Abstract
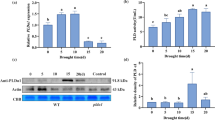
Comparative analyses of the responses to NaCl in Cynodon dactylon and a sensitive crop species like rice could effectively unravel the salt tolerance mechanism in the former. C. dactylon, a wild perennial chloridoid grass having a wide range of ecological distribution is generally adaptable to varying degrees of salinity stress. The role of salt exclusion mechanism present exclusively in the wild grass was one of the major factors contributing to its tolerance. Salt exclusion was found to be induced at 4 days when the plants were treated with a minimum conc. of 200 mM NaCl. The structural peculiarities of the salt exuding glands were elucidated by the SEM and TEM studies, which clearly revealed the presence of a bicellular salt gland actively functioning under NaCl stress to remove the excess amount of Na+ ion from the mesophyll tissues. Moreover, the intracellular effect of NaCl on the photosynthetic apparatus was found to be lower in C. dactylon in comparison to rice; at the same time, the vacuolization process increased in the former. Accumulation of osmolytes like proline and glycine betaine also increased significantly in C. dactylon with a concurrent check on the H2O2 levels, electrolyte leakage and membrane lipid peroxidation. This accounted for the proper functioning of the Na+ ion transporters in the salt glands and also in the vacuoles for the exudation and loading of excess salts, respectively, to maintain the osmotic balance of the protoplasm. In real-time PCR analyses, CdSOS1 expression was found to increase by 2.5- and 5-fold, respectively, and CdNHX expression increased by 1.5- and 2-fold, respectively, in plants subjected to 100 and 200 mM NaCl treatment for 72 h. Thus, the comparative analyses of the expression pattern of the plasma membrane and tonoplast Na+ ion transporters, SOS1 and NHX in both the plants revealed the significant role of these two ion transporters in conferring salinity tolerance in Cynodon.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso-Blanco C, Aarts MGM, Bentsink L, Keurentjes JJB, Reymond M, Vreugdenhil D, Koornneef M (2009) What has natural variation taught us about plant development, physiology, and adaptation? Plant Cell 21(7):1877–1896
Apel K, Hirt H (2004) Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:373–399
Ashraf M, Foolad MR (2007) Roles of glycine betaine and proline in improving plant abiotic stress resistance. Environ Exp Bot 59:206–216
Assaha DVM, Ueda A, Saneoka H (2013) Comparison of growth and mineral accumulation of two solanaceous species, Solanum scabrum mill. (huckleberry) and S. melongena L. (eggplant), under salinity stress. Soil Sci Plant Nut 59:912–920
Bagci SA, Ekiz H, Yilmaz A (2003) Determination of the salt tolerance of some barley genotypes and the characteristics affecting tolerance. Turk J Agric For 27:253–260
Ball MC (1988) Salinity tolerance in the mangroves, Aegiceras corniculatum and Avicennia marina. I. Water use in relation to growth, carbon partitioning and salt balance. Aust J Plant Physiol 15:447–464
Barhoumi Z, Djebali W, Abdelly C, Chaibi W, Smaoui A (2008) Ultrastructure of Aeluropus littoralis leaf salt glands under NaCl stress. Protoplasma 233(3–4):195–202
Barhoumi Z, Djebali W, Smaoui A, Chaibi W, Abdelly C (2007) Contribution of NaCl excretion to salt resistance of Aeluropus littoralis (Willd) Parl. J Plant Physiol 164(7):842–850
Barr HD, Weatherley PE (1962) A re-examination of the relative turgidity technique for estimating water deficit in leaves. Aust J Biol Sci 15:413–428
Bates HS, Waldren RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid estimation of free proline for drought stress determination. Plant Soil 39:205–208
Beard JB, Sifers SI (1997) Genetic diversity in dehydration avoidance and drought resistance within the Cynodon and Zoysia species. Int Turfgrass Soc Res J 8:603–610
Blumwald E (2000) Sodium transport and salt tolerance in plants. Curr Opin Cell Biol 12:431–434
Bortner CD, Hughes FM Jr, Cidlowski JA (1997) A primary role for K+ and Na+ efflux in the activation of apoptosis. J Biol Chem 272:32436–32442
Campbell RJ, Grayson RL, Marini RP (1990) Surface and ultrastructural feeding injury to strawberry leaves by the two spotted spider mite. Hort Sci 25(8):948–951
Ceccoli G, Ramos J, Vanesa P, Dellaferrera I, Tivano JC, Taleisnik E, Vegetti AC (2015) Salt glands in the Poaceae family and their relationship to salinity tolerance. Bot Rev 81:162–178
Chen THH, Murata N (2011) Glycine betaine protects plants against abiotic stress: mechanisms and biotechnological applications. Plant Cell Environ 34(1):1–20
Clayton WD, Renvoize SA (1986) Genera Graminum: grasses of the world. Her Majesty’s Stationery Office, London
Du Y, Hei Q, Liu Y, Zhang H, Xu K, Xia T (2010) Isolation and characterization of a putative vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene from Zoysia japonica L. J Plant Biol 53(4):251–258
Faiyue B, Vijayalakshmi C, Nawaz S, Nagato Y, Taketa S, Ichii M, Al-Azzawi MJ, Flowers TJ (2010) Studies on sodium bypass flow in lateral rootless mutants Irt1 and Irt2, and crown rootless mutant crl1 of rice (Oryza sativa L.) Plant Cell Environ 33:687–701
Farkhondeh R, Nabizadeh E, Jalilnezhad N (2012) Effect of salinity stress on proline content, membrane stability and water relations in two sugar beet cultivars. Int J Agr Sci 2(5):385–392
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2010) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:909–930
Grieve CM, Grattan SR (1983) Rapid assay for the determination of water soluble quarternary ammonium compounds. Plant Soil 70:303–307
Hauser F, Horie T (2010) A conserved primary salt tolerance mechanism mediated by HKT transporters: a mechanism for sodium exclusion and maintenance of high K+/Na+ ratio in leaves during salinity stress. Plant Cell Environ 33:552–565
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts. I: kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophysics 125:189–198
Hien DT, Jacobs M, Angenon G, Hermans C, Thu TT, Son LV, Roosens NH (2003) Proline accumulation and Δ1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase gene properties in three rice cultivars differing in salinity and drought tolerance. Plant Sci 165:1059–1068
Horie T, Karahara I, Katsuhara M (2012) Salinity tolerance mechanisms in glycophytes: an overview with the central focus on rice plants. Rice 5:11
Huang Z, Zhao L, Chen D, Liang M, Liu Z, Shao H, Long X (2013) Salt stress encourages proline accumulation by regulating proline biosynthesis and degradation in Jerusalem artichoke plantlets. PLoS One 8(4):e62085
Jana S, Choudhuri MA (1981) Glycolate metabolism of three submerged aquatic angiosperms during aging. Aquatic Bot 12:345–354
Kamel M, Hammad S (2015) Is the soil K/Na ratio the first defense line against salinity? European J Biol Res 5(3):42–51
Kobayashi H, Masaoka Y (2008) Salt secretion in Rhodes grass (Chloris gayana Kunth) under conditions of excess magnesium. Soil Sci Plant Nut 54:393–399
Lee GJ, Carrow RN, Duncan RR, Eiteman MA, Rieger MW (2008) Synthesis of organic osmolytes and salt tolerance mechanisms in Paspalum vaginatum. Environ Exp Bot 63:19–27
Lessani H, Marschner H (1978) Relation between salt tolerance and long-distance transport of sodium and chloride in various crop species. Aust J Plant Physiol 5:27–37
Lin CC, Kao CH (1998) Effect of oxidative stress caused by hydrogen peroxide on senescence of rice leaves. Bot Bull Acad Sin 39:161–165
Liphschitz N, Waisel Y (1974) Existence of salt glands in various genera of the Gramineae. New Phytol 73:507–513
Lutts S, Kinet JM, Bouharmont J (1996) Effect of various salts and of mannitol on ion and proline accumulation in relation to osmotic adjustment in rice (Oryza sativa L.) callus cultures. J. Plant Physiol 149:186–195
Maathuis FJM, Amtmann A (1999) K+ nutrition and Na+ toxicity: the basis of cellular K+/Na+ ratios. Ann Bot 84:123–133
Mahajan S, Pandey GK, Tuteja N (2008) Calcium and salt stress signalling in plants: shedding light on SOS pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys 471:146–158
Marcum KB (1999) Salinity tolerance mechanism of grasses in the sub-family Chloridoideae. Crop Sci 39(4):1153–1160
Marcum KB, Wess G, Ray DT, Engelke MC (2003) Zoysia grasses, salt glands, and salt tolerance. USGA Turfgrass Environ Res 2(14):1–6
Martinez-Atienza J, Jiang X, Garciadeblas B, Mendoza I, Zhu J-K, Pardo JM, Quintero FJ (2006) Conservation of the salt overly sensitive pathway in rice. Plant Physiol 143:1001–1012
McDonald AJS, Davies WJ (1996) Keeping in touch: responses of the whole plant to deficits in water and nitrogen supply. Adv Bot Res 22:229–300
Mimura T, Kura-Hotta M, Tsujimura T, Ohnishi M, Miura M, Okazaki Y, Mimura M, Maeshima M, Washitani-Nemoto S (2003) Rapid increase in vacuolar volume in response to salt stress. Planta 216(3):397–402
Moinuddin M, Gulzar S, Ahmed MZ, Gul B, Koyro HW, Khan MA (2014) Excreting and non-excreting grasses exhibit different salt resistance strategies. AoB plants 6:plu038
Moore G, Sanford P, Wiley T (2006) Perennial pastures for Western Australia. Perth: Department of Agriculture and Food, Western Australia, Bulletin 4690
Munns R (2002) Comparative physiology of salt and water stress. Plant Cell Environ 25:239–250
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681
Naidoo Y, Naidoo G (1998) Sporobolus virginicus leaf salt glands: morphology and ultrastructure. South Afr J Bot 64(3):198–204
Nellemann C, Devette MM, Manders T (2009) The environmental food crisis: the environment’s role in averting future food crisis: a UNEP rapid response assessment. United Nations Environment Programme of the United Nations, Nairobi
Ong JE, Gong WK (2013) Structure, function and management of mangrove ecosystems. ISME mangrove educational book series no. 2, International Society for Mangrove Ecosystems (ISME), Okinawa, Japan and International Tropical Timber Organization (ITTO), Yokohama, Japan
Panahi B, Ahmadi FS, Mehrjerdi MZ, Moshtaghi N (2013) Molecular cloning and the expression of the Na+/H+ antiporter in the monocot halophyte Leptochloa fusca (L.) Kunth. NJAS - Wageningen J Life Sci 65:87–93
Passioura JB, Angus JF (2010) Improving productivity of crops in water limited environments. In: Sparks DL (ed) Advances in agronomy. Academic Press, Burlington, pp 37–75
Pathan AK, Bond J, Gaskin RE (2008) Sample preparation for scanning electron microscopy of plant surfaces—horses for courses. Micron 39:1049–1061
Plazek A, Tatrzanska M, Maciejewski M, Koscielniak J, Gondek K, Bojarczuk J, Dubert F (2013) Investigation of the salt tolerance of new polish bread and durum wheat cultivars. Acta Physiol Plant 35:2513–2523
Rajendran K, Tester M, Roy SJ (2009) Quantifying the three main components of salinity tolerance in cereals. Plant Cell Environ 32(3):237–249
Rio DC, Ares M Jr, Hannon GJ, Nilsen TW (2010) Purification of RNA using TRIzol (TRI reagent). Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2010(6):pdb.prot5439
Roy S, Chakraborty U (2014) Salt tolerance mechanisms in salt tolerant grasses (STGs) and their prospects in cereal crop improvement. Bot Stud 55:31
Roy S, Chakraborty U (2015) Cross-generic studies with rice indicate that ion homeostasis and antioxidant defense is associated with superior salinity tolerance in Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers. Ind J Plant Physiol 20(1):14–22
Saleh B (2012) Salt stress alters physiological indicators in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) Soil Environ 31(2):113–118
Sanadhya P, Agarwal P, Agarwal PK (2015) Ion homeostasis in a salt-secreting halophytic grass. AoB Plants 7:plv055
Shabala S, Cuin TA (2008) Potassium transport and plant salt tolerance. Physiol Plant 133(4):651–669
Sharpe RM, Dunn SN, Cahoon AB (2008) A plastome primer set for comprehensive quantitative real time RT-PCR analysis of Zea mays: a starter primer set for other Poaceae species. Plant Methods 4:14
Szabados L, Savoure A (2010) Proline: a multifunctional amino acid. Trends Plant Sci 15(2):89–97
Takahashi R, Liu S, Takano T (2009) Isolation and characterization of plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter genes from salt-sensitive and salt-tolerant reed plants. J Plant Physiol 166(3):301–309
Takao O, Hirunagi K, Taniguchi M, Miyake H (2013) Salt excretion from the salt glands in Rhodes grass (Chloris gayana Kunth) as evidenced by low-vacuum scanning electron microscopy. Flora 208(1):52–57
Takao O, Taniguchi M, Miyake H (2012) Morphology and ultrastructure of the salt glands on the leaf surface of rhodes grass (Chloris gayana Kunth). Intl J Plant Sci 173(5):454–463
Tester M, Bacic A (2005) Abiotic stress tolerance in grasses - from model plants to crop plants. Plant Physiol 137:791–793
Tester M, Davenport RJ (2003) Na+ tolerance and Na+ transport in higher plants. Ann Bot 91:503–527
Thomson WW, Faraday CD, Oross JW (1988) Salt glands. In: Baker DA, Hall JL (eds) Solute transport in plant cells and tissues. Longman, Essex, pp 498–537
Thordal-Christensen H, Zhang Z, Wei Y, Collinge DB (1997) Subcellular localization of H2O2 in plants. H2O2 accumulation in papillae and hypersensitive response during the barley- powdery mildew interaction. Plant J 11(6):1187–1194
Tseng MJ, Liu CW, Yiu JC (2007) Enhanced tolerance to sulfur dioxide and salt stress of transgenic Chinese cabbage plants expressing both superoxide dismutase and catalase in chloroplasts. Plant Physiol Biochem 45:822–833
Yadav NS, Shukla PS, Jha A, Agarwal PK, Jha B (2012) The SbSOS1 gene from the extreme halophyte Salicornia Brachiata enhances Na+ loading in xylem and confers salt tolerance in transgenic tobacco. BMC Plant Biol 12:188
Yang CW, Zhang ML, Liu J, Shi DC, Wang DL (2009) Effects of buffer capacity on growth, photosynthesis, and solute accumulation of a glycophyte (wheat) and a halophyte (Chloris virgata). Photosynthetica 47:55–60
Zhang G-H, Su Q, Wu S (2008) Characterization and expression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene from the monocot halophyte Aeluropus littoralis. Plant Physiol Biochem 46:117–126
Zheng Y, Wang Z, Sunb X, Jia A, Jiang G, Li Z (2008) Higher salinity tolerance cultivars of winter wheat relieved senescence at reproductive stage. Environ Exp Bot 62:129–138
Zhu J-K (2001) Plant salt tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 6(2):66–71
Zhu J-K (2003) Regulation of ion homeostasis under salt stress. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:441–445
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to CSIR, New Delhi (Award No. 09/285(0046)/2008-EMR-I), and UGC, ERO, Kolkata (Minor Research Project No. PSW-80/12-13), for the financial support for carrying out this work. The authors are also grateful to the EM Facility, AIIMS, New Delhi, and USIC, Burdwan University, Burdwan, respectively, for TEM and SEM studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Peter Nick
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, S., Chakraborty, U. Role of sodium ion transporters and osmotic adjustments in stress alleviation of Cynodon dactylon under NaCl treatment: a parallel investigation with rice. Protoplasma 255, 175–191 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-017-1138-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-017-1138-4