Abstract
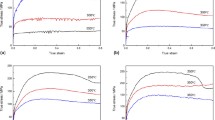
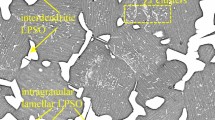
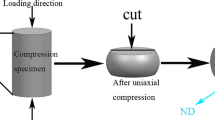
In this paper, the microstructures with two different morphologies of intragranular lamellar 14H long-period stacking-ordered (LPSO) phase were designed in Mg–4.7Gd–3.4Y–1.2Zn–0.5Zr (wt pct) alloy, and their hot processing maps were established based on a series of hot compression tests. The deformation behavior and microstructure evolution of the two alloys during hot compression were investigated, the effect of 14H LPSO phase on dynamic recrystallization (DRX), texture, and hot workability also discussed. The alloy annealed at 400 °C (400AT alloy) with densely distributed 14H LPSO phase and the alloy annealed at 450 °C (450AT alloy) with sparsely distributed 14H LPSO phase has the approximate peak stress and activation energy values. However, the 400AT alloy offers a greater hot processing window than the 450AT alloy. With the compressive temperature increasing or the strain rate decreasing, 14H LPSO phase gradually changes from a metastable state to a stable state in 400AT alloys, while it gradually dissolves in 450AT alloy. In addition, necklace-shaped discontinuous dynamic recrystallization (DDRX) grains were mainly distributed around the original deformed grains, continuous dynamic recrystallization (CDRX) grains were primarily located in the kink boundary, triangular grain boundary and widely spaced LPSO phase lamella in both alloys. For the 450AT alloy, more 14H LPSO phase kink boundary and lager space between LPSO phase lamellae promotes to the formation of CDRX grains, while limit the texture weakening. The 400AT alloy exhibits a weaker texture intensity and more randomly distributed grain orientation, which was related to the existence of large amount of DDRX grains. The weaker basal texture was beneficial to the hot workability and well corresponding to the larger appropriate hot processing region of 400 AT alloy.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Matsushita, K. Masuda, R. Waki, H. Ohfuji, M. Yamasaki, Y. Kawamura, and Y. Higo: J. Alloys Compd., 2019, vol. 784, pp. 1284–89.
B.L. Mordike and T. Ebert: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2001, vol. 302, pp. 37–45.
G.L. Bi, D.Q. Fang, W.C. Zhang, J. Sudagar, Q.X. Zhang, J.S. Lian, and Z.H. Jiang: J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2012, vol. 28, pp. 543–51.
Y. Kawamura, K. Hayashi, A. Inoue, and T. Masumoto: Mater. Trans., 2001, vol. 42, pp. 1172–76.
L.Y. Feng, X.X. Dong, Q. Cai, B. Wang, and S.X. Ji: J. Alloys Compd., 2019, vol. 793, 166364.
J.S. Zhang, C. Xin, W.L. Cheng, L.P. Bian, H.X. Wang, and C.X. Xu: J. Alloys Compd., 2013, vol. 558, pp. 195–202.
C. Xu, M.Y. Zheng, S.W. Xu, K. Wu, E.D. Wang, S. Kamado, G.J. Wang, and X.Y. Lv: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, vol. 547, pp. 93–98.
S.M. Ramezani, A. Zarei-Hanzaki, H.R. Abedi, A. Salandari-Rabori, and P. Minarik: J. Alloys Compd., 2019, vol. 793, pp. 134–45.
H. Okuda, T. Horiuchi, S. Hifumi, M. Yamasaki, Y. Kawamura, and S. Kimura: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2014, vol. 45A, pp. 4780–785.
Y. Tang, Q.C. Le, R.D.K. Misra, G.Q. Su, and J.Z. Cui: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2018, vol. 712, pp. 266–80.
C. Xu, M.Y. Zheng, K. Wu, E.D. Wang, G.H. Fan, S.W. Xu, S. Kamado, X.D. Liu, G.J. Wang, and X.Y. Lv: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, vol. 559, pp. 615–22.
X.J. Zhou, C.M. Liu, Y.H. Gao, S.N. Jiang, X.Z. Han, and Z.Y. Chen: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2017, vol. 48A, pp. 3060–72.
G. Liu, Z.D. Ma, G.B. Wei, T.C. Xu, X. Zhang, Y. Yang, W.D. Xie, and X.D. Peng: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2019, vol. 267, pp. 393–402.
H. Somekawa and D. Ando: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2020, vol. 780, 139144.
C.R. Liu, L. Li, W. Zhou, X. Bai, H.L. Zhong, Z.Q. Zhang, and Z.Z. Wen: J. Alloys Compd., 2023, vol. 937, 168356.
K. Hagihara, T. Mayama, M. Honnami, M. Yamasaki, H. Izuno, T. Okamoto, T. Ohashi, T. Nakano, and Y. Kawamura: Int. J. Plasticity, 2016, vol. 77, pp. 174–91.
M. Yamasaki, K. Hagihara, S. Inoue, J.P. Hadorn, and Y. Kawamura: Acta Mater., 2013, vol. 61, pp. 2065–76.
E. Oñorbe, P. Pérez Zubiaur, G. Garcés, and P. Adeva: J. Mater. Sci., 2012, vol. 47, pp. 1085–93.
G.X. Wang, P.L. Mao, Z. Wang, L. Zhou, F. Wang, and Z. Liu: J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2022, vol. 21, pp. 40–53.
J.H. Zhang, S.J. Liu, R.Z. Wu, L.G. Hou, and M.L. Zhang: J. Magnes. Alloy., 2018, vol. 6, pp. 277–91.
J.B. Lyu, J. Kim, H.X. Liao, J. She, J.F. Song, J. Peng, F.S. Pan, and B. Jiang: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2020, vol. 773, 138735.
G. Garces, D.G. Morris, M.A. Muñoz-Morris, P. Perez, D. Tolnai, C. Mendis, A. Stark, H.K. Lim, S. Kim, N. Shell, and P. Adeva: Acta Mater., 2015, vol. 94, pp. 78–86.
Y. Chino, M. Mabuchi, S. Hagiwara, H. Iwasaki, A. Yamamoto, and H. Tsubakino: Scr. Mater., 2004, vol. 51, pp. 711–14.
M. Li, X. Wang, Q.Y. Feng, J. Wang, Z. Xu, and P.H. Zhang: Mater. Charact., 2017, vol. 125, pp. 123–33.
X. Wu, F.S. Pan, R.J. Cheng, and S.Q. Luo: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2018, vol. 726, pp. 64–68.
Y.F. Wang, F. Zhang, Y.T. Wang, Y.B. Duan, K.J. Wang, W.J. Zhang, and J. Hu: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2019, vol. 745, pp. 149–58.
B.J. Lv, J. Peng, L.L. Zhu, Y.J. Wang, and A.T. Tang: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, vol. 599, pp. 150–59.
D.X. Zhang, Z. Tan, Q.H. Huo, Z.Y. Xiao, Z.W. Fang, and X.Y. Yang: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2018, vol. 715, pp. 389–403.
C. Xu, T. Nakata, X. Qiao, M. Zheng, K. Wu, and S. Kamado: Sci. Rep., 2017, vol. 7, pp. 1–10.
J.X. Xiao, Z.Y. Chen, J.B. Shao, T. Chen, X. Lin, and C.M. Liu: Mater. Charact., 2020, vol. 167, 110515.
Y.X. Han, S.H. He, T. Chen, J.B. Shao, C.M. Liu, Z.Y. Chen, and Z. Yang: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2022, vol. 856, 144002.
T. Chen, Z.Y. Chen, J.B. Shao, and R.K. Wang: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2019, vol. 750, pp. 31–39.
T. Chen, Z.Y. Chen, J.B. Shao, R.K. Wang, L.H. Mao, and C.M. Liu: Mater. Des., 2018, vol. 152, pp. 1–9.
J.K. Kim, W.S. Ko, S. Sandlöbes, M. Heidelmann, B. Grabowski, and D. Raabe: Acta Mater., 2016, vol. 112, pp. 171–83.
H. Liu, K. Yan, J.L. Yan, F. Xue, J.P. Sun, J.H. Jiang, and A.B. Ma: Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc., 2017, vol. 27, pp. 63–72.
Y.M. Zhu, A.J. Morton, and J.F. Nie: Acta Mater., 2010, vol. 58, pp. 2936–47.
Z.C. Sun, H.L. Wu, J. Cao, and Z.K. Yin: Int. J. Plasticity, 2018, vol. 106, pp. 73–87.
J.R. Kang, X. Liu, and T.Z. Wang: Scr. Mater., 2023, vol. 224, 115121.
L.H. Li, F.G. Qi, Q. Wang, C.H. Hou, N. Zhao, Y. Yang, S.S. Chai, and X.P. Ouyang: Mater. Charact., 2020, vol. 169, 110649.
X.J. Zhou, C.M. Liu, Y.H. Gao, S.N. Jiang, W.H. Liu, and L.W. Lu: J. Alloys Compd., 2017, vol. 724, pp. 528–36.
B.J. Lv, J. Peng, Y. Peng, A.T. Tang, and F.S. Pan: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, vol. 579, pp. 209–16.
A. Hadadzadeh, F. Mokdad, M.A. Wells, and D.L. Chen: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2018a, vol. 709, pp. 285–89.
M. Calcagnotto, D. Ponge, E. Demir, and D. Raabe: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, vol. 527, pp. 2738–46.
Y.B. Chun, M. Battaini, C.H.J. Davies, and S.K. Hwang: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2010, vol. 41A, pp. 3473–87.
Y. Yao, C.M. Liu, Y.C. Wan, S.L. Yu, Y.H. Gao, and S.N. Jiang: Mater. Charact., 2020, vol. 161, p. 1110120.
X.H. Shao, Z.Q. Yang, and X.L. Ma: Acta Mater., 2010, vol. 58, pp. 4760–71.
J.Y. Li, F.L. Wang, J. Zeng, C.Y. Zhao, L. Jin, and J. Dong: Mater. Charact., 2022, vol. 193, p. 112326.
D.F. Zheng, Q.C. Zhu, X.Q. Zeng, and Y.X. Li: Mater. Lett., 2022, vol. 311, p. 131524.
L.S. Toth, Y. Estrin, R. Lapovok, and C.F. Gu: Acta Mater., 2010, vol. 58, pp. 1782–94.
D.H. Qin, M.J. Wang, C.Y. Sun, Z.X. Su, L.Y. Qian, and Z.H. Sun: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2020, vol. 788, p. 139537.
J.K. Kim, S. Sandlöbes, and D. Raabe: Acta Mater., 2015, vol. 82, pp. 414–23.
A. Galiyev, R. Kaibyshev, and G. Gottstein: Acta Mater., 2001, vol. 49, pp. 1199–1207.
D.D. Zhang, C.M. Liu, S.N. Jiang, Y.H. Gao, Y.C. Wan, and Z.Y. Chen: J. Alloys Compd., 2023, vol. 944, p. 169190.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the Key Research and Development Project of Hunan Province (No. 2023GK2020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Han, Y., Chen, Z., Chen, H. et al. Hot Compression Behavior and Microstructure Evolution of an Mg–Gd–Y–Zn–Zr Alloy Containing the 14H LPSO Phase with Different Morphologies. Metall Mater Trans A 54, 4806–4824 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-023-07203-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-023-07203-9