Abstract
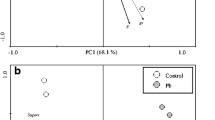
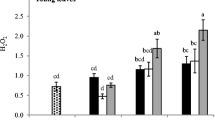
Lead (Pb) is a ubiquitous environmental pollutant capable to induce various morphological, physiological, and biochemical functions in plants. Only few publications focus on the influence of Pb speciation both on its phytoavailability and phytotoxicity. Therefore, Pb toxicity (in terms of lipid peroxidation, hydrogen peroxide induction, and photosynthetic pigments contents) was studied in Vicia faba plants in relation with Pb uptake and speciation. V. faba seedlings were exposed to Pb supplied as Pb(NO3)2 or complexed by two fulvic acids (FAs), i.e. Suwannee River fulvic acid (SRFA) and Elliott Soil fulvic acid (ESFA), for 1, 12, and 24 h under controlled hydroponic conditions. For both FAs, Pb uptake and translocation by Vicia faba increased at low level (5 mg l−1), whereas decreased at high level of application (25 mg l−1). Despite the increased Pb uptake with FAs at low concentrations, there was no influence on the Pb toxicity to the plants. However, at high concentrations, FAs reduced Pb toxicity by reducing its uptake. These results highlighted the role of the dilution factor for FAs reactivity in relation with structure; SRFA was more effective than ESFA in reducing Pb uptake and alleviating Pb toxicity to V. faba due to comparatively strong binding affinity for the heavy metal.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Chl-a:
-
Chlorophyll a
- Chl-b:
-
Chlorophyll b
- EDTA:
-
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- ESFA:
-
Elliott Soil fulvic acid
- FAs:
-
Fulvic acids
- HSs:
-
Humic substances
- PCs:
-
Phytochelatins
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- V. faba :
-
Vicia faba
- SRFA:
-
Suwannee River fulvic acid
- TBARS:
-
Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances
- WHAM VI:
-
Windermere humic aqueous model VI
References
Aarti P, Tanaka R, Tanaka A (2006) Effects of oxidative stress on chlorophyll biosynthesis in cucumber (Cucumis sativus) cotyledons. Physiol Plant 128:186–197
Babich H, Stotzky G (1979) Abiotic factors affecting the toxicity of lead to fungi. Appl Environ Microbiol 38:506–513
Cenkci S, Cigerci IH, YildIz M, Özay C, Bozdag A, Terzi H (2010) Lead contamination reduces chlorophyll biosynthesis and genomic template stability in Brassica rapa L. Environ Exp Bot 67:467–473
Debenest T, Silvestre J, Coste M, Delmas F, Pinelli E (2008) A new cell primo-culture method for freshwater benthic diatom communities. J Appl Phycol 21:65–73
Debenest T, Silvestre J, Coste M, Delmas F, Pinelli E (2009) Herbicide effects on freshwater benthic diatoms: induction of nucleus alterations and silica cell wall abnormalities. Aquat Toxicol 88:88–94
Dumat C, Staunton S (1999) Reduced adsorption of caesium on clay minerals caused by various humic substances. J Environ Radioactiv 46:187–200
Dumat C, Quiquampoix H, Staunton S (2000) Adsorption of cesium by synthetic clay−organic matter complexes: effect of the nature of organic polymers. Environ Sci Technol 34:2985–2989
Dumat C, Quenea K, Bermond A, Toinen S, Benedetti M (2006) Study of the trace metal ion influence on the turnover of soil organic matter in cultivated contaminated soils. Environ Pollut 142:521–529
El Hajjouji H, Pinelli E, Guiresse M, Merlina G, Revel J, Hafidi M (2007) Assessment of the genotoxicity of olive mill waste water (OMWW) with the Vicia faba micronucleus test. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 634:25–31
El-Ghamry AM, Abd El-Hai KM, Ghoneem KM (2009) Amino and humic acids promote growth, yield and disease resistance of faba bean cultivated in clayey soil. Aust J Basic Appl Sci 3:731–739
Ennever FK, Andreano G, Rosenkranz HS (1988) The ability of plant genotoxicity assays to predict carcinogenicity Mutat Res/Gen Tox Environ Mutagen 205:99–105
Essington ME (2004) Soil and water chemistry: an integrative approach, 1st edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Evangelou MWH, Daghan H, Schaeffer A (2004) The influence of humic acids on the phytoextraction of cadmium from soil. Chemosphere 57:207–213
Halim M, Conte P, Piccolo A (2003) Potential availability of heavy metals to phytoextraction from contaminated soils induced by exogenous humic substances. Chemosphere 52:265–275
Hodges DM, DeLong JM, Forney CF, Prange RK (1999) Improving the thiobarbituric acid-reactive-substances assay for estimating lipid peroxidation in plant tissues containing anthocyanin and other interfering compounds. Planta 207:604–611
IHSS, International Humic Substances Society, Denver, Colorado-USA. Available at http://www.ihss.gatech.edu/index.html. Accessed 8 Oct 2010
Islam E, Liu D, Li T, Yang X, Jin X, Mahmood Q, Shengke T, Junying L (2008) Effect of Pb toxicity on leaf growth, physiology and ultrastructure in the two ecotypes of Elsholtzia argyi. J Hazard Mater 154:914–926
Karaca A, Turgay OC, Tamer N (2006) Effects of a humic deposit (gyttja) on soil chemical and microbiological properties and heavy metal availability. Biol Fertil Soils 42:585–592
Kleber M, Johnson MG (2010) Advances in understanding the molecular structure of soil organic matter: implications for interactions in the environment. Adv Agron 106:77–142
Kruatrachue M, Jarupan W, Chitramvong YP, Pokethitiyook P, Upatham ES, Parkpoomkamol K (2002) Combined effects of lead and humic acid on growth and lead uptake of Duckweed, Lemna minor. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 69:655–661
Lichtenthaler HK (1987) Chlorophylls and carotenoids: pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. Methods Enzymol 148:350–382
Marcato-Romain C, Pinelli E, Pourrut B, Silvestre J, Guiresse M (2009a) Assessment of the genotoxicity of Cu and Zn in raw and anaerobically digested slurry with the Vicia faba micronucleus test. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 672:113–118
Marcato-Romain C, Guiresse M, Cecchi M, Cotelle S, Pinelli E (2009b) New direct contact approach to evaluate soil genotoxicity using the Vicia faba micronucleus test. Chemosphere 77:345–350
Mishra S, Srivastava S, Tripathi R, Kumar R, Seth C, Gupta D (2006) Lead detoxification by coontail (Ceratophyllum demersum L.) involves induction of phytochelatins and antioxidant system in response to its accumulation. Chemosphere 65:1027–1039
Nardi S, Pizzeghello D, Muscolo A, Vianello A (2002) Physiological effects of humic substances on higher plants. Soil Biol Biochem 34:1527–1536
Nedelkoska TV, Doran PM (2000) Characteristics of heavy metal uptake by plant species with potential for phytoremediation and phytomining. Miner Eng 13:549–561
Piccolo A, Nardi S, Concheri G (1992) Structural characteristics of humic substances as related to nitrate uptake and growth regulation in plant systems. Soil Biol Biochem 24:373–380
Pourrut B, Perchet G, Silvestre J, Cecchi M, Guiresse M, Pinelli E (2008) Potential role of NADPH-oxidase in early steps of lead-induced oxidative burst in Vicia faba roots. J Plant Physiol 165:571–579
Ruley AT, Sharma NC, Sahi SV, Singh SR, Sajwan KS (2006) Effects of lead and chelators on growth, photosynthetic activity and Pb uptake in Sesbania drummondii grown in soil. Environ Pollut 144:11–18
Salati S, Quadri G, Tambone F, Adani F (2010) Fresh organic matter of municipal solid waste enhances phytoextraction of heavy metals from contaminated soil. Environ Pollut 158:1899–1906
Sgherri C, Quartacci MF, Navari-Izzo F (2007) Early production of activated oxygen species in root apoplast of wheat following copper excess. J Plant Physiol 64:1152–1160
Shahid M (2010) Lead-induced toxicity to Vicia faba L. in relation with metal cell uptake and speciation. PhD Thesis, INP-ENSAT, Toulouse-France
Shahid M, Arshad M, Kaemmerer M, Pinelli E, Probst A, Baque D, Pradere P, Dumat C (2011a) Long term field metal extraction by pelargonium: Phytoextraction efficiency in relation with plant maturity. Int J Phytorem. doi:10.1080/15226514.2011.604689
Shahid M, Pourrut B, Dumat C, Winterton P, Pinelli E (2011b) Lead uptake, toxicity and detoxification in plants. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 213:113–136
Shahid M, Pinelli E, Pourrut B, Silvestre J, Dumat C (2011c) Lead-induced genotoxicity to Vicia faba L. roots in relation with metal cell uptake and initial speciation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:78–84
Shahid M, Pinelli E, Dumat C (2012) Review of Pb availability and toxicity to plants in relation with metal speciation; role of synthetic and natural organic ligands. J Hazard Mater. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.01.060
Singh R, Tripathi RD, Dwivedi S, Kumar A, Trivedi PK, Chakrabarty D (2010) Lead bioaccumulation potential of an aquatic macrophyte Najas indica are related to antioxidant system. Bioresour Technol 101:3025–3032
Staunton S, Dumat C, Zsolnay A (2002) Possible role of organic matter in radiocaesium adsorption in soils. J Environ Radioact 58:163–173
Tipping E, Lofts S, Lawlor A (1998) Modelling the chemical speciation of trace metals in the surface waters of the Humber system. Sci Total Environ 210(211):63–77
Uzu G, Sobanska S, Aliouane Y, Pradere P, Dumat C (2009) Study of lead phytoavailability for atmospheric industrial micronic and sub-micronic particles in relation with lead speciation. Environ Pollut 157:1178–1185
Uzu G, Sobanska S, Sarret G, Muñoz M, Dumat C (2010) Foliar lead uptake by lettuce exposed to atmospheric fallouts. Environ Sci Technol 44:1036–1042
Worms IA, Traber J, Kistler D, Sigg L, Slaveykova VI (2010) Uptake of Cd(II) and Pb(II) by microalgae in presence of colloidal organic matter from wastewater treatment plant effluents. Environ Pollut 158:369–374
Zeng K, Hwang H, Yu H (2002) Effect of dissolved humic substances on the photochemical degradation rate of 1-aminopyrene and atrazine. Int J Mol Sci 3:1048–1057
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Higher Education Commission of Pakistan (www.hec.gov.pk) and the French Society for Export of Educative Resources (SFERE, http://www.sfere.fr/) for the scholarship granted to M. Shahid. The experimental work was funded by the “French Ministry of Higher Education and Research” (MESR, enseignementsup-recherche.gouv.fr) and a national project EC2CO-CYTRIX. We thank these organizations for their support which has enabled the realization of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahid, M., Dumat, C., Silvestre, J. et al. Effect of fulvic acids on lead-induced oxidative stress to metal sensitive Vicia faba L. plant. Biol Fertil Soils 48, 689–697 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-012-0662-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-012-0662-9