Abstract
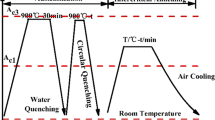
To develop an appropriate quenching process to produce Fe-0.9Mn-0.5Cr-2.4Ni-0.5Mo-C steel, the microstructures and mechanical properties of this steel were investigated under the direct quenching and tempering (DQT) and the direct quenching, reheated quenching and tempering (DQQT) heat treatment processes. The microstructure of the DQQT specimen was basically tempered sorbite with spherical precipitates, while quite a bit of tempered martensite was in the DQT specimen with dispersive nanoscaled precipitates. The yield strengths of the DQT and DQQT specimens were 1154 and 955 MPa, respectively. The yield strength of the DQT specimen was higher than that of the DQQT specimen because of its finer grain size, higher density of dislocations and dispersed precipitates. The DQQT specimen had spherical precipitates, which hindered the propagation of the crack. Moreover, the high-angle grain boundaries in the DQQT specimen took a higher proportion. Therefore, the Charpy impact values of DQT and DQQT specimens at − 60 °C were 38 and 75 J, respectively. Consequently, the mechanical properties of the Fe-0.9Mn-0.5Cr-2.4Ni-0.5Mo-C steel, which met the standard of 1000 MPa grade steel plate for hydropower station, were acquired by the DQQT process.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Li and W.L. Jiang, The Application and the Problems of High Strength Steel on Penstock in Chinese Hydroelectric Station, ISIJ Int., 2012, 42(12), p 1419–1422
G.Z. Xiao, H.S. Di, F.X. Zhu, B.Z. Chen, and B. Qiu, Influence of Direct Quenching on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Steel Plate for Large Oil Storage Tanks, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2010, 19(6), p 868–872
C. Ouchi, Development of Steel Plates by Intensive Use of TMCP and Direct Quenching Processes, ISIJ Int., 2001, 41(6), p 542–553
S.K. Ghosh, A. Haldar, and P.P. Chattopadhyay, Effect of Pre-strain on the Ageing Behavior of Directly Quenched Copper Containing Micro-alloy Steel, Mater. Charact., 2008, 59(9), p 1227–1233
W.S. Chang, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 780 MPa High Strength Steels Produced by Direct-Quenching and Tempering Process, J. Mater. Sci., 2002, 37(10), p 1973–1979
J. Qiu, X. Ju, Y. Xin, S. Liu, Y.L. Wang, H.B. Wu, and D. Tang, Effect of Direct and Reheated Quenching on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of CLAM Steel, J. Nucl. Mater., 2010, 407(3), p 189–194
A.H. Meysami, R. Ghasemzadeh, S.H. Seyedein, and M.R. Aboutalebi, An Investigation on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Direct-Quenched and Tempered AISI, 4140 Steel, Mater. Des., 2010, 31(3), p 1570–1575
A.E. Amer, M.Y. Koo, K.H. Lee, S.H. Kim, and S.H. Hong, Effect of Welding Heat Input on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Simulated HAZ in Cu Containing Microalloyed Steel, J. Mater. Sci., 2010, 45(5), p 1248–1254
L. Lan, C. Qiu, D. Zhao, X. Gao, and L. Du, Analysis of Martensite-austenite Constituent and Its Effect on Toughness in Submerged Arc Welded Joint of Low Carbon Bainitic Steel, J. Mater. Sci., 2012, 47(11), p 4732–4742
A.F. Gourgues, H.M. Flower, and T.C. Lindley, Electron Backscattering Diffraction Study of Acicular Ferrite, Bainite, and Martensite Steel Microstructures, Mater. Sci. Tech., 2000, 16(1), p 26–40
L. Feng, C. Wang, L. Lu, Z.D. Wang, G.D. Wang, and R.D.K. Misra, Microstructural Evolution and Properties of a High Strength Steel with Different Direct Quenching Processes, J. Iron. Steel Res. Int., 2015, 22(4), p 344–351
J.W. Morris, Jr., On the Ductile-Brittle Transition in Lath Martensitic Steel, ISIJ Int., 2011, 51(10), p 1569–1575
A. Ghosh, A. Ray, D. Chakrabarti, and C.L. Davis, Cleavage Initiation in Steel: Competition Between Large Grains and Large Particles, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 561, p 126–135
T. Karthikeyan, V. Thomas Paul, S. Saroja, A. Moitra, G. Sasikala, and M. Vijayalakshmi, Grain Refinement to Improve Toughness in 9Cr-1Mo Steel Through a Double Austenitization Treatment, J. Nucl. Mater., 2011, 419, p 256–262
S. Morito, H. Saito, T. Ogawa, T. Furuhara, and T. Maki, Effect of Austenite Grain Size on the Morphology and Crystallography of Lath Martensite in Low Carbon Steels, ISIJ Int., 2005, 45(1), p 91–94
A. Chatterjee, D. Chakrabarti, A. Moitra, R. Mitra, and A.K. Bhaduri, Effect of Normalization Temperatures on Ductile-Brittle Transition Temperature of a Modified 9Cr-1Mo Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 618, p 219–231
J. Hu, L.X. Du, J.J. Wang, and Q.Y. Sun, Cooling Process and Mechanical Properties Design of Hot-Rolled Low Carbon High Strength Microalloyed Steel for Automotive Wheel Usage, Mater. Des., 2014, 53, p 332–337
I.A. Yakubtsov and J.D. Boyd, Effect of Alloying on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Bainitic High Strength Plate Steels, Mater. Sci. Tech., 2008, 24(2), p 221–227
H. Kitahara, R. Ueji, N. Tsuji, and Y. Minamino, Crystallographic Features of Lath Martensite in Low-Carbon Steel, Acta Mater., 2006, 54(5), p 1279–1288
R.D.K. Misra, H. Nathani, J.E. Hartmann, and F. Siciliano, Microstructural Evolution in a New 770 Mpa Hot Rolled Nb-Ti Microalloyed Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 394, p 339–352
I.A. Yakubtsov, P. Poruks, and J.D. Boyd, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Bainitic Low Carbon High Strength Plate Steels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, 480, p 109–116
H.J. Kestenbach, S.S. Campos, and E.V. Morales, Role of Interphase Precipitation in Microalloyed Hot Strip Steels, Mater. Sci. Tech., 2006, 22(6), p 615–626
J. Hu, L.X. Du, J.J. Wang, H. Xie, C.R. Gao, and R.D.K. Misra, Structure-mechanical Property Relationship in Low Carbon Microalloyed Steel Plate Processed Using Controlled Rolling and Two-Stage Continuous Cooling, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 585, p 197–204
H. Xie, L.X. Du, J. Hu, and R.D.K. Misra, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Novel 1000 MPa Grade TMCP Low Carbon Microalloyed Steel with Combination of High Strength and Excellent Toughness, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 612, p 123–130
J. Speer, D.K. Matlock, B.C. De Cooman, and J.G. Schroth, Carbon Partitioning into Austenite after Martensite Transformation, Acta Mater., 2003, 51(9), p 2611–2622
A. Lambert-Perlade, A.F. Gourgues, and A. Pineau, Austenite to Bainite Phase Transformation in the Heat-Affect Zone of a High Strength Low Alloy Steel, Acta Mater., 2004, 52(8), p 2337–2348
A.F. Gourgues, Electron Backscatter Diffraction and Cracking, Mater. Sci. Tech., 2002, 18(2), p 119–133
Acknowledgments
The authors are very grateful to the financial support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51274062) and Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (20130042110040).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Li, C., Jin, X. et al. Effect of Quenching Process on Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Fe-0.9Mn-0.5Cr-2.4Ni-0.5Mo-C Steel. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 27, 1505–1513 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3163-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3163-7