Abstract
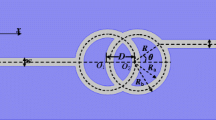
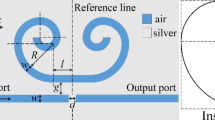
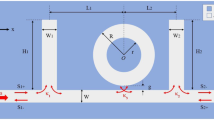
The filter function of the metal–insulator–metal (MIM) waveguide with a gear-shaped nanocavity is investigated using the finite-difference time-domain method. Since the gear breaks the symmetric distribution of the resonance, Fano resonance occurs in the gear-shaped nanocavity. Fano resonance strongly depends on the structural parameters of the gear. Compared to the MIM waveguide with a disk-shaped nanocavity, the MIM waveguide with a gear-shaped nanocavity allows for a much more sensitive detection of small refractive index changes of the filled media inside the nanocavity, which reveals a potential sensor application of the MIM waveguide with a gear-shaped nanocavity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raether H (1988) Surface plasmons on smooth and rough surfaces and gratings. Springer, Berlin
Gramotnev DK, Bozhevolnyi SI (2010) Plasmonics beyond the diffraction limit. Nat Photonics 4:83–91. doi:10.1038/nphoton.2009.282
Bonod N, Reinisch R, Popov E, Nevière M (2004) Optimization of surface-plasmon-enhanced magneto-optical effects. J Opt Soc Am B 21:791–797. doi:10.1364/JOSAB.21.000791
Derkacs D, Lim SH, Matheu P, Mar W, Yu ET (2006) Improved performance of amorphous silicon solar cells via scattering from surface plasmon polaritons in nearby metallic nanoparticles. Appl Phys Lett 89:093103–093105. doi:10.1063/1.2336629
Charbonneau R, Tencer M, Lahoud N, Berini P (2008) Demonstration of surface sensing using long-range surface plasmon waveguides on silica. Sens Actuators B: Chem 134:455–461. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2008.05.034
Rosenzveig T, Hermannsson PG, Leosson K (2010) Modeling of polarization-dependent loss in plasmonic nanowire waveguides. Plasmonics 5:75–77. doi:10.1007/s11468-009-9118-y
Fang YR, Li ZP, Huang YZ, Zhang SP, Nordlander P, Halas NJ, Xu HX (2010) Branched silver nanowires as controllable plasmon routers. Nano Lett 10:1950–1954. doi:10.1021/nl101168u
Zhang ZY, Wang JD, Zhao YN, Lu D, Xiong ZH (2011) Numerical investigation of a branch-shaped filter based on metal-insulator-metal waveguide. Plasmonics 6:773–778. doi:10.1007/s11468-011-9263-y
Jin XP, Huang XG, Tao J, Lin XS, Zhang Q (2010) A novel nanometeric plasmonic refractive index sensor. IEEE T Nanotechnol 9:134–137. doi:10.1109/TNANO.2009.2038909
Veronis G, Fan S (2005) Bends and splitters in metal-dielectric-metal subwavelength plasmonic waveguides. Appl Phys Lett 87:131102–131104. doi:10.1063/1.2056594
Nikolajsen T, Leosson K, Bozhevolnyi SI (2004) Surface plasmon polariton based modulators and switches operating at telecom wavelengths. Appl Phys Lett 85:5833–5835. doi:10.1063/1.1835997
Luk’yanchuk B, Zheludev NI, Maier SA, Halas NJ, Nordlander P, Giessen H, Chong CT (2010) The Fano resonance in plasmonic nanostructures and metamaterials. Nat Mater 9:707–715. doi:10.1038/nmat2810
Zhang SP, Bao K, Halas NJ, Xu HX, Nordlander P (2011) Substrate-induced Fano resonances of a plasmonic nanocube: a route to increased-sensitivity localized surface plasmon resonance sensors revealed. Nano Lett 11:1657–1663. doi:10.1021/nl200135r
Hao F, Sonnefraud Y, Van Dorpe P, Maier SA, Halas NJ, Nordlander P (2008) Symmetry breaking in plasmonic nanocavities: subradiant LSPR sensing and a tunable Fano resonance. Nano Lett 8:3983–3988. doi:10.1021/nl802509r
Spinelli P, van Lare C, Verhagen E, Polman A (2011) Controlling Fano lineshapes in plasmon-mediated light coupling into a substrate. Opt Express 19:A303–A311. doi:10.1364/OE.19.00A303
Tam F, Moran C, Halas N (2004) Geometrical parameters controlling sensitivity of nanoshell Plasmon resonances to changes in dielectric environment. J Phys Chem B 108:17290–17294. doi:10.1021/jp048499x
Verellen N, Sonnefraud Y, Sobhani H, Hao F, Moshchalkov VV, Dorpe PV, Nordlander P, Maier SA (2009) Fano resonances in individual coherent plasmonic nanocavities. Nano Lett 9:1663–1667. doi:10.1021/nl9001876
Lassiter JB, Sobhani H, Fan JA, Kundu J, Capasso F, Nordlander P, Halas NJ (2010) Fano resonances in plasmonic nanoclusters: geometrical and chemical tunability. Nano Lett 10:3184–3189. doi:10.1021/nl102108u
Fang ZY, Cai JY, Yan ZB, Nordlander P, Halas NJ, Zhu X (2011) Removing a wedge from a metallic nanodisk reveals a Fano resonance. Nano Lett 11:4475–4479. doi:10.1021/nl202804y
Kekatpure RD, Hryciw AC, Barnard ES, Brongersma ML (2009) Solving dielectric and plasmonic waveguide dispersion relations on a pocket calculator. Opt Express 17:24112–24129. doi:10.1364/OE.17.024112
Yun BF, Hu GH, Cui YP (2010) Theoretical analysis of a nanoscale plasmonic filter based on a rectangular metal-insulator-metal waveguide. J Phys D Appl Phys 43:35102–35109. doi:10.1088/0022-3727/43/38/385102
Gai H, Wang J, Tian Q (2007) Modified Debye model parameters of metals applicable for broadband calculations. Appl Opt 46:2229–2233. doi:10.1364/AO.46.002229
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the National Natural Foundation of China (grant nos. 11004160 and 10974161) and the Innovation Fund for Ph.D. students of Southwest Jiaotong University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, ZD., Wang, HY. & Zhang, ZY. Fano Resonance in a Gear-Shaped Nanocavity of the Metal–Insulator–Metal Waveguide. Plasmonics 8, 797–801 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-012-9475-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-012-9475-9