinity stress. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 112:33–42
Yasar F, Uzal O, Tufenkcil S, Yildiz K (2006) Ion accumulation in different organs of green bean genotypes grown under salt stress. Plant Soil Environ 52:476–480
Yuan XT, Liu W, Xuan YN, Zhang YY, Yan YQ (2014) Physiological effects of exogenous Ca2+ on Nitraria tangutorum under salt stress. Plant Physiol J 50:88–94
Zhang HX, Hodson JN, Williams JP, Blumwald E (2001) Engineering salt-tolerant Brassica plants: characterization of yield and seed oil quality in transgenic plants with increased vacuolar sodium accumulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:12832–12836
Zhang Y, Liu W, Xuan Y, Yuan X, Yan Y (2013) Effects of salicylic acid mitigating under salt stress on active oxygen metabolism and membrane stability in Nitratia tangutorum. J Northeast Forest Univ 41:56–59
Zhao F, Wang Z, Zhang Q, Zhao Y, Zhang H (2006) Analysis of the physiological mechanism of salt-tolerant transgenic rice carrying a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene from Suaeda salsa. J Plant Res 119:95–104
Zhen RG, Kim EJ, Rea PA (1997) The molecular and biochemical basis of pyrophosphate-energized proton translocation at the vacuolar membrane. Adv Bot Res 25:298–337
Zhu JK (2000) Genetic analysis of plant salt tolerance using Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 124:941–948
Zhu JK (2002) Salt and drought stress signal transduction in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:247–273
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial supports by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2014M551209), Scientific Research Fund of Heilongjiang Provincial Education Department (11551052, 12521030) and Doctor Research Startup Foundation of Northeast Agricultural University (2012RCB63, 2012RCB107).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by R. Aroca.
X. Yuan is the co-first author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W., Yuan, X., Zhang, Y. et al. Effects of salt stress and exogenous Ca2+ on Na+ compartmentalization, ion pump activities of tonoplast and plasma membrane in Nitraria tangutorum Bobr. leaves. Acta Physiol Plant 36, 2183–2193 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-014-1595-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-014-1595-8