Abstract
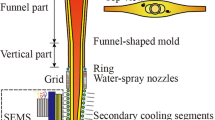
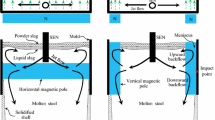
During continuous casting of steel slabs, the application of electromagnetic braking technology (EMBr) provides an effective tool to influence solidification by controlling the pattern of melt flow in the mold. Thus, the quality of the final product can be improved considerably. A new electromagnetic braking (EMBr) method, named vertical-combined electromagnetic braking (VC-EMBr), is proposed to be applied to a flexible thin slab casting (FTSC) mold. To evaluate the beneficial effects of the VC-EMBr, the melt flow, heat transfer, and solidification processes in the FTSC mold are studied by means of numerical simulations. In detail, a Reynolds-averaged Navier–Stokes turbulence model together with an enthalpy-porosity approach was used. The numerical findings are compared with respective simulations using the traditional Ruler-EMBr. The results demonstrate that the application of the VC-EMBr contributes significantly to preventing relative slab defects. In contrast to the Ruler-EMBr, the additional vertical magnetic poles of the VC-EMBr preferentially suppress the direct impact of jet flow on the narrow face of FSTC mold and considerably diminish the level fluctuation near the meniscus region. For instance, by applying a magnetic flux density of 0.3 T, the maximum amplitude of meniscus deflection reduces by about 80%. Moreover, the braking effect of the VC-EMBr effectively improves the homogeneity of temperature distribution in the upper recirculation region and increases the solidified shell thickness along the casting direction. On this basis, the newly proposed VC-EMBr shows a beneficial effect in preventing relative slab defects for FTSC thin slab continuous casting.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Zhang, X. Zhang, B. Wang, Q. Liu, Z. Hu, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 45 (2014) 295–306.
L. Xu, Q. Pei, Z. Han, S. Yang, J. Wang, Y. Yao, Processes 10 (2022) 2738–2757.
A. Vakhrushev, M. Wu, A. Ludwig, Y. Tang, G. Hackl, G. Nitzl, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 45 (2014) 1024–1037.
M. Thunman, S. Eckert, O. Hennig, J. Björkvall, S. Du, Steel Res. Int. 78 (2007) 849–856.
D.S. Kim, W.S. Kim, K.H. Cho, ISIJ Int. 40 (2000) 670–676.
Y.S. Hwang, P.R. Cha, H.S. Nam, K.H. Moon, J.K. Yoon, ISIJ Int. 37 (1997) 659–667.
J.K. Park, I.V. Samarasekera, B.G. Thomas, U.S. Yoon, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 33 (2002) 437–449.
E. Torres-Alonso, R.D. Morales, L.G. Demedices, A. Nájera, J. Palafox-Ramos, P. Ramirez-Lopez, ISIJ Int. 47 (2007) 679–688.
T. Honeyands, J. Herbertson, Steel Res. Int. 66 (1995) 287–293.
H. Liu, J. Zhang, H. Tao, H. Zhang, Metall. Res. Technol. 117 (2020) 602–617.
H. Liu, C. Yang, H. Zhang, Q. Zhai, Y. Gan, ISIJ Int. 51 (2011) 392–401.
D. Schurmann, I. Glavinić, B. Willers, K. Timmel, S. Eckert, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 51 (2020) 61–78.
B. Li, T. Okane, T. Umeda, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 31 (2000) 1491–1503.
Y. Wang, L. Zhang, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 42 (2011) 1319–1351.
Z. Qian, Y. Wu, ISIJ Int. 44 (2004) 100–107.
L. Xu, Q. Pei, Z. Han, J. Cui, H. Pan, Y. Yao, Processes 11 (2022) 33–49.
A. Idogawa, M. Sugizawa, S. Takeuchi, K. Sorimachi, T. Fujii, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 173 (1993) 293–297.
K. Jin, S.P. Vanka, B.G. Thomas, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 48 (2017) 162–178.
H. Yu, M. Zhu, ISIJ Int. 48 (2008) 584–591.
S. Sarkar, V. Singh, S.K. Ajmani, R. Ranjan, K. Rajasekar, ISIJ Int. 56 (2016) 2181–2190.
L. Xu, E. Wang, C. Karcher, A. Deng, X. Xu, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 49 (2018) 2779–2793.
B.G. Thomas, R. Singh, S.P. Vanka, K. Timmel, S. Eckert, G. Gerbeth, J. Manuf. Sci. Prod. 15 (2015) 93–104.
R. Singh, B.G. Thomas, S.P. Vanka, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 44 (2013) 1201–1221.
R. Chaudhary, B.G. Thomas, S.P. Vanka, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 43 (2012) 532–553.
Y. Yin, J. Zhang, ISIJ Int. 61 (2021) 853–864.
S. Sarkar, V. Singh, S.K. Ajmani, R.K. Singh, E.Z. Chacko, ISIJ Int. 58 (2018) 68–77.
R. Singh, B.G. Thomas, S.P. Vanka, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 45 (2014) 1098–1115.
S.M. Cho, B.G. Thomas, S.H. Kim, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 47 (2016) 3080–3098.
E. Wang, Z. Li, L. Xu, F. Li, A. Deng, X. Zhang, L. Zhang, Vertical electromagnetic braking device for controlling flow of molten steel in continuous casting crystallizer, European Patent, EP 3441158B1, 2020.
B.G. Thomas, Steel Res. Int. 89 (2018) 312–332.
Z. Liu, B. Li, Powder Technol. 287 (2016) 315–329.
H. Yang, X. Zhang, K. Deng, W. Li, Y. Gan, L. Zhao, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 29 (1998) 1345–1356.
V.C. Patel, W. Rodi, G. Scheuerer, AIAA J. 23 (1985) 1308–1319.
R.A.W.M. Henkes, C.J. Hoogendoorn, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 32 (1989) 157–169.
M.R. Aboutalebi, M. Hasan, R.I.L. Guthrie, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 26 (1995) 731–744.
S. Garcia-Hernandez, R.D. Morales, E. Torres-Alonso, Ironmak. Steelmak. 37 (2010) 360–368.
Z. Liu, L. Li, B. Li, M. Jiang, JOM 66 (2014) 1184–1196.
H.S. Park, H. Nam, J.K. Yoon, ISIJ Int. 41 (2001) 974–980.
Z. Li, E. Wang, L. Zhang, Y. Xu, A. Deng, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 48 (2017) 2389–2402.
X. Sun, B. Li, H. Lu, Y. Zhong, Z. Ren, Z. Lei, Metals 9 (2019) 983–999.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. U1760206 and 51574083) and the 111 Project (2.0) of China (No. BP0719037) for the financial support. The first author is grateful for financial support provided by the Institute of Thermodynamics and Fluid Mechanics at Technische Universität Ilmenau, Germany, and the Verein zur Förderung der Thermo-und Fluiddynamik e.V. Furthermore, the authors are grateful to Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) for the financial support in the framework of the Research Training Group Lorentz Force Velocimetry and Lorentz Force Eddy Current Testing (GRK 1567). Finally, the authors acknowledge support by the Computer Center at TU Ilmenau for providing the computational resources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, L., Han, Zf., Karcher, C. et al. Melt flow, heat transfer and solidification in a flexible thin slab continuous casting mold with vertical-combined electromagnetic braking. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 31, 401–415 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-023-01062-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-023-01062-9