Abstract
The effect of electromagnetic stirring at a continuous casting strand on the distribution of inclusions along the thickness of gear steel blooms was investigated. Inclusions in the subsurface of continuous casting blooms were Al2O3·CaO·CaS·MgO, similar to those in the molten steel of continuous casting tundish. Inclusions at 1/4 thickness from the loose side and the center of the bloom were Al2O3·CaS·MgO. The spatial distribution in the number density and composition of inclusions along the thickness from the loose side to the fixed side of the bloom was non-uniform but symmetric. The electromagnetic stirring efficiently improved steel cleanliness by lowering the average number density and area fraction of inclusions in the whole section of the CC bloom from 58.14 #/mm2 and 176.82 ppm to 30.90 #/mm2 and 111.67 ppm, respectively, and by increasing the average size and the maximum size of inclusions from 2.73 and 20.84 μm to 2.99 and 76.02 μm, respectively. More large-size inclusions contained K and Na by the slag entrainment in the mold with electromagnetic stirring were detected than those without electromagnetic stirring. Seven mm of the bloom from the loose side was analyzed for inclusions with size > 1.0 μm every 1 mm depth. The average CaO content of inclusions with size > 1.0 μm within the 7 mm subsurface of the bloom increased from 5.67 wt pct without electromagnetic stirring to 16.12 wt pct with electromagnetic stirring and increased from 10.24 wt pct without electromagnetic stirring to 21.31 wt pct with electromagnetic stirring for > 3.0 μm inclusions, which confirmed that unreasonable current electromagnetic stirring operation parameters will lead to slag entrainment.








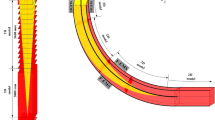
(adapted from Ref. [31])

adapted from Ref. [31])









Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.F. Zhang: Non-metallic Inclusions in Steels: Industrial Practice. Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, 2019.
[2] N. Verma, P.C. Pistorius, R.J. Fruehan, M.S. Potter, H.G. Oltmann and E.B. Pretorius: Metallurgical & Materials Transactions B, 2012, 43, 830.
[3] S. Yang, Q. Wang, L.F. Zhang, J. Li and K. Peaslee: Metallurgical & Materials Transactions B, 2012, 43, 731.
[4] N. Verma, P.C. Pistorius, R.J. Fruehan, M. Potter, M. Lind and S.R. Story: Metallurgical & Materials Transactions B, 2011, 42, 720.
L.F. Zhang (2016) Steelmaking, 32: 1.
[6] L.F. Zhang, Y.F. Wang and X.J. Zuo: Metallurgical & Materials Transactions B, 2008, 39, 534.
[7] W. Yang, L.F. Zhang, X.H. Wang, Y. Ren, X.F. Liu and Q.L. Shan: ISIJ Int., 2013, 53, 1401.
L.F. Zhang: Non-metallic Inclusions in Steels: Fundamentals (in Chinese). Metallurgical Industry Press, 2019.
[9] L.F. Zhang, F. li and W. Fang: Steelmaking, 2016, 32, 1.
Y. Liu: Doctor Thesis, University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2018.
[11] Y. Chu, W. Li, Y. Ren and L.F. Zhang: Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2019, 50, 2047.
[12] G. Cheng, W. Li, X. Zhang and L.F. Zhang: Metals, 2019, 9, 642.
[13] Y. Ren, L.F. Zhang and S.S. Li: ISIJ Int., 2014, 54, 2772.
[14] W. Yang, C. Guo, C. Li and L.F. Zhang: Metallurgical & Materials Transactions B, 2017, 48, 2267.
W. Chen and C. Wang: Journal of Hebei Polytechnic University Natural Science Edition, 2011, 33, 39.
J. Zhang and W. Song: Xinjiang Iron and Steel, 2006, 6.
[17] G. Zhang and Y. Chen: Foundry Technology, 2005, 26, 720.
[18] L. Wang, Y. Bao, H. An, P. Li, Z. Peng and M. Wang: Continuous Casting, 2015, 40, 62.
[19] G. Li, F. Chen, W. Chen, J. Feng and R. Hui: Steelmaking, 2008, 24, 40.
[20] G. Zhang and Y. Chen: Steelmaking, 2008, 24, 21.
[21] W. Zhang, S. Luo, Y. Chen, W. Wang and M. Zhu: Metals, 2019, 9, 66.
[22] H. Li, X. Zhang, T. Chen, L. Chen and W. Yang: Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2018, 39, 137.
H. Sun, L. Li, X. Wu and C. Liu (2018) Metall. Res. Technol. 115, 100.
[24] S. Hayakawa, T. Shibata, H. Takahashi and H. Amano: Journal of the Iron and Steel Institute of Japan, 1989, 60, 216.
K. Sakamoto, T. Yamamoto, H. Ohkawa, J.I. Nishi, Y. Hatsuse and K.I. Morita: Journal of the Iron and Steel Institute of Japan, 1987, 73, 321.
[26] Y. Yin, J. Zhang, Q. Dong and Q. Zhou: Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 2019, 46, 855.
[27] Y.B. Yin, J.M. Zhang, S.W. Lei and Q.P. Dong: ISIJ Int., 2017, 57, 2165.
M.L. Yang, Z.S. Li, F.L. Wei, C.G. Cheng, X. Chen and S.B. Qi: Advanced Research on Engineering Materials, Energy, Management and Control, Pts 1 and 2, 2012, 424-425, 811-+.
[29] H. Lei, J.M. Jiang, B. Yang, Y. Zhao, H.W. Zhang, W.X. Wang and G.W. Dong: Metallurgical & Materials Transactions B, 2018, 49, 666.
[30] H. Fukaya and T. Miki: ISIJ Int., 2011, 51, 2007.
S. Ji, Y. Wang, W. Chen, L.F. Zhang, W. Jia, W. Zhang, H. Liu and J. Zhang: Proceedings of the 21st national steelmaking conference in 2019, Xi’an, China, 2019.
Y.D. Wang, W. Chen, D.B. Jiang and L.F. Zhang: Steel Res. Int., 2019, 92, 1900470(1).
W. Chen, Y. Wang and L.F. Zhang: (under preparation).
[34] H. Liu, M. Xu, S. Qiu and H. Zhang: Metallurgical & Materials Transactions B, 2012, 43, 1657.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for support from the National Natural Science Foundation China (Grant Nos. U1860206, 51725402), S&T Program of Hebei (Grant No. 20311005D), the High Steel Center (HSC) at Yanshan University, and Beijing International Center of Advanced and Intelligent Manufacturing of High Quality Steel Materials (ICSM), Beijing Key Laboratory of Green Recycling and Extraction of Metals (GREM) and the High Quality Steel Consortium (HQSC) at University of Science and Technology Beijing, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted April 16, 2020; accepted April 9, 2021.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, S., Zhang, L., Wang, Y. et al. Effect of Electromagnetic Stirring on Inclusions in Continuous Casting Blooms of a Gear Steel. Metall Mater Trans B 52, 2341–2354 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-021-02176-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-021-02176-9