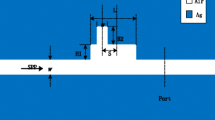
Abstract
We proposed a plasmonic nanosensor with an ultra-high sensitivity based on groove and ring resonator. Simulation results show that these sharp Fano profiles originate from the interference between the groove and ring resonator. The profile can be easily tuned by changing the parameters of the structure. Moreover, we introduce a new way to achieve multiple Fano resonances through independent processes by adding a side-coupled stub cavity, and the Fano resonances can be tuned independently. These characteristics offer flexibility in the design of the devices. This nanosensor yields an ultra-high sensitivity of ∼2000 nm/RIU, which is rarely seen in the previous report. Our structures may have potential applications for nanosensors, slow light, and nonlinear devices in highly integrated circuits.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miroshnichenko AE, Flach S, Kivshar YS (2009) Fano resonances in nanoscale structures. Rev Mod Phys 82(3):2257–2298
Zhang ZD, Wang HY, Zhang ZY (2012) Fano resonance in a gear-shaped Nanocavity of the metal–insulator–metal waveguide. Plasmonics 8(2):797–801
Chen Z, Cao X, Song X et al (2016) Side-coupled cavity-induced Fano resonance and its application in nanosensor. Plasmonics 11(1):307–313
Verellen N, Sonnefraud Y, Sobhani H et al (2009) Fano resonances in individual coherent plasmonic nanocavities. Nano Lett 9(4):1663–1667
Heuck M, Kristensen PT, Elesin Y et al (2013) Improved switching using Fano resonances in photonic crystal structures. Opt Lett 38(14):2466–2468
Xu T, Wu YK, Luo X et al (2010) Plasmonic nanoresonators for high-resolution colour filtering and spectral imaging. Nat Commun 1(5):118–124
Fang Z, Cai J, Yan Z et al (2011) Removing a wedge from a metallic Nanodisk reveals a Fano resonance. Nano Lett 11(10):4475–4479
Economou EN (1969) Surface plasmons in thin films. Phys Rev 182(2):539–554
Chen J, Li Z, Yue S et al (2012) Plasmon-induced transparency in asymmetric T-shape single slit. Nano Lett 12(12):2494–2498
Zia R, Schuller JA, Chandran A et al (2006) Plasmonics: the next chip-scale technology. Mater Today 9(7–8):20–27
Lu H, Liu X, Mao D et al (2012) Plasmonic nanosensor based on Fano resonance in waveguide-coupled resonators. Opt Lett 37(18):3780–3782
Chen Z, Chen J, Yu L et al (2015) Sharp trapped resonances by exciting the anti-symmetric waveguide mode in a metal-insulator-metal resonator. Plasmonics 10(1):131–137
Chen J, Li Z, Li J et al (2011) Compact and high-resolution plasmonic wavelength demultiplexers based on Fano interference. Opt Express 19(10):9976–9985
Chheang V, Lee TK, Oh GY et al (2013) Compact polarizing beam splitter based on a metal-insulator-metal inserted into multimode interference coupler. Opt Express 21(18):20880–20887
Cao G, Li H, Deng Y et al (2014) Systematic theoretical analysis of selective-mode plasmonic filter based on aperture-side-coupled slot cavity. Plasmonics 9(5):1163–1169
Taheri AN, Kaatuzian H (2014) Design and simulation of a nanoscale electro-plasmonic 1 × 2 switch based on asymmetric metal-insulator-metal stub filters. Appl Opt 53(28):6546–6553
Tao J, Huang XG, Lin X et al (2009) A narrow-band subwavelength plasmonic waveguide filter with asymmetrical multiple-teeth-shaped structure. Opt Express 17(16):13989–13994
Lu H, Liu XM, Wang LR et al (2011) Nanoplasmonic triple-wavelength demultiplexers in two-dimensional metallic waveguides. Appl Phys B Lasers Opt 103(4):877–881
Lu H, Liu X, Gong Y et al (2011) Enhancement of transmission efficiency of nanoplasmonic wavelength demultiplexer based on channel drop filters and reflection nanocavities. Opt Express 19(14):12885–12890
Chen Z, Yu L, Wang L et al (2015) A refractive index nanosensor based on Fano resonance in the plasmonic waveguide system. IEEE Photonics Tech Lett 27(16):1695–1698
Wen K, Hu Y, Chen L et al (2014) Fano resonance with ultra-high figure of merits based on plasmonic metal-insulator-metal waveguide. Plasmonics 10(1):27–32
Qi J, Chen Z, Chen J et al (2014) Independently tunable double Fano resonances in asymmetric MIM waveguide structure. Opt Express 22(12):14688–14695
Liu N, Langguth L, Weiss T et al (2009) Plasmonic analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency at the Drude damping limit. Nat Mater 8(9):758–762
Hao F, Sonnefraud Y, Van DP et al (2008) Symmetry breaking in plasmonic nanocavities: subradiant LSPR sensing and a tunable Fano resonance. Nano Lett 8(11):3983–3988
Pang S, Huo Y, Xie Y et al (2016) Fano resonance in MIM waveguide structure with oblique rectangular cavity and its application in sensor. Opt Commun 381:409–413
Chen Y, Liu Y, Chen Z et al (2016) Fano resonance in a symmetric waveguide system with different filled insulators. Opt Commun 371:184–188
Zhang Y, Li S, Zhang X et al (2016) Evolution of Fano resonance based on symmetric/asymmetric plasmonic waveguide system and its application in nanosensor. Opt Commun 370:203–208
Li S, Zhang Y, Song X et al (2016) Tunable triple Fano resonances based on multimode interference in coupled plasmonic resonator system. Opt Express 24(14):15351–15361
Han Z, Forsberg E, He S (2007) Surface Plasmon Bragg gratings formed in metal-insulator-metal waveguides. IEEE Photonics Tech L 19(2):91–93
Johnson PB (1972) Optical constants of the Noble metals. Phys Rev B 6(12):4370–4379
Dash JN, Jha R (2015) On the performance of graphene-based D-shaped photonic crystal fibre biosensor using surface Plasmon resonance. Plasmonics 10(5):1123–1131
Salihoglu O, Balci S, Kocabas C (2012) Plasmon-polaritons on graphene-metal surface and their use in biosensors. Appl Phys Lett 100(21):1–5
Hu F, Yi H, Zhou Z (2011) Wavelength demultiplexing structure based on arrayed plasmonic slot cavities. Opt Lett 36(8):1500–1502
Becker J, Trügler A, Jakab A et al (2010) The optimal aspect ratio of gold Nanorods for plasmonic bio-sensing. Plasmonics 5(2):161–167
Liu N, Weiss T, Mesch M (2010) Planar metamaterial analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency for plasmonic sensing. Nano Lett 10(4):1103–1107
Dash JN, Jha R (2016) Highly sensitive side-polished birefringent PCF-based SPR sensor in near IR. Plasmonics 11:1505–1509
Dash JN, Jha R (2014) SPR biosensor based on polymer PCF coated with conducting metal oxide. IEEE Photonics Tech L 26(6):595–598
Homola J, Yee SS, Gauglitz G (1999) Surface plasmon resonance sensors: review. Sensors & Actuators B Chemical 54(1):3–15
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Grant No. 2016YFA0301300) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 11374041, Grant 11574035 and Grant 11404030 and Fund of State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications (Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications), PR China
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Li, S., Zhang, Y. et al. Independently Formed Multiple Fano Resonances for Ultra-High Sensitivity Plasmonic Nanosensor. Plasmonics 13, 107–113 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0489-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0489-6