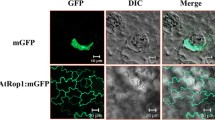
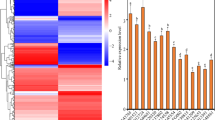
Abstract
Transcription factors can be used to engineer plants for enhanced productivity. However, the mechanism(s) by which the C2H2-type zinc finger transcription factor enhances pathogen resistance in cells is not fully understood. Here, Agrobacterium tumefaciens carrying the gene for Arabidopsis thaliana cysteine2/histidine2-type transcription factor 6 (ZAT6) was used to engineer rice (Oryza sativa L.), cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.), and slash pine (Pinus elliottii Engelm.) to generate transgenic cell lines. Transgenic cells were then inoculated with the pathogenic bacterium Pseudomonas syringae. Compared to the control, cell viability of transgenic cells increased 39–47% and growth rate increased 9–15% by 7 days after inoculation in rice, cotton and slash pine. Acid phosphatase activity and alkaline phosphatase activity and transcript levels of Ca2+-dependent protein kinase genes OsCPK1, OsCPK2, OsCPK6, and OsCPK8 and mitogen-activated protein kinase genes OsMAPK1, OsMAPK2, OsMAPK3, and OsMAPK8 increased significantly in transgenic rice cells by 3 day after inoculation, and extracellular pH had decreased by 10–14% by 96 min after inoculation in transgenic rice, cotton and slash pine cells. These results suggest that ZAT6 enhances P. syringae resistance in plant cells by modulating transcription of CPK and MAPK and oxidase activity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abuqamar S, Luo H, Laluk K, Mickelbart MV, Mengiste T (2009) Crosstalk between biotic and abiotic stress responses in tomato is mediated by the AIM1 transcription factor. Plant J 58:347–360
Barbez E, Dunser K, Gaidora A, Lendl T, Busch W (2017) Auxin steers root cell expansion via apoplastic pH regulation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci 114:E4884–E4893
Bogoslavsky L, Neumann PM (1998) Rapid regulation by acid pH of cell wall adjustment and leaf growth in maize plants responding to reversal of water stress. Plant Physiol 118:701–709
Bulgakov VP, Tchernoded GK, Mischenko NP, Shkryl YN, Glazunov VP, Fedoreyev SA, Zhuravlev YN (2003) Increase in anthraquinone content in Rubia cordifolia cells transformed by rol genes does not involve activation of the NADPH oxidase signaling pathway. Biochemistry 68:795–801
Campos JF, Cara B, Perez-Martin F, Pineda B, Egea I, Flores FB, Fernandez-Garcia N, Capel J, Moreno V, Angosto T, Lozano R, Bolarin MC (2016) The tomato mutant ars1 (altered response to salt stress 1) identifies an R1-type MYB transcription factor involved in stomatal closure under salt acclimation. Plant Biotech J 14:1345–1356
Chen J, Yang LB, Yan XX, Liu YL, Wang R, Fan TT, Ren YB, Tang XF, Xiao FM, Liu YS, Cao SQ (2016) Zinc-finger transcription factor ZAT6 Positively regulates cadmium tolerance through the glutathione-dependent pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 171:707–719
Cheng LQ, Li XX, Huang X, Ma T, Liang Y, Ma XY, Peng XJ, Jia JT, Chen SY, Chen Y, Deng B, Liu GS (2013a) Overexpression of sheepgrass R1-MYB transcription factor LcMYB1 confers salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol Biochem 70:252–260
Cheng YJ, Kim MD, Deng XP, Kwak SS, Chen W (2013b) Enhanced salt stress tolerance in transgenic potato plants expressing IbMYB1, a sweet potato transcription factor. J Microbiol Biotech 23:1737–1746
Cui MH, Yoo KS, Hyoung S, Nguyen HT, Kim YY, Kim HJ, Ok SH, Yoo SD, Shin JS (2013) An Arabidopsis R2R3-MYB transcription factor, AtMYB20, negatively regulates type 2C serine/threonine protein phosphatases to enhance salt tolerance. FEBS Lett 587:1773–1778
Devaiah BN, Nagarajan VK, Raghothama KG (2007) Phosphate homeostasis and root development in Arabidopsis are synchronized by the zinc finger transcription factor ZAT6. Plant Physiol 145:147–159
Englbrecht CC, Schoof H, Bohm S (2004) Conservation, diversification and expansion of C2H2 zinc finger proteins in the Arabidopsis thaliana genome. BMC Genomics 5:39
Felix G, Duran JD, Volko S, Boller T (1999) Plants have a sensitive perception system for the most conserved domain of bacterial flagellin. Plant J 18:265–276
Flythe MD, Russell JB (2004) The effect of pH and a bacteriocin (bovicin HC5) on Clostridium sporogenes MD1, a bacterium that has the ability to degrade amino acids in ensiled plant materials. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 47:215–222
Gonzalez-Fontes A, Rexach J, Quiles-Pando C, Herrera-Rodriguez MB, Camacho-Cristobal JJ, Navarro-Gochicoa MT (2013) Transcription factors as potential participants in the signal transduction pathway of boron deficiency. Plant Sign & Behavior 8:e26114
Guo HY, Wang YC, Wang LQ, Hu P, Wang YM, Jia YY, Zhang CR, Zhang Y, Zhang YM, Wang C, Yang CP (2017) Expression of the MYB transcription factor gene BplMYB46 affects abiotic stress tolerance and secondary cell wall deposition in Betula platyphylla. Plant Biotech J 15:107–121
Jin X, Zhu LP, Yao Q, Meng XR, Ding GH, Wang D, Xie QL, Tong Z, Tao CC, Yu L, Li HB, Wang XC (2017) Expression profiling of mitogen-activated protein kinase genes reveals their evolutionary and functional diversity in different rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis) Cultivars. Genes 8:261
Johnson KL, Ramm S, Kappel C, Ward S, Leyser O, Sakamoto T, Kurata T, Bevan MW, Lenhard M (2015) The Tinkerbell (Tink) mutation identifies the dual-specificity MAPK phosphatase INDOLE-3-BUTYRIC ACID-RESPONSE5 (IBR5) as a novel regulator of organ size in Arabidopsis. PLoS ONE 10:e0131103
Jung C, Seo JS, Han SW, Koo YJ, Kim CH, Song SI, Nahm BH, Choi YD, Cheong JJ (2008) Overexpression of AtMYB44 enhances stomatal closure to confer abiotic stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 146:623–635
Kaida R, Satoh Y, Bulone V, Yamada Y, Kaku T, Hayashi T, Kaneko TS (2009) Activation of beta-glucan synthases by wall-bound purple acid phosphatase in tobacco cells. Plant Physiol 150:1822–1830
Kim CY, Zhang SQ (2004) Activation of a mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade induces WRKY family of transcription factors and defense genes in tobacco. Plant J 38:142–151
Kim K, Messinger LA, Nelson DL (1998) Ca2+-dependent protein kinases of Paramecium—cloning provides evidence of a multigene family. European J Biochem 251:605–612
Koiwai H, Tagiri A, Katoh S, Katoh E, Ichikawa H, Minami E, Nishizawa Y (2007) RING-H2 type ubiquitin ligase EL5 is involved in root development through the maintenance of cell viability in rice. Plant J 51:92–104
Lalau CM, Mohedano Rde A, Schmidt EC, Bouzon ZL, Ouriques LC, dos Santos RW, da Costa CH, Vicentini DS, Matias WG (2015) Toxicological effects of copper oxide nanoparticles on the growth rate, photosynthetic pigment content, and cell morphology of the duckweed Landoltia punctata. Protoplasma 252:221–229
Lassig R, Gutermuth T, Bey TD, Konrad KR, Romeis T (2014) Pollen tube NAD(P)H oxidases act as a speed control to dampen growth rate oscillations during polarized cell growth. Plant J 78:94–106
Leroch M, Neuhaus HE, Kirchberger S, Zimmermann S, Melzer M, Gerhold J, Tjaden J (2008) Identification of a novel adenine nucleotide transporter in the endoplasmic reticulum of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 20:438–451
Lev S, Horwitz BA (2003) A mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway modulates the expression of two cellulase genes in Cochliobolus heterostrophus during plant infection. Plant Cell 15:835–844
Li C, Chang PP, Ghebremariam KM, Qin L, Liang Y (2014) Overexpression of tomato SpMPK3 gene in Arabidopsis enhances the osmotic tolerance. Biochem Biophy Res Commun 443:357–362
Li XW, Wang Y, Yan F, Li JW, Zhao Y, Zhao X et al (2016) Overexpression of soybean R2R3-MYB transcription factor, GmMYB12B2, and tolerance to UV radiation and salt stress in transgenic Arabidopsis. Genet Mol Res 15:1–15
Liu ZH, Xia M, Poovaiah BW (1998) Chimeric calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase in tobacco: differential regulation by calmodulin isoforms. Plant Mol Biol 38:889–897
Liu XM, Nguyen XC, Kim KE, Han HJ, Yoo J, Lee K, Kim MC, Yun DJ, Chung WS (2013) Phosphorylation of the zinc finger transcriptional regulator ZAT6 by MPK6 regulates Arabidopsis seed germination under salt and osmotic stress. Biochem Biophy Res Commun 430:1054–1059
Liu ZQ, Shi LP, Liu YY, Tang Q, Shen L, Yang S, Cai JS, Yu HX, Wang RZ, Wen JY, Lin YQ, Hu J, Liu CL, Zhang YW, Mou SL, He SL (2015) Genome-wide identification and transcriptional expression analysis of mitogen-activated protein kinase and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase genes in Capsicum annuum. Frontiers Plant Sci 6:780
Ma HR, Wei HB, Chen Z, Yang Y, Wang ZH, Madina H, Cao X, Akber AH (2013) The estrogenic activity of isoflavones extracted from chickpea Cicer arietinum L. sprouts in vitro. Phytotherapy Res 27:1237–1242
Martinez-Noel G, Nagaraj VJ, Calo G, Wiemken A, Pontis HG (2007) Sucrose regulated expression of a Ca2+-dependent protein kinase (TaCDPK1) gene in excised leaves of wheat. Plant Physiol Biochem 45:410–419
Mehlmer N, Wurzinger B, Stael S, Hofmann-Rodrigues D, Csaszar E, Pfister B, Bayer R, Teige M (2010) The Ca2+-dependent protein kinase CPK3 is required for MAPK-independent salt-stress acclimation in Arabidopsis. Plant J 63:484–498
Mei C, Michaud M, Cussac M, Albrieux C, Gros V, Marechal E, Block MA, Jouhet J, Rebeille F (2015) Levels of polyunsaturated fatty acids correlate with growth rate in plant cell cultures. Sci Rep 5:15207
Mito T, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Ohme-Takagi M, Matsui K (2011) Generation of chimeric repressors that confer salt tolerance in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Biotech J 9:736–746
Mizoguchi T, Irie K, Hirayama T, Hayashida N, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Matsumoto K, Shinozaki K (1996) A gene encoding a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase is induced simultaneously with genes for a mitogen-activated protein kinase and an S6 ribosomal protein kinase by touch, cold, and water stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci 93:765–769
Nagai T, Ishihara S, Yokoyama A, Iwafune T (2011) Effects of four rice paddy herbicides on algal cell viability and the relationship with population recovery. Environ Toxicol Chem 30:1898–1905
Nagaoka S, Takano T (2003) Salt tolerance-related protein STO binds to a Myb transcription factor homologue and confers salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 54:2231–2237
Nath M, Yadav S, Kumar Sahoo R, Passricha N, Tuteja R, Tuteja N (2016) PDH45 transgenic rice maintain cell viability through lower accumulation of Na+, ROS and calcium homeostasis in roots under salinity stress. J Plant Physiol 191:1–11
Neupane A, Nepal MP, Benson BV, Macarthur KJ, Piya S (2013a) Evolutionary history of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) genes in Lotus, Medicago, and Phaseolus. Plant Sign & behavior 8:e27189
Neupane A, Nepal MP, Piya S, Subramanian S, Rohila JS, Reese RN, Benson BV (2013b) Identification, nomenclature, and evolutionary relationships of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) genes in soybean. Evol Bioinform Online 9:363–386
Peng XJ, Liu H, Wang D, Shen SH (2016) Genome-wide identification of the Jatropha curcas MYB family and functional analysis of the abiotic stress responsive gene JcMYB2. BMC genomics 17:251
Preuss ML, Schmitz AJ, Thole JM, Bonner HK, Otegui MS, Nielsen E (2006) A role for the RabA4b effector protein PI-4Kbeta1 in polarized expansion of root hair cells in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Cell Biol 172:991–998
Qin YX, Wang MC, Tian YC, He WX, Han L, Xia GM (2012) Over-expression of TaMYB33 encoding a novel wheat MYB transcription factor increases salt and drought tolerance in Arabidopsis. Molecular Biol Rep 39:7183–7192
Riondet C, Morel S, Alcaraz G (2005) Determination of total ribonucleotide pool in plant materials by high-pH anion-exchange high-performance liquid chromatography following extraction with potassium hydroxide. J Chromatogr A 1077:120–127
Ronzier E, Corratge-Faillie C, Sanchez F, Prado K, Briere C, Leonhardt N, Thibaud JB, Xiong TC (2014) CPK13, a noncanonical Ca2+-dependent protein kinase, specifically inhibits KAT2 and KAT1 shaker K+ channels and reduces stomatal opening. Plant Physiol 166:314–326
Saijo Y, Hata S, Kyozuka J, Shimamoto K, Izui K (2000) Over-expression of a single Ca2+-dependent protein kinase confers both cold and salt/drought tolerance on rice plants. Plant J 23:319–327
Sakthivel KM, Guruvayoorappan C (2013) Acacia ferruginea inhibits tumor progression by regulating inflammatory mediators-(TNF-a, iNOS, COX-2, IL-1beta, IL-6, IFN-gamma, IL-2, GM-CSF) and pro-angiogenic growth factor-VEGF. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 14:3909–3919
Selin-Rani S, Senthil-Nathan S, Revathi K, Chandrasekaran R, Thanigaivel A, Vasantha-Srinivasan P, Ponsankar A, Edwin ES, Pradeepa V (2016) Toxicity of Alangium salvifolium Wang chemical constituents against the tobacco cutworm Spodoptera litura Fab. Pestic Biochem Physiol 126:92–101
Shan H, Chen SM, Jiang JF, Chen FD, Chen Y, Gu CS, Li PL, Song AP, Zhu XR, Gao HS, Zhou GQ, Li T, Yang X (2012) Heterologous expression of the chrysanthemum R2R3-MYB transcription factor CmMYB2 enhances drought and salinity tolerance, increases hypersensitivity to ABA and delays flowering in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Biotech 51:160–173
Sheen J (1996) Ca2+-dependent protein kinases and stress signal transduction in plants. Science 274:1900–1902
Shi HT, Chan ZL (2014) The cysteine2/histidine2-type transcription factor ZINC FINGER OF ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA 6-activated C-REPEAT-BINDING FACTOR pathway is essential for melatonin-mediated freezing stress resistance in Arabidopsis. J Pineal Res 57:185–191
Sun Y, Wang C, Yang B, Wu FF, Hao XY, Liang WW, Niu FF, Yan JL, Zhang HF, Wang BY, Deyholos MK, Jiang YQ (2014) Identification and functional analysis of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase (MAPKKK) genes in canola (Brassica napus L.). J Exp Bot 65:2171–2188
Tang W, Page M (2013) Transcription factor AtbZIP60 regulates expression of Ca2+-dependent protein kinase genes in transgenic cells. Mol Biol Rep 40:2723–2732
Tang W, Charles TM, Newton RJ (2005) Overexpression of the pepper transcription factor CaPF1 in transgenic Virginia pine (Pinus virginiana Mill.) confers multiple stress tolerance and enhances organ growth. Plant Mol Biol 59:603–617
Tang W, Newton RJ, Lin J, Charles TM (2006) Expression of a transcription factor from Capsicum annuum in pine calli counteracts the inhibitory effects of salt stress on adventitious shoot formation. Mol Genet Genomics 276:242–253
Tang W, Newton RJ, Li C, Charles TM (2007a) Enhanced stress tolerance in transgenic pine expressing the pepper CaPF1 gene is associated with the polyamine biosynthesis. Plant Cell Rep 26:115–124
Tang W, Newton RJ, Weidner DA (2007b) Genetic transformation and gene silencing mediated by multiple copies of a transgene in eastern white pine. J Exp Bot 58:545–554
Villalobos MA, Bartels D, Iturriaga G (2004) Stress tolerance and glucose insensitive phenotypes in Arabidopsis overexpressing the CpMYB10 transcription factor gene. Plant Physiol 135:309–324
Wan BL, Lin YJ, Mou TM (2007) Expression of rice Ca2+-dependent protein kinases (CDPKs) genes under different environmental stresses. FEBS Lett 581:1179–1189
Wang W, Poovaiah BW (1999) Interaction of plant chimeric calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase with a homolog of eukaryotic elongation factor-1alpha. J Biol Chem 274:12001–12008
Yang A, Dai XY, Zhang WH (2012) A R2R3-type MYB gene, OsMYB2, is involved in salt, cold, and dehydration tolerance in rice. J Exp Bot 63:2541–2556
Zhou LY, Lv CG, Kang CZ, Wang S, Tang JF, Kang LP, Guo LP (2016) Mitogen-activated protein kinase genes of Artemisia annua and their expression analysis under cadmium stress. China J Chin Materia Medica 41:1016–1020 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the University Council of Scientific Research and thank Dr. Page, Dr. Bradshaw, Dr. Lischewski, and Dr. Thompson for their critical reading and suggestions during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Project funding: The author declares that there is no funding.
The online version is available at http://www.springerlink.com
Corresponding editor: Tao Xu.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, W., Tang, A.Y. Overexpression of Arabidopsis thaliana cysteine2/histidine2-type transcription factor 6 gene enhances plant resistance to a bacterial pathogen. J. For. Res. 32, 249–262 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-019-01093-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-019-01093-7