Abstract
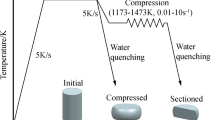
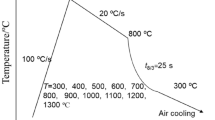
The microstructure plays a major role in the performance of metallic materials, which can be tailored through the composition and/or processing technique. In this study, a heterogeneous microstructure was developed for low-carbon microalloyed API X65 steel, the most commonly used pipeline steel for oil and gas transportation, using a heat treatment process. The heat treatment process involved intercritical heating of the steel followed by high-temperature isotheral cooling, allowing for phase transformation, as well as alloying element partitioning. The heat treatment transformed the banded ferrite–pearlite microstructure of rolled steel to a quasi-polygonal ferrite microstructure, with the sporadic presence of austenite at the grain boundaries. The quasi-polygonal ferrite was distributed in a heterogeneous form with a fine-grain shell surrounding the coarse-grained core. The heterogeneity in the microstructure, despite being single phase, led to a significant improvement in the tensile yield strength, ultimate tensile strength, ductility and toughness of the steel, with a marginal reduction in microhardness values.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Wu and Y. Zhu, Heterogeneous Materials: A New Class of Materials with Unprecedented Mechanical Properties, Mater. Res. Lett., 2017, 5(8), p 527–532
X.L. Wu, M.X. Yang, F.P. Yuan, G.L. Wu, Y.J. Wei, X.X. Huang, and Y.T. Zhu, Heterogeneous Lamella Structure unites Ultrafine-Grain Strength with Coarse-Grain Ductility, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2015, 112, p 14501–14505
R. Zheng, G. Li, Z. Zhang, Y. Zhang, S. Yue, X. Chen, K. Ameyama, and C. Ma, Manipulating the Powder Size to Achieve Enhanced Strength and Ductility in Harmonic Structured Al Alloy, Mater. Res. Let., 2019, 7(6), p 217–224
H. Zhou, C.X. Huang, X.C. Sha, L.R. Xiao, X.L. Ma, H.W. Höppel, M. Göken, X.L. Wu, K. Ameyama, X.D. Han, and Y.T. Zhu, In-Situ Observation of Dislocation Dynamics Near Heterostructured Interfaces, Mater. Res. Lett., 2019, 7, p 376–382
X.L. Wu, M.X. Yang, F.P. Yuan, L. Chen, and Y.T. Zhu, Combining Gradient Structure and TRIP Effect to Produce Austenite Stainless Steel with High Strength and Ductility, Acta Mater., 2016, 112, p 337–346
B. Raeisinia, C.W. Sinclair, W.J. Poole, and C.N. Tome, On the Impact of Grain Size Distribution on the Plastic Behaviour of Polycrystalline Metals, Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2008, 16, p Art. No. 025001
S.F. Hassan, O. Siddiqui, M.F. Ahmed, and A.I. Al Nawwah, Development of Gradient Concentrated Single Phase Fine Mg-Zn Particles and Effect on Structure and Mechanical Properties, J. Eng. Mater. Technol., 2018, 141(2), p Art. no. 021007
Y.M. Wang, M.W. Chen, F.H. Zhou, and E. Ma, High Tensile Ductility in a Nanostructured Metal, Nature, 2002, 419(2002), p 912–915
X.L. Ma, C.X. Huang, J. Moering, M. Ruppert, H.W. Hoppel, M. Goken, J. Narayan, and Y.T. Zhu, Mechanical Properties in Copper/Bronze Laminates: Role of Interfaces, Acta Mater., 2016, 116, p 43–52
S. Nikkhah, H. Mirzadeh, and M. Zamani, Improved Mechanical Properties of Mild Steel via Combination of Deformation, Intercritical Annealing, and Quench Aging, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2019, 756, p 268–271
E. El-Danaf, M. Baig, A. Almajid, W. Alshalfan, M. Al-Mojil, and S. Al-Shahrani, Mechanical, Microstructure and Texture Characterization of API, X65 Steel, Mater. Des., 2013, 47, p 529–538
J.A. Ronevich, B.P. Somerday, and C.W. San Marchi, Effects of Microstructure Banding on Hydrogen Assisted Fatigue Crack Growth in X65 Pipeline Steels, Int. J. Fatigue, 2016, 82, p 497–504
M.C. Zhao, K. Yang, F.R. Xiao, and Y.Y. Shan, Continuous Cooling Transformation of Undeformed and Deformed Low Carbon Pipeline Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2003, 355, p 126–136
A.B. Cota, F.L.G. Oliveira, A.L.R. Barbosa, C.A.M. Lacerda, and F.G.S. Araújo, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Microalloyed Steel After Thermal Treatments, Mater. Res., 2003, 6(2), p 117–121
L. Zhongqiua, F. Jiana, Z. Yonga, and Y. Zexi, Influence of Quenching On-line on Properties of X70 Steel for Sour Service Seamless Pipe, Energy Procedia, 2012, 16, p 444–450
J. Xu, R.D.K. Misra, B. Guo, V.S.A. Challa, and L. Zheng, High Strength (560 MPa) Quenched and Tempered Pipeline Steels, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2013, 29(10), p 1241–1246
P.A. Wycliffe, G.R. Purdy, and J.D. Embury, Austenite Growth in the Intercritical Annealing of Ternary and Quaternary Dual-Phase Steels, Fundamentals of Dual-Phase Steels, R.A. Kot and B.L. Bramfitt, Ed., TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1981, p 59–83
J.M. Rigsbee, Inhibition of Martensite Transformation in Small Austenite Particles in Low Alloy Steels, Proceedings of International Conference on Martensitic Transformations, MIT, Cambridge, MA, 1979, p 381–385
G. Krauss and S.W. Thompson, Ferritic Microstructures in Continuously Cooled Low- and Ultralow-Carbon Steels, ISIJ Int., 1995, 35, p 937–945
M.A. Smirnov, I.Y. Pyshmintsev, and A.N. Boryakova, Classification of Low-Carbon Pipe Steel Microstructure, Metallurgist, 2010, 54(7–8), p 444–454
T.B. Massalski, Phase Transformations, Metals Park, Ohio, ASM, 1970, p 433
B.L. Bramfiti and J.G. Speer, A Perspective on the Morphology of Bainite, Metall. Trans. A, 1990, 21, p 818–829
S. Yan, X. Liu, T. Liang, J. Chen, and Y. Zhao, Effect of Micro-Alloying Elements on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties in C-Mn–Si Quenching and Partitioning (Q&P) Steels, Steel Res. Int., 2019, 90, p Art. no. 1800257
C. Suryanarayana and M.G. Norton, X-Ray Diffraction: A Practical Approach, Springer, US, 1998
NACE Standard Test Method TM0175, Sulfide Stress Cracking Resistant Metallic Materials for Oilfield Equipment, NACE, Huston, USA, (2009).
Q.H. Han, A. Asgari, P.D. Hodgson, and N. Stanford, Strain Partitioning in Dual-Phase Steels Containing Tempered Martensite, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2014, 611, p 90–99
Z.H. Cong, N. Jia, X. Sun, Y. Ren, J. Almer, and Y.D. Wang, Stress and Strain Partitioning of Ferrite and Martensite During Deformation, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2009, 40, p 1383–1387
H.F. Lan, L.X. Du, and R.D.K. Misra, Effect of Microstructural Constituents on Strength-Toughness Combination in a Low Carbon Bainitic Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2014, 611, p 194–200
J.H. Chen, Y. Kikuta, T. Araki, M. Yoneda, and Y. Matsuda, Micro-fracture Behaviour Induced by M-A Constituent (Island Martensite) in Simulated Welding Heat Affected Zone of HT80 High Strength Low Alloyed Steel, Acta Metall., 1984, 32, p 1779–1788
B. Verhaeghe, F. Louchet, Y. Brechet, and J.P. Massoud, Damage and Rupture Mechanisms in an Austenoferritic Duplex steel, Acta Mater., 1997, 45(5), p 1811–1819
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support provided by Department of Mechanical Engineering of King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals for supporting this work through Graduate Research Course MSE 610.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassan, S.F., Al-Wadei, H. Heterogeneous Microstructure of Low-Carbon Microalloyed Steel and Mechanical Properties. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 29, 7045–7051 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-05217-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-05217-7