Abstract
Purpose
In spite of substantial advancement in recent past, the role of metal speciation in assessing biogeochemical behaviour of Pb is still topical. Organic ligands are capable to modify Pb speciation in nutrient/soil solution and in turn its soil–plant transfer and toxicity. In this sense, the main objective of this study was to evaluate the effect of organic ligands on Pb-induced oxidative stress to Vicia faba roots.
Materials and methods
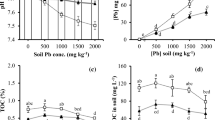
V. faba seedlings grown to controlled hydroponic system were treated with 5 μM Pb as lead nitrate in the presence and absence of organic ligands viz ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) and citric acid (CA) for 1, 4, 8, 12, and 24 h. The chemical speciation of Pb (percent free and chelated Pb) in nutrient solution in the presence and absence of organic ligands was calculated using Visual Minteq speciation model. The effect of chemical speciation on Pb-induced oxidative stress to V. faba roots was investigated using plant enzymatic antioxidative system [superoxide dismutases (SOD), guaiacol peroxidise (GPX), ascorbate peroxidase (APX), glutathione reductase (GR), and catalase (CAT)]. The antioxidant enzymes activities were determined using ultraviolet spectrophotometer.
Results and discussion
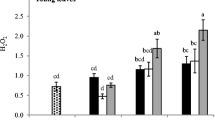
The activities of SOD, GPX, APX, and GR significantly increased whereas that of CAT decreased in V. faba roots under Pb alone treatment. Lead-induced increase/decrease in antioxidant enzymes activities was not linear but varies with treatment exposure time. EDTA dose dependently inhibited Pb-induced changes in antioxidant enzymes activities. However, CA did not cause any significant change in Pb-induced variation in antioxidant enzymes activities, but delayed or slightly reduced the Pb effect.
Conclusions
The present study suggested that physiological responses of V. faba roots to Pb toxicity vary with applied Pb form and duration of exposure. EDTA can inhibit Pb-induced toxicity to V. faba seedlings by forming stable Pb-EDTA complexes due to its high binding strength for Pb. However, CA had no effect on Pb-induced toxicity to V. faba roots due to weak complexation with Pb.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Meth Enzymol 105:121–126
Arshad M, Silvestre J, Pinelli E, Kallerhoff J, Kaemmerer M, Tarigo A, Shahid M, Guiresse M, Pradere P, Dumat C (2008) A field study of lead phytoextraction by various scented Pelargonium cultivars. Chemosphere 71:2187–2192
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Cheng Z, Lee L, Dayan S, Grinshtein M, Shaw R (2011) Speciation of heavy metals in garden soils: evidences from selective and sequential chemical leaching. J Soils Sediments 11:628–638
Chen YX, Lin Q, Luo YM, He YF, Zhen SJ, Yu YL, Tian GM, Wong MH (2003) The role of citric acid on the phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil. Chemosphere 50:807–811
Dipu S, Kumar AA, Thanga SG (2012) Effect of chelating agents in phytoremediation of heavy metals. Remediat J 22:133–146
Dringen R, Gutterer JM (2002) Glutathione reductase from bovine brain. Meth Enzymol 348:281–288
Evangelou MWH, Ebel M, Schaeffer A (2007) Chelate assisted phytoextraction of heavy metals from soil. Effect, mechanism, toxicity, and fate of chelating agents. Chemosphere 68:989–1003
Giannopolitis CN, Ries SK (1977) Superoxide dismutases: I. Occurrence in higher plants. Plant Physiol 59:309–314
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2010) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:909–930
Gill SS, Khan NA, Tuteja N (2012) Cadmium at high dose perturbs growth, photosynthesis and nitrogen metabolism while at low dose it up regulates sulfur assimilation and antioxidant machinery in garden cress (Lepidium sativum L.). Plant Sci 182:112–120
Hemeda HM, Klein BP (1990) Effects of Naturally Occurring Antioxidants on Peroxidase Activity of Vegetable Extracts. J Food Sc 55:184–185
Horvat T, Vidaković-Cifrek Z, Orescanin V, Tkalec M, Pevalek-Kozlina B (2007) Toxicity assessment of heavy metal mixtures by Lemna minor L. Sci Total Environ 384:229–238
Islam E, Liu D, Li T, Yang X, Jin X, Mahmood Q, Tian S, Li J (2008) Effect of Pb toxicity on leaf growth, physiology and ultrastructure in the two ecotypes of Elsholtzia argyi. J Hazard Mater 154:914–926
Kopittke PM, Asher CJ, Menzies NW (2008) Prediction of Pb speciation in concentrated and dilute nutrient solutions. Environ Pollut 153:548–554
Lorestani B, Cheraghi M, Yousefi N (2012) The potential of phytoremediation using hyperaccumulator plants: a case study at a lead–zinc mine site. Int J Phytorem 14:786–795
Luciano A, Viotti P, Torretta V, Mancini G (2013) Numerical approach to modelling pulse-mode soil flushing on a Pb-contaminated soil. J Soils Sediments 13:43–55
Madejón P, Ramírez-Benítez JE, Corrales I, Barceló J, Poschenrieder C (2009) Copper-induced oxidative damage and enhanced antioxidant defenses in the root apex of maize cultivars differing in Cu tolerance. Environ Exp Bot 67:415–420
Marcato-Romain CE, Pinelli E, Pourrut B, Silvestre J, Guiresse M (2009) Assessment of the genotoxicity of Cu and Zn in raw and anaerobically digested slurry with the Vicia faba micronucleus test. Mutat Res 672:113–118
Minibayeva F, Dmitrieva S, Ponomareva A, Ryabovol V (2012) Oxidative stress-induced autophagy in plants: the role of mitochondria. Plant Physiol Biochem 59:11–19
Mittler R (2002) Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 7:405–410
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22:867–880
Nguyen LTH, Vandegehuchte MB, van der Geest HG, Janssen CR (2012) Evaluation of the mayfly Ephoron virgo for European sediment toxicity assessment. J Soils Sediments 12:749–757
Opdenakker K, Remans T, Vangronsveld J, Cuypers A (2012) Mitogen-Activated Protein (MAP) kinases in plant metal stress: regulation and responses in comparison to other biotic and abiotic stresses. Int J Mol Sci 13:7828–7853
Piechalak A, Tomaszewska B, Baralkiewicz D (2003) Enhancing phytoremediative ability of Pisum sativum by EDTA application. Phytochemistry 64:1239–1251
Piotrowska-Niczyporuk A, Bajguz A, Zambrzycka E, Godlewska-Żyłkiewicz B (2012) Phytohormones as regulators of heavy metal biosorption and toxicity in green alga Chlorella vulgaris (Chlorophyceae). Plant Physiol Biochem 52:52–65
Pourrut B, Perchet G, Silvestre J, Cecchi M, Guiresse M, Pinelli E (2008) Potential role of NADPH-oxidase in early steps of lead-induced oxidative burst in Vicia faba roots. J Plant Physiol 165:571–579
Pourrut B, Jean S, Silvestre J, Pinelli E (2011a) Lead-induced DNA damage in Vicia faba root cells: potential involvement of oxidative stress. Mutat Res 726:123–128
Pourrut B, Shahid M, Dumat C, Winterton P, Pinelli E (2011b) Lead uptake, toxicity, and detoxification in plants. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 213:113–136
Probst A, Liu H, Fanju M, Liao B, Holland E (2009) Response of Vicia faba L. to metal toxicity on mine tailing substrate: geochemical and morphological changes in leaf and root. Environ Exp Bot 66:297–308
Qiu R, Zou Z, Zhao Z, Zhang W, Zhang T, Dong H, Wei X (2009) Removal of trace and major metals by soil washing with Na2EDTA and oxalate. J Soils Sediments 10:45–53
Ruley AT, Sharma NC, Sahi SV, Singh SR, Sajwan KS (2006) Effects of lead and chelators on growth, photosynthetic activity and Pb uptake in Sesbania drummondii grown in soil. Environ Pollut 144:11–18
Schreck E, Foucault Y, Sarret G, Sobanska S, Cécillon L, Castrec-Rouelle M, Uzu G, Dumat C (2012) Metal and metalloid foliar uptake by various plant species exposed to atmospheric industrial fallout: mechanisms involved for lead. Sci Total Environ 427–428:253–262
Seth CS, Misra V, Singh RR, Zolla L (2011) EDTA-enhanced lead phytoremediation in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) hydroponic culture. Plant Soil 347:231–242
Sgherri C, Quartacci MF, Navari-Izzo F (2007) Early production of activated oxygen species in root apoplast of wheat following copper excess. J Plant Physiol 164:1152–1160
Shahid M, Pinelli E, Pourrut B, Silvestre J, Dumat C (2011) Lead-induced genotoxicity to Vicia faba L. roots in relation with metal cell uptake and initial speciation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:78–84
Shahid M, Arshad M, Kaemmerer M, Pinelli E, Probst A, Baque D, Pradere P, Dumat C (2012a) Long-term field metal extraction by Pelargonium: phytoextraction efficiency in relation to plant maturity. Int J Phytorem 14:493–505
Shahid M, Dumat C, Silvestre J, Pinelli E (2012b) Effect of fulvic acids on lead-induced oxidative stress to metal sensitive Vicia faba L. plant. Biol Fert Soils 48:689–697
Shahid M, Pinelli E, Dumat C (2012c) Review of Pb availability and toxicity to plants in relation with metal speciation; role of synthetic and natural organic ligands. J Hazard Mater 219–220:1–12
Shahid M, Dumat C, Aslam M, Pinelli (2012d) Assessment of lead speciation by organic ligands using speciation models. Chem Speciat Bioavailab 24:248–252
Shahid M, Ferrand E, Schreck E, Dumat C (2013a) Behavior and impact of zirconium in the soil–plant system: plant uptake and phytotoxicity. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 221:107–127
Shahid M, Xiong T, Castrec-Rouelle M, Leveque T, Dumat C (2013b) Water extraction kinetics of metals, arsenic and dissolved organic carbon from industrial contaminated poplar leaves. J Environ Sci. doi:10.1016/S1001-0742(12)60197-1
Thounaojam TC, Panda P, Mazumdar P, Kumar D, Sharma GD, Sahoo L, Panda SK (2012) Excess copper induced oxidative stress and response of antioxidants in rice. Plant Physiol Biochem 53:33–39
Uzu G, Sobanska S, Aliouane Y, Pradere P, Dumat C (2009) Study of lead phytoavailability for atmospheric industrial micronic and sub-micronic particles in relation with lead speciation. Environ Pollut 157:1178–1185
Uzu G, Sobanska S, Sarret G, Muñoz M, Dumat C (2010) Foliar lead uptake by lettuce exposed to atmospheric fallouts. Environ Sci Technol 44:1036–1042
Wang S, Mulligan CN (2013) Effects of three low-molecular-weight organic acids (LMWOAs) and pH on the mobilization of arsenic and heavy metals (Cu, Pb, and Zn) from mine tailings. Environ Geochem Health 35:111–118
Zhang W, Tsang DCW, Chen H, Huang L (2013) Remediation of an electroplating contaminated soil by EDTA flushing: chromium release and soil dissolution. J Soils Sediments 13:354–363
Zheng L, Peer T, Seybold V, Lütz-Meindl U (2012) Pb-induced ultrastructural alterations and subcellular localization of Pb in two species of Lespedeza by TEM-coupled electron energy loss spectroscopy. Environ Exp Bot 77:196–206
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by the Higher Education Commission of Pakistan (www.hec.gov.pk) and the French Society for Export of Educative Resources (SFERE, http://www.sfere.fr/).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Jaume Bech
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahid, M., Dumat, C., Pourrut, B. et al. Influence of EDTA and citric acid on lead-induced oxidative stress to Vicia faba roots. J Soils Sediments 14, 835–843 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-013-0724-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-013-0724-0