Abstract
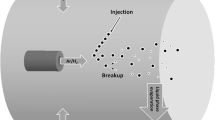
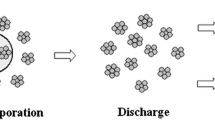
Numerical analysis is conducted for the evolution of suspension particles in an inductively coupled plasma (ICP). The mathematical model based on the Lagrangian tracking method incorporates a nanoparticle model into the ICP code. This comprehensive model considers entire physical phenomena of the in-flight particle such as injection, accelerating, solvent evaporation, solid particle discharge, heating, melting, and evaporation. After validating the computational results of the flow field with published experimental data, parametric analysis has been performed to find the way of controlling the operating conditions for desirable final particle status. The influences of injection position, carrier gas velocity, power level, particle initial size on particle size, temperature, and velocity evolution have been in detail discussed. The relationship between the predicted height of droplet complete evaporation and the droplet initial diameter is deduced. Finally, results also calculate the critical size of an ethanol droplet suspended with zirconia particles, which will be completely vaporized under present conditions.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Magnetic vector potential, (A H)/m
- C p :
-
Specific heat, J/(kg K)
- C D, c d :
-
Drag coefficient
- D :
-
Diffusion coefficients, m2/s
- E :
-
Electric field, V/m
- e :
-
Internal energy, J
- f :
-
Frequency, Hz
- g :
-
Gravity force, N
- H :
-
Magnetic field, A/m
- h :
-
Heat-transfer coefficient
- J :
-
Current density, A/m2
- Kn :
-
Knudsen number
- L m :
-
Latent heat of fusion, J/kg
- L v :
-
Latent heat of evaporation, J/kg
- m :
-
Mass, kg
- Nu :
-
Nusselt number
- P, p :
-
Pressure, kg/(m s2)
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number
- Q J :
-
Joule heating, W/m3
- Re :
-
Reynolds number
- Sh :
-
Sherwood number
- Sc :
-
Schmidt number
- SMD/SMR:
-
Sauter mean diameter/radius (m)
- T :
-
Temperature, K
- u, v, w :
-
Velocity component, m/s
- α:
-
Volume fraction
- μ0 :
-
Permeability in vacuum (4π × 10−7 H/m)
- ϑp :
-
Melt fraction of the particle
- c:
-
Cell
- g:
-
Gas
- ind:
-
Induce
- l:
-
Liquid
- p:
-
Particle
- rel:
-
Relative
- s:
-
Surface
- v:
-
Vapor
References
P. Fauchais, R. Etchart-Salas, C. Delbos, M. Tognonvi, V. Rat, J.F. Coudert, and T. Chartier, Suspension and Solution Plasma Spraying of Finely Structured Layers: Potential Application to SOFCs, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys., 2007, 40, p 2394-2406
P. Fauchais, Understanding Plasma Spraying, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys., 2004, 37, p 86-108
O. Marchand, P. Bertrand, J. Mougin, C. Comminges, M.P. Planche, and G. Bertrand, Characterization of Suspension Plasma-Sprayed Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Electrodes, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2010, 205, p 993-998
E. Bouyer, G. Schiller, M. Muller, and R.H. Henne, Thermal Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition of Si-Based Ceramic Coatings from Liquid Precursors, Plasma Chem. Plasma Process., 2001, 21, p 523-546
O. Tingaud, A. Grimaud, A. Denoirjean, G. Montavon, V. Rat, J.F. Coudert, P. Fauchais, and T. Chartier, Suspension Plasma-Sprayed Alumina Coating Structures: Operating Parameters Versus Coating Architecture, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2008, 17, p 662-670
C. Delbos, J. Fazilleau, V. Rat, J.F. Coudert, P. Fauchais, and B. Pateyron, Phenomena Involved in Suspension Plasma Spraying Part 2: Zirconia Particle Treatment and Coating Formation, Plasma Chem. Plasma Process., 2006, 26, p 393-414
P. Fauchais, R. Etchart-Salas, V. Rat, J.F. Coudert, N. Caron, and K. Wittmann-Teneze, Parameters Controlling Liquid Plasma Spraying: Solutions, Sols, or Suspensions, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2008, 17, p 31-59
E. Bouyer, F. Gitzhofer, and M.I. Boulos, Suspension Plasma Spraying for Hydroxyapatite Powder Preparation by RF Plasma, IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci., 1997, 25, p 1066-1072
M. Shigeta and Watanabe. Takayuki, Multi-Component Co-Condensation Model of Ti-Based Boride/Silicide Nanoparticle Growth in Induction Thermal Plasmas, Thin Solid Film, 2007, 515, p 4217-4227
W.J. Oleslk and S.E. Hobbs, Momodisperse Dried Microparticulate Injector: A New Tool for Study Fundamental Processes in Inductively Coupled Plasmas, Anal. Chem., 1994, 66, p 3371-3378
P. Buchner, H. Schubert, J. Uhlenbusch, and M. Weiss, Evaporation of Zirconia Powders in a Thermal Radio-Frequency Plasma, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2001, 10, p 666-672
B.G. Ravi, A.S. Gandhi, X.Z. Guo, J. Margolies, and S. Sampath, Liquid Precursor Plasma Spraying of Functional Materials: A Case Study for Yttrium Aluminum Garnet (YAG), J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2008, 17, p 82-90
F. Tarasi, M. Medraj, A. Dolatabadi, J. Oberste-Berghaus, and C. Moreau, Effective Parameters in Axial Injection Suspension Plasma Spray Process of Alumina-Zirconia Ceramics, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2008, 17(5-6), p 685-691
X.L. Sun, A.I.Y. Tok, S.L. Lim, F.Y.C. Boey, C.W. Kang, and H.W. Ng, Combustion-Aided Suspension Plasma Spraying of Y2O3 Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Modeling, J. Appl. Phys., 2008, 103, p p1-p13
X. Siwen, P. Proulx, and M.I. Boulos, Extended-Field Electromagnetic Model for Inductively Coupled Plasma, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys., 2001, 34, p p1897-p1906
J.A. Horner, S.A. Lehn, and G.M. Hieftje, Computerized Simulation of Aerosol-Droplet Desolvation in an Inductively Coupled Plasma, Spectrochim. Acta B, 2002, 57, p 1025-1042
X.L. Sun, A.I.Y. Tok, R. Huebner, and F.Y.C. Boey, Phase Transformation of Ultrafine Rare Earth Oxide Powders Synthesized by Radio Frequency Plasma Spraying, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2007, 27, p p125-p130
Y. Shan and J. Mostaghimi, Numerical Simulation of Aerosol Droplets Desolvation in a Radio Frequency Inductively Coupled Plasma, Spectrochim. Acta B, 2003, 58, p 1959-1977
Y. Shan and Y. Hu, Heat and Mass Transfer Within an Evaporating Solution Droplet in a Plasma Jet, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2012, 21(3-4), p 676-688
S.V. Patankar, Numerical Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer, Hemisphere, New York, 1980
L.J. Qian, J.Z. Lin, and H.B. Xiong, Numerical Modeling in Radio Frequency Suspension Plasma Spray of Zirconia Powders, Plasma Chem. Plasma Process., 2010, 30, p 733-760
L.J. Qian, J.Z. Lin, and H.B. Xiong, A Fitting Formula for Predicting Droplet Mean Diameter for Various Liquid in Effervescent Atomization Spray, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2010, 19(3), p 586-601
M. Cai, D.A. Haydar, A. Montaser, and Mostaghimi, Computer Simulation of Argon-Nitrogen and Argon-Oxygen Inductively Coupled Plasmas, J. Spectrochim. Acta B, 1997, 52, p 369-386
Y.P. Wan, V. Prasad, G.X. Wang, S. Sampath, and J.R. Fincke, Model and Powder Particle Heating, Melting, Resolidification and Evaporation in Plasma Spraying Processes, J. Heat Transf., 1999, 121, p 691-699
Acknowledgment
The authors gratefully acknowledge the supports received from the National Natural Science Foundation of China under grant Nos. 11002136 and 11132008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qian, L., Lin, J. & Yu, M. Parametric Study on Suspension Behavior in an Inductively Coupled Plasma. J Therm Spray Tech 22, 1024–1034 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-013-9943-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-013-9943-6