Abstract
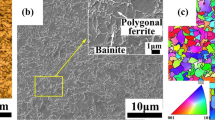
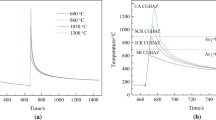
The evolution of the microstructure and toughness of APL5L X80 pipeline steel after thermal welding simulation was investigated by X-ray diffraction, electron backscatter diffraction, and transmission electron microscopy. The results indicated that primary heat-affected zones can be divided into weld, coarse-grained, fine-grained, intercritical, and subcritical zones. The microstructure of the weld zone is mainly composed of bainitic ferrite and a small amount of granular bainite; however, the original austenite grains are distributed in the columnar grains. The structure of the coarse-grained zone is similar to that of the weld zone, but the original austenite grains are equiaxed. In contrast, the microstructure in the fine-grained zone is dominated by fine granular bainite, and the effective grain size is only 8.15 μm, thus providing the highest toughness in the entire heat-affected zone. The intercritical and subcritical zones were brittle valley regions, and the microstructure was dominated by granular bainite. However, the martensite–austenite (M/A) constituents are present in island chains along the grain boundaries, and the coarse size of the M/A constituents seriously reduces the toughness. The results of the crack propagation analyzes revealed that high-angle grain boundaries can significantly slow down crack growth and change the crack direction, thereby increasing the material toughness. The impact toughness of the low-temperature tempering zone was equivalent to that of the columnar grain zone, and the impact toughness was between those of the critical and fine-grained zones.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Zhang, J. Wang, S. Liu, L. Yan, C. Song, H. Yu, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 861 (2022) 144355.
L. Wang, S. Wang, Materials 16 (2023) 3578.
L.Y. Sun, X. Liu, X. Xu, S.W. Lei, H.G. Li, Q.J. Zhai, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 29 (2022) 1513–1525.
O. Panchenko, I. Kladov, D. Kurushkin, L. Zhabrev, E. Ryl'kov, M. Zamozdra, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 851 (2022) 143569.
X. Ye, S. Cui, T. Liu, Q. Ma, G. Liu, Z. Huang, J. Guo, S. Yin, Coatings 13 (2023) 706.
G. Ma, Y. Chen, G. Wu, S. Wang, T. Li, W. Liu, H. Wu, J. Gao, H. Zhao, C. Zhang, X. Mao, Crystals 13 (2023) 714.
Q. Chang, Y. Cao, Y. Zhen, G. Wu, F. Li, Int. J. Pres. Ves. Pip. 20 (2023) 104940.
Y. Wang, Z. Guo, X. Bai, C. Yuan, Ocean Eng. 235 (2021) 109385.
X. Wang, D. Wang, L. Dai, C. Deng, C. Li, Y. Wang, K. Shen, Materials 15 (2022) 6646.
G. Wang, J. Wang, L. Yin, H. Hu, Z. Yao, Materials 13 (2020) 121.
Y. Dong, D. Liu, L. Hong, J. Liu, X. Zuo, Metals 12 (2022) 716.
Y. Liu, R. Liu, B. Liu, Z. Zhu, Y. Li, H. Chen, Mater. Charact. 186 (2022) 111811.
J. Luo, S. Luo, L. Li, L. Zhang, G. Wu, L. Zhu, Nat. Gas Ind. B 6 (2019) 138–144.
X. Wang, D. Wang, C. Deng, C. Li, Materials 15 (2022) 4458.
Z. Gao, B. Gong, B. Wang, D. Wang, C. Deng, Y. Yu, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 46 (2021) 38535–38550.
Z. Gu, X. Zhu, Q. Ding, S. Duan, P. Wang, X. Lu, Eng. Fail. Anal. 150 (2023) 107299.
M. Aranđelović, S. Sedmak, R. Jovičić, A. Petrović, S. Dikić, Procedia Struct. Integr. 42 (2022) 985–991.
X. Qi, P. Huan, X. Wang, Z. Liu, X. Shen, Y. Gao, H. Di, Mater. Today Commun. 31 (2022) 103413.
J.M. Giarola, J.W. Calderón-Hernández, J.M. Quispe-Avilés, J.A. Avila, W.W. Bose Filho, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 46 (2021) 28166–28179.
M. St. Węglowski, S. Dymek, M. Kopyściański, J. Niagaj, J. Rykała, W. De Waele, S. Hertelé, Archiv. Civ. Mech. Eng. 20 (2020) 14.
J. Jiang, Z.Y. Peng, M. Ye, Y.B. Wang, X. Wang, W. Bao, J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 33 (2021) 04021186.
M. Mahmoudiniya, A.H. Kokabi, M. Goodarzi, L.A.I. Kestens, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 769 (2020) 138490.
J. Du, J. Li, Y. Feng, J. Ning, S. Liu, F. Zhang, Mater. Des. 221 (2022) 110953.
K.S. Arora, S.R. Pandu, N. Shajan, P. Pathak, M. Shome, Int. J. Pres. Ves. Pip. 163 (2018) 36–44.
J.C.F. Jorge, L.F.G. de Souza, M.C. Mendes, I.S. Bott, L.S. Araújo, V.R. dos Santos, J.M.A. Rebello, G.M. Evans, J. Mater. Res. Technol. 10 (2021) 471–501.
X. Yang, X. Di, X. Liu, D. Wang, C. Li, Mater. Charact. 155 (2019) 109818.
M.F.G. Ramirez, J.W.C. Hernández, D.H. Ladino, M. Masoumi, H. Goldenstein, J. Mater. Res. Technol. 14 (2021) 1848–1861.
N. Huda, Y. Wang, L. Li, A.P. Gerlich, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 765 (2019) 138301.
K. Yin, F. Wei, J. Wang, H. Ma, P. Jin, Mater. Today Commun. 35 (2023) 106234.
R. Chen, Z. Li, Q. Zhang, X. Li, Corros. Sci. 209 (2022) 110784.
S. Chen, Q. Yu, Scripta Mater. 163 (2019) 148–151.
R. Song, D. Ponge, R. Kaspar, D. Raabe, Int. J. Mater. Res. 95 (2004) 513–517.
M. Glienke, M. Vaidya, K. Gururaj, L. Daum, B. Tas, L. Rogal, K.G. Pradeep, S.V. Divinski, G. Wilde, Acta Mater. 195 (2020) 304–316.
Y. Wang, X. Ma, G. Zhao, X. Xu, X. Chen, C. Zhang, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 82 (2021) 161–178.
Q. Ren, Z. Kou, J. Wu, T. Hou, P. Xu, Metals 13 (2023) 771.
Y. Fan, G. Gao, X. Gui, B. Bai, Z. Yang, Int. J. Fatigue 173 (2023) 107706.
S.G. Lee, S.S. Sohn, B. Kim, W.G. Kim, K.K. Um, S. Lee, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 715 (2018) 332–339.
X. Wang, Z. Wang, Z. Xie, X. Ma, S. Subramanian, C. Shang, X. Li, J. Wang, Math. Biosci. Eng. 16 (2019) 7494–7509.
S.G. Lee, B. Kim, S.S. Sohn, W.G. Kim, K.K. Um, S. Lee, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 760 (2019) 125–133.
N. Huda, A. Midawi, J.A. Gianetto, A.P. Gerlich, J. Mater. Res. Technol. 12 (2021) 613–628.
Z. Liao, Y. Dong, Y. Du, X. Wang, M. Qi, H. Wu, X. Gao, L. Du, J. Mater. Res. Technol. 23 (2023) 1471–1486.
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate the financial support from National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFBO304900).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors disclosed no relevant relationships.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, Sj., Ma, Ql., Hou, Y. et al. Changes in microstructure and properties of weld heat-affected zone of high-strength low-alloy steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-023-01133-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-023-01133-x