Abstract
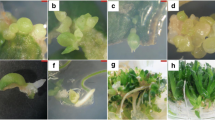
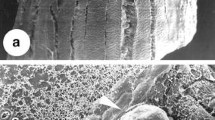
Gentiana kurroo (Royle), Gentiana cruciata (L.), Gentiana tibetica (King. ex Hook. f.), Gentiana lutea (L.), and Gentiana pannonica (Scop.) leaves derived from axenic shoot culture were used as explants. For culture initiation, leaves from the first and second whorls from the apical dome were dissected and cultured on Murashige and Skoog (MS) basal medium supplemented with three different auxins: 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, 1-naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA), or 3,6-dichloro-o-anisic acid (dicamba) in concentrations of 0.5, 1.0, or 2.0 mg/l; and five different cytokinins: zeatin, 6-furfurylamonopurine (kinetin), N-phenyl-N′-1,2,3-thiadiazol-5-ylurea (TDZ), N-(2-chloro-4-pyridyl)N′-phenylurea, or 6-benzylaminopurine (BAP). The cytokinin concentrations used were dependent on the type of cytokinin and varied between 0.25 and 3.0 mg/l. After 2 mo. of culture, the morphogenic response of explants was assessed. Frequency of embryogenesis was the highest for G. kurroo (54.7%) and dependent on plant growth hormones (PGRs). This gentian was the only species showing morphogenic capabilities on media supplemented with all applied combinations of PGRs, while none of the 189 induction media permutations stimulated somatic embryogenesis from G. lutea explants. G. tibetica and G. cruciata both produced an average of 6.6 somatic embryos per explant, while G. pannonica and G. kurroo regenerated at 15.7 and 14.2 somatic embryos per explant, respectively. Optimum regeneration was achieved in the presence of NAA combined with BAP or TDZ. This auxin also stimulated abundant rhizogenesis. Somatic embryos were also regenerated from adventitious roots of G. kurroo, G. cruciata, and G. pannonica. Somatic embryos converted into plantlets on half strength MS medium.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bach A.; Pawłowska B. Somatic embryogenesis in Gentiana pneumonanthe L. Acta Biol. Cracov. Bot. 45: 79–86; 2003.
Bonacin G. A.; Di Mauro A. O.; Oliveira R. C.; Perecin D. Induction of somatic embryogenesis in soybean: physicochemical factors influencing the development of somatic embryos. Genet. Mol. Biol. 23: 4–12; 2000.
Brown D. C. W.; Finstad K. I.; Watson E. M. Somatic embryogenesis in herbaceous dicots. In: ThorpeA. T. (ed) In vitro embryogenesis in plants. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, pp 345–415; 1995.
Canhoto J. C.; Lopes M. L.; Cruz G. S. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in myrtle (Myrtaceae). Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 57: 13–21; 1999.
Chavez V. M.; Litz R. E.; Norstog K. Somatic embryogenesis and organogenesis in Zamia fischeri, Z. furfuracea and Z. pumila. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 30: 99–105; 1992.
Clarke R. T.; Thomas J. A.; Elmes G. W.; Wardlaw J. C.; Munguira M. L.; Hochberg M. E. Population modeling of the spatial interactions between Maculinea rebeli, their initial foodplant Gentiana cruciata and Myrmica ants within a site. J. Insect Conserv. 2: 29–37; 1998.
Craig W.; Wiegand A.; O’Neill C. M.; Mathias R. J.; Power J. B.; Davey M. R. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from stem explants of Moricandia arvensis. Plant Cell Rep. 17: 27–31; 1997.
Fay, M. F. Practical considerations in the development of a botanic garden micropropagation laboratory. Botanic gardens in changing world. The Proceedings of the Third International Botanic Gardens Conservation Congress. 19–25 October, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil; 1992.
Fiuk A.; Rajkiewicz M.; Rybczyński J. J. In vitro culture of Gentiana kurroo (Royle). Biotechnology. 62: 267–274; 2003.
Guerra M. P.; Dal Vesco L. L.; Ducroquet J. P.; Nodari R. O.; Dos Reis M. S. Somatic embryogenesis in goober serrana: genotype response, auxinic shock and synthetic seeds. R. Bras. Fisiol. Veg. 13: 17–128; 2001.
Hamama L.; Baaziz M.; Letouzé R. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from leaf tissue of jojoba. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 65: 109–113; 2001.
Hempel M. Does micropropagation influence plant quality? Australian Hort. 56: 51–53; 1989.
Hosokawa K.; Nakano M.; Oikawa Y.; Yamamura S. Adventitious shoot regeneration from leaf, stem and root explants of commercial cultivars of Gentiana. Plant Cell Rep. 15: 578–581; 1996.
Jain A.; Rout G. R.; Raina S. N. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from callus cultures of Phlox paniculata Linn. Sci. Hortic. 94: 137–143; 2002.
Karamian, R. Plantlet regeneration via somatic embryogenesis in four species of Crocus. In: J.-A. Fernández, F. Abdullaevs (eds) I International Symposium on Saffron Biology and Biotechnology. Acta Hort. 650: 10–15; 2004.
Kintzios S.; Manos C.; Makir O. Somatic embryogenesis from mature leaves of rose (Rosa sp.). Plant Cell Rep. 18: 467–472; 1999.
Köhlein F. Gentians. Timber, Portland, Oregon; 1991.
Kurtén U.; Nuutila A. M.; Kauppinen V.; Rousi M. Somatic embryogenesis in cell cultures of birch (Betula pendula Roth.). Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 23: 101–105; 1990.
Mandal A. K. A.; Gupta S. D.; Chatterji A. K. Factors affecting somatic embryogenesis cotyledonary explants of safflower. Biol. Plant. 44: 503–507; 2001.
Mikuła A.; Rybczyński J. J. Somatic embryogenesis of Gentiana genus I. The effect of the preculture treatment and primary explant origin on somatic embryogenesis of Gentiana cruciata (L.), G. pannonica (Scop.), and G. tibetica (King). Acta Physiol. Plant. 23: 15–25; 2001.
Mikuła A.; Rybczyński J. J.; Skierski J.; Latkowska M. J.; Fiuk A. Somatic embryogenesis of Gentiana genus IV.: Characterization of Gentiana cruciata and Gentiana tibetica embryogenic cell suspensions. In: Hvoslef-Eide A. K.; Preil W. (eds) Liquid culture systems for in vitro plant propagation. Springer, Netherlands, pp 345–356; 2005.
Mikuła A.; Skierski J.; Rybczyński J. J. Somatic embryogenesis of Gentiana genus III. Characterization of three-year old embryogenic suspensions of G. pannonica originated from various seedling explants. Acta Physiol. Plant. 24: 311–322; 2002.
Mikuła, A.; Tykarska, T.; Kuraś, M.; Iwanowska, A.; Rybczyński, J. J. Studies on the morphogenic potential of gentians in cell suspension. Symposium Breeding Research on Medicinal and Aromatic Plants, Quedlinburg, Germany; 1996: pp. 290–295.
Momčilovič I.; Grubišić D.; Nešković M. Micropropagation of four Gentiana species (G. lutea, G. cruciata, G. purpurea, G. acaulis). Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 49: 141–144; 1997.
Morgan E. R.; Butler R. M.; Bicknell R. A. In vitro propagation of Gentiana cerina and Gentiana corymbifera. New Zeal. J. Crop. Hort. 25: 1–8; 1997.
Murashige T.; Skoog F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15: 473–497; 1962.
Pinto G.; Santos C.; Neves L.; Araújo C. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in Eucalyptus globulus Labill. Plant Cell Rep. 21: 208–213; 2002.
Sharma N.; Chandel K. P. S.; Paul A. In vitro propagation of Gentiana kurroo—an indigenous threatened plant of medicinal importance. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 34: 307–309; 1993.
Thiem B.; Śliwińska E. Flow cytometric analysis of nuclear DNA content in cloudberry (Rubus chamaemorus L.) in vitro cultures. Plant Sci. 164: 129–134; 2003.
Vieitez A. M.; San-Jose C.; Vieitez F. J.; Ballester A. Somatic embryogenesis from roots of Camellia japonica plantlets cultured in vitro. J. Am. Soc. Hort. Sci. 116: 753–757; 1991.
Zhang Q.; Chen J.; Henny R. J. Direct somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from leaf, petiole, and stem explants of Golden Pothos. Plant Cell Rep. 23: 587–595; 2005.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editor: Nigel Taylor
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fiuk, A., Rybczyński, J.J. Genotype and plant growth regulator-dependent response of somatic embryogenesis from Gentiana spp. leaf explants. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Plant 44, 90–99 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-008-9124-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-008-9124-3