Abstract
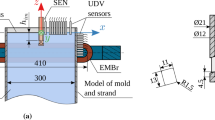
Electromagnetic braking (EMBr) is critical for suppressing the turbulence in the mold and developing a high-speed thin-slab continuous casting technology. The main problem is that the relationship between EMBr strength and flow patterns in a funnel mold is still inconclusive. Effects of magnetic induction intensity on the flow pattern and slag-metal behavior were numerically analyzed using the potential method. The variation of the electrical conductivity during solidification was considered to predict a physical-justified distribution of induced current. Results show that the induced current is mainly distributed in nozzle jets and solidified shells. Two induced e-current loops in opposite-rotated directions can be observed between the nozzle jet and solid shell, indicating that the shear stress caused by the induced e-current loops is a potential disadvantage for the thermal-mechanical behavior of the solidified shell. The flow pattern changes from classic double-roll flow to three-roll flow and then to single-roll flow with the increase of magnetic induction intensity. Backflows form near nozzle outlets at 0.17 T and occupy the entire slag-metal interface at 0.215 T. The core of the upward reverse flow from nozzle jets moves down, and the downward reverse flow gradually converges inward with EMBr intensity. Particular attention should be paid to the three-roll flow pattern. The flow field on the slag-metal interface will become unstable and asymmetrical, especially at 0.193 T. The plug-like flow is formed only when the magnetic induction is strong enough.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y.L. Kang, H. Yu, J. Fu, K. Wang, and Z.B. Wang: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, vol. 351, pp. 265–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(02)00845-6.
J.K. Park, B.G. Thomas, I.V. Samarasekera, and U.S. Yoon: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2002, vol. 33B, pp. 425–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-002-0054-x.
H.P. Liu, C.Z. Yang, H. Zhang, Q.J. Zhai, and Y. Gan: ISIJ Int., 2011, vol. 51, pp. 392–401. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.51.392.
R.D. Morales, Y. Tang, G. Nitzl, C. Eglsaeer, and G. Hackl: ISIJ Int., 2012, vol. 52, pp. 1607–15. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.52.1607.
Z. Liu, L. Li, and B. Li: JOM, 2016, vol. 68, pp. 2180–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-016-1988-9.
Z.D. Qian and Y.L. Wu: ISIJ Int., 2004, vol. 44, pp. 100–07. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.44.100.
R. Singh, B.G. Thomas, and S.P. Vanka: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2013, vol. 44B, pp. 1201–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-013-9877-x.
B.G. Thomas, R. Singh, S.P. Vanka, K. Timmel, S. Eckert, and G. Gerbeth: J. Manuf. Sci. Prod., 2015, vol. 15, p. 93. https://doi.org/10.1515/jmsp-2014-0047.
R. Chaudhary, B.G. Thomas, and S.P. Vanka: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2012, vol. 43B, pp. 532–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-012-9634-6.
D. Schurmann, I. Glavinic, B. Willers, K. Timmel, and S. Eckert: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2020, vol. 51B, pp. 61–78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-019-01721-x.
A. Vakhrushev, A. Kharicha, E. Karimi-Sibaki, M. Wu, A. Ludwig, G. Nitzl, Y. Tang, G. Hackl, J. Watzinger, and S. Eckert: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2021, vol. 52B, pp. 3193–3207. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-021-02247-x.
L.S. Zhang, X.F. Zhang, B. Wang, Q. Liu, and Z.G. Hu: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2014, vol. 45B, pp. 295–306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-013-9948-z.
H.P. Liu, J.J. Zhang, H.B. Tao, and H. Zhang: Metall. Res. Technol., 2020, vol. 117, p. 602. https://doi.org/10.1051/metal/2020044.
L. Xu, E.G. Wang, C. Karcher, A.Y. Deng, and X.J. Xu: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2018, vol. 49, pp. 2779–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-018-1342-4.
F. Li, E.G. Wang, M.J. Feng, and Z. Li: ISIJ Int., 2015, vol. 55, pp. 814–20. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.55.814.
A.Y. Deng, L. Xu, E.G. Wang, and J.C. He: J. Iron. Steel Res. Int., 2014, vol. 21, pp. 809–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1006-706x(14)60146-1.
L. Xu, E. Wang, C. Karcher, A. Deng, X. Xu, and Z. Han: Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech., 2020, vol. 63, pp. S85-92. https://doi.org/10.3233/jae-209106.
L. Xu, C. Karcher, and E. Wang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-023-02784-7.
F. Nicoud and F. Ducros: Flow Turbul. Combust., 1999, vol. 62, pp. 183–200. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009995426001.
K. Cukierski and B.G. Thomas: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2008, vol. 39, pp. 94–107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-007-9109-3.
A. Vakhrushev, A. Kharicha, M.H. Wu, A. Ludwig, G. Nitzl, Y. Tang, G. Hackl, J. Watzinger, and C.M.G. Rodrigues: IOP Conf. Ser., 2020, vol. 861, p. 012015. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/861/1/012015.
A. Vakhrushev, M.H. Wu, A. Ludwig, Y. Tang, G. Hackl, and G. Nitzl: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2014, vol. 45B, pp. 1024–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-014-0030-2.
M.C. Schneider, J.P. Gu, C. Beckermann, W.J. Boettinger, and U.R. Kattner: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1997, vol. 28, pp. 1517–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-997-0214-3.
Y.F. Wang and L.F. Zhang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2011, vol. 42B, pp. 1319–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-011-9554-x.
X.Y. Tian, B.W. Li, and J.C. He: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2009, vol. 40B, pp. 596–604. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-009-9246-y.
X.Y. Tian, F. Zou, B.W. Li, and J.C. He: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2010, vol. 41B, pp. 112–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-009-9314-3.
C.J. Wang, Z.Q. Liu, and B.K. Li: Metals, 2021, vol. 11, p. 948. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11060948.
B. Petrus, K. Zheng, X. Zhou, B.G. Thomas, and J. Bentsman: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2011, vol. 42B, pp. 87–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-010-9452-7.
R. Moreau: Magnetohydrodynamics, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Norwell, MA, 1990.
J.E. Camporredondo, A.H. Castillejos, F.A. Acosta, E.P. Gutiérrez, and M.A. Herrera: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2004, vol. 35B, pp. 541–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-004-0054-0.
Z.Q. Liu, A. Vakhrushev, M.H. Wu, E. Karimi-Sibaki, A. Kharicha, A. Ludwig, and B.K. Li: Metals, 2018, vol. 8, p. 609. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8080609.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51974071); the Excellent Youth Fund of Liaoning Natural Science Foundation (No. 2023JH3/10200001); and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. N2225011).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Liu, Z. & Li, B. Effect of the Intensity of Single-Ruler Electromagnetic Braking on the Flow Pattern in a Thin-Slab Funnel Mold. Metall Mater Trans B 54, 3438–3450 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-023-02923-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-023-02923-0