Abstract
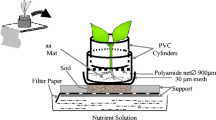
Availability of lead (Pb) in soil is a major factor controlling the phytoremediation efficiency of plants. This study was focused on investigating the plant-induced changes in rhizosphere and corresponding effect on bioavailable fraction of Pb and accumulation in different plant parts. For rhizosphere study, special cropping device was designed locally. Two Pb accumulator plants Stigmatocarpum criniflorum (L. f.) L. Bolus and Pelargonium × hortorum L.H. Bailey were grown in cropping device setup containing Pb spiked soil (500, 1000, 1500, and 2000 mg kg−1) for a period of 3 weeks. Further plants were also analyzed for Pb-induced oxidative stress. The results indicated higher ability of soil adjustment for Pb uptake by P. hortorum. The soil pH was (p < 0.05) decreased (ΔpH = − 0.22 pH), and dissolved organic carbon (DOC) content was significantly increased (by 1.7-fold) in rhizosphere of P. hortorum. The bioavailable fraction of Pb was twofold higher in rhizosphere of P. hortorum than S. criniflorum at the same soil Pb concentration (2000 mg kg−1). Maximum Pb concentration in root and shoot of S. criniflorum was 755 ± 99 and 207 ± 12 mg Pb/kg DW and for P. hortorum was 1281 ± 77 and 275 ± 7 mg Pb/kg DW. P. hortorum uptakes more Pb per plant by threefold compared with S. criniflorum. The oxidative stress results indicated higher Pb tolerance and suitability of P. hortorum for phytoextraction of Pb-contaminated soil.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adejumo SA, Tiwari S, Shinde V, Sarangi BK (2018) Heavy metal (Pb) accumulation in metallophytes as influenced by the variations in rhizospheric and non-rhizospheric soils physico-chemical characteristics. Int J Phytorem 20(3):237–248
AFNOR (1994) Qualite´ des sols, Paris, 250 pp
Arshad M, Silvestre J, Pinelli E, Kallerhoff J, Kaemmerer M, Tarigo A, Shahid M, Guiresse M, Pradère P, Dumat C (2008) A field study of lead phytoextraction by various scented Pelargonium cultivars. Chemosphere 71(11):2187–2192
Arshad M, Merlina G, Uzu G, Sobanska S, Sarret G, Dumat C, Silvestre J, Pinelli E, Kallerhoff J (2016) Phytoavailability of lead altered by two Pelargonium cultivars grown on contrasting lead-spiked soils. J Soils Sediments 16(2):581–591
Das S, de Oliveira LM, da Silva E, Ma LQ (2017) Arsenate and fluoride enhanced each other’s uptake in as-sensitive plant Pteris ensiformis. Chemosphere 180:448–454
de Oliveira LM, Suchismita D, Gress J, Rathinasabapathi B, Chen Y, Ma LQ (2017) Arsenic uptake by lettuce from as-contaminated soil remediated with Pteris vittata and organic amendment. Chemosphere 176:249–254
Grzelak A, Rychlik B, Bartosz G (2001) Light-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species in cell culture media. Free Radic Biol Med 30(12):1418–1425
Gul I, Manzoor M, Silvestre J, Rizwan M, Hina K, Kallerhoff J, Arshad M (2019) EDTA−assisted phytoextraction of lead and cadmium by Pelargonium cultivars grown on spiked soil. Int J Phytorem 21(2):101–110
Jena V, Gupta S, Dhundhel RS, Matić N, Frančišković-Bilinski S, Dević N (2013) Determination of total heavy metal by sequential extraction from soil. Int J Environ Sci Technol 3(1):35
Junglee S, Urban L, Sallanon H, Lopez-Lauri F (2014) Optimized assay for hydrogen peroxide determination in plant tissue using potassium iodide. Am J Anal Chem 5:730–736
Khoshgoftarmanesh AH, Afyuni M, Norouzi M, Ghiasi S, Schulin R (2018) Fractionation and bioavailability of zinc (Zn) in the rhizosphere of two wheat cultivars with different Zn deficiency tolerance. Geoderma 309:1–6
Kushwaha A, Hans N, Kumar S, Rani R (2018) A critical review on speciation, mobilization and toxicity of lead in soil-microbe-plant system and bioremediation strategies. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 147:1035–1045
Manzoor M, Gul I, Silvestre J, Kallerhoff J, Arshad M (2018) Screening of indigenous ornamental species from different plant families for Pb accumulation potential exposed to metal gradient in spiked soils. Soil Sediment Contam 27(5):439–453
Manzoor M, Abid R, Rathinasabapathi B, De Oliveira LM, da Silva E, Deng F, Rensing C, Arshad M, Gul I, Xiang P, Ma LQ (2019a) Metal tolerance of arsenic–resistant bacteria and their ability to promote plant growth of Pteris vittata in Pb–contaminated soil. Sci Total Environ 660:18–24
Manzoor M, Gul I, Ahmed I, Zeeshan M, Hashmi I, Amin BAZ, Kallerhoff J, Arshad M (2019b) Metal tolerant bacteria enhanced phytoextraction of lead by two accumulator ornamental species. Chemosphere 227:561–569
Manzoor M, Gul I, Kallerhoff J, Arshad M (2019c) Fungi-assisted phytoextraction of lead: tolerance, plant growth–promoting activities and phytoavailability. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(23):23788–23797
Petruzzelli G, Pedron F, Rosellini I, Barbafieri M (2015) The bioavailability processes as a keyto evaluate phytoremediation efficiency. In: Phytoremediation. Springer, Cham 1: 31–43
Pourrut B, Shahid M, Dumat C, Winterton P, Pinelli E. (2011). Lead uptake, toxicity, and detoxification in plants. In: Reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology. Springer, New York, 213: 113–136
Shahid M (2010) Lead-induced toxicity to Vicia faba L. in relation with metal cell uptake and speciation. PhD thesis, INP-ENSAT, University of Toulouse, Toulouse-FRANCE
Shahid M, Pinelli E, Pourrut B, Dumat C (2014) Effect of organic ligands on lead-induced oxidative damage and enhanced antioxidant defense in the leaves of Vicia faba plants. Journal of Geochemical Exploration 144:282–289
Shahid M, Shamshad S, Rafiq M, Khalid S, Bibi I, Niazi NK, Dumat C, Rashid MI (2017) Chromium speciation, bioavailability, uptake, toxicity and detoxification in soil-plant system: a review. Chemosphere 178:513–533
Sun X, Zhou Y, Tan Y, Wu Z, Lu P, Zhang G, Yu F (2018) Restoration with pioneer plants changes soil properties and remodels the diversity and structure of bacterial communities in rhizosphere and bulk soil of copper mine tailings in Jiangxi Province, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int:1–14
Wierzbicka MH, Przedpełska E, Ruzik R, Ouerdane L, Połeć-Pawlak K, Jarosz M, Szpunar J, Szakiel A (2007) Comparison of the toxicity and distribution of cadmium and lead in plant cells. Protoplasma 231(1-2):99–111
Yu Q, Tian H, Yue K, Liu J, Zhang B, Li X, Ding Z (2016) A P-loop NTPase regulates quiescent center cell division and distal stem cell identity through the regulation of ROS homeostasis in Arabidopsis root. PLoS Genet 12(9):e1006175
Zhan J, Li T, Zhang X, Yu H, Zhao L (2018) Rhizosphere characteristics of phytostabilizer Athyrium wardii (hook.) involved in cd and Pb accumulation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:892–900
Funding
This work is a part of international collaborative research project (#1–1/PERIDOT/R&D/HEC/201, jointly funded by HEC, Pakistan, and Campus France. The technical support was provided by National University of Sciences and Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Elena Maestri
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1782 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manzoor, M., Gul, I., Manzoor, A. et al. Lead availability and phytoextraction in the rhizosphere of Pelargonium species. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 39753–39762 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08226-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08226-0