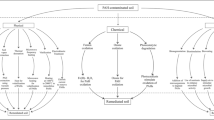
Abstract
The study of the soil microbial community represents an important step in better understanding the environmental context. Therefore, biological characterisation and physicochemical integration are keys when defining contaminated sites. Fungi play a fundamental role in the soil, by providing and supporting ecological services for ecosystems and human wellbeing. In this research, 52 soil fungal taxa were isolated from in situ pilot reactors installed to a contaminated site in Czech Republic with a high concentration of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH). Among the identified isolates, 12 strains were selected to evaluate their tolerance to different isomers of HCH by using specific indices (Rt:Rc; T.I.) and to test their potential in xenobiotic biotransformation. Most of the selected taxa was not significantly affected by exposure to HCH, underlining the elevated tolerance of all the tested fungal taxa, and different metabolic intermediates of HCH dechlorination were observed. The oxidative stress responses to HCH for two selected species, Penicillium simplicissimum and Trichoderma harzianum, were investigated in order to explore their toxic responses and to evaluate their potential functioning in bioremediation of contaminated environments. This research suggests that the isolated fungal species may provide opportunities for new eco-friendly, integrated and cost-effective solutions for environmental management and remediation, considering their efficient adaptation to stressful conditions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abarenkov K, Henrik Nilsson R, Larsson K-H, Alexander IJ, Eberhardt U, Erland S, Høiland K, Kjøller R, Larsson E, Pennanen T, Sen R, Taylor AFS, Tedersoo L, Ursing BM, Vrålstad T, Liimatainen K, Peintner U, Kõljalg U (2010) The UNITE database for molecular identification of fungi - recent updates and future perspectives: letters. New Phytol 186:281–285. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.03160.x
Adams GO, Fufeyin PT, Okoro SE, Ehinomen I (2015) Bioremediation, biostimulation and bioaugmention: a review. Int J Environ Bioremediat Biodegrad 3:28–39. https://doi.org/10.12691/ijebb-3-1-5
Alkan N, Espeso EA, Prusky D (2013) Virulence regulation of phytopathogenic fungi by pH. Antioxid Redox Signal 19:1012–1025. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2012.5062
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997). Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Research, 25:3389-3402. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.17.3389
Alvarenga N, Birolli WG, Seleghim MHR, Porto ALM (2014) Biodegradation of methyl parathion by whole cells of marine-derived fungi Aspergillus sydowii and Penicillium decaturense. Chemosphere 117:47–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.05.069
Anastasi A, Tigini V, Varese GC (2013) The bioremediation potential of different ecophysiological groups of fungi. In: Goltapeh EM, Danesh YR, Varma A (eds) Fungi as bioremediators, Soil Biology, vol 32. Springer, Berlin, pp 29–49. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-33811-3_2
Angelova MB, Pashova SB, Spasova BK, Vassilev SV, Slokoska LS (2005) Oxidative stress response of filamentous fungi induced by hydrogen peroxide and paraquat. Mycol Res 109:150–158. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0953756204001352
Argumedo-Delira R, Alarcón A, Ferrera-Cerrato R, Almaraz JJ, Peña-Cabriales JJ (2012) Tolerance and growth of 11 Trichoderma strains to crude oil, naphthalene, phenanthrene and benzo[a]pyrene. J Environ Manag 95:S291–S299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.08.011
Asemoloye MD, Ahmad R, Jonathan SG (2017) Synergistic rhizosphere degradation of γ-hexachlorocyclohexane (lindane) through the combinatorial plant-fungal action. PLoS One 12:e0183373. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0183373
Ashraf MA (2017) Persistent organic pollutants (POPs): a global issue, a global challenge. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:4223–4227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5225-9
Awasthi AK, Pandey AK, Khan J (2017) A preliminary report of indigenous fungal isolates from contaminated municipal solid waste site in India. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:8880–8888. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8472-0
Bai Z, Harvey LM, McNeil B (2003) Oxidative stress in submerged cultures of fungi. Crit Rev Biotechnol 23:267–302. https://doi.org/10.1080/07388550390449294
Benoit-Guyod J-L, Seigle-Murandi F, Steiman R, Sage L, Toe A (1994) Biodegradation of pentachlorophenol by micromycetes. III. Deuteromycetes. Environ Toxicol Water Qual 9:33–44. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.2530090106
Borgå K, Gabrielsen G, Skaare J (2001) Biomagnification of organochlorines along a Barents Sea food chain. Environ Pollut 113:187–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(00)00171-8
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Caicedo P, Schröder A, Ulrich N, Schröter U, Paschke A, Schüürmann G, Ahumada I, Richter P (2011) Determination of lindane leachability in soil–biosolid systems and its bioavailability in wheat plants. Chemosphere 84:397–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.03.070
Camacho-Pérez B, Ríos-Leal E, Rinderknecht-Seijas N, Poggi-Varaldo HM (2012) Enzymes involved in the biodegradation of hexachlorocyclohexane: a mini review. J Environ Manag 95:S306–S318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2011.06.047
Ceci A, Pierro L, Riccardi C, Pinzari F, Maggi O, Persiani AM, Gadd GM, Petrangeli Papini M (2015a) Biotransformation of β-hexachlorocyclohexane by the saprotrophic soil fungus Penicillium griseofulvum. Chemosphere 137:101–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.05.074
Ceci A, Rhee YJ, Kierans M, Hillier S, Pendlowski H, Gray N, Persiani AM, Gadd GM (2015b) Transformation of vanadinite [Pb5(VO4)3Cl] by fungi: fungal biotransformation of vanadinite. Environ Microbiol 17:2018–2034. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.12612
Ceci A, Pinzari F, Riccardi C, Maggi O, Pierro L, Petrangeli Papini M, Gadd GM, Persiani AM (2018) Metabolic synergies in the biotransformation of organic and metallic toxic compounds by a saprotrophic soil fungus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:1019–1033. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8614-9
Chakraborty S, Mukherjee A, Das TK (2013) Biochemical characterization of a lead-tolerant strain of Aspergillus foetidus: an implication of bioremediation of lead from liquid media. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 84:134–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2012.05.031
Chen R, Zhou Z, Liu Y, Jiang J, Li Q, Song H, Pei D, Xu H (2015) Mycoremediation potential and tolerance responses of Oudemansiella radicata in cadmium-pyrene co-contaminated soil. J Soils Sediments 15:1083–1093. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1093-7
Czaplicki LM, Cooper E, Ferguson PL, Stapleton HM, Vilgalys R, Gunsch CK (2016) A new perspective on sustainable soil remediation-case study suggests novel fungal genera could facilitate in situ biodegradation of hazardous contaminants: a new perspective on sustainable soil remediation. Remediat J 26:59–72. https://doi.org/10.1002/rem.21458
D’Annibale A, Rosetto F, Leonardi V et al (2006) Role of autochthonous filamentous fungi in bioremediation of a soil historically contaminated with aromatic hydrocarbons. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:28–36. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.72.1.28-36.2006
Deshmukh R, Khardenavis AA, Purohit HJ (2016) Diverse metabolic capacities of fungi for bioremediation. Indian J Microbiol 56:247–264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-016-0584-6
Diez M (2010) Biological aspects involved in the degradation of organic pollutants. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 10:244–267
Domsch KH, Gams W, Anderson T-H (2007) Compendium of soil fungi, 2. ed., taxonomically rev. IHW-Verl, Eching
Druzhinina IS, Kopchinskiy AG, Komoń M, Bissett J, Szakacs G, Kubicek CP (2005) An oligonucleotide barcode for species identification in Trichoderma and Hypocrea. Fungal Genet Biol 42:813–828. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2005.06.007
du Jardin P (2015) Plant biostimulants: definition, concept, main categories and regulation. Sci Hortic 196:3–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2015.09.021
Ellis MB (1976) More dematiaceous hyphomycetes. Commonwealth Mycological Institute, Kew
Emri T, Pócsi I, Szentirmai A (1997) Glutathione metabolism and protection against oxidative stress caused by peroxides in Penicillium chrysogenum. Free Radic Biol Med 23:809–814. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0891-5849(97)00065-8
Erguven GO (2018) Comparison of some soil fungi in bioremediation of herbicide acetochlor under agitated culture media. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 100:570–575. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2280-1
Esterhuizen-Londt M, Hendel A-L, Pflugmacher S (2017) Mycoremediation of diclofenac using Mucor hiemalis. Toxicol Environ Chem 99:795–808. https://doi.org/10.1080/02772248.2017.1296444
Fernandes JP, Guiomar N (2018) Nature-based solutions: the need to increase the knowledge on their potentialities and limits. Land Degrad Dev 29:1925–1939. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.2935
Gadd GM (2001) Fungi in bioremediation. Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge
Galdiero E, Siciliano A, Maselli V, Gesuele R, Guida M, Fulgione D, Galdiero S, Lombardi L, Falanga A (2016) An integrated study on antimicrobial activity and ecotoxicity of quantum dots and quantum dots coated with the antimicrobial peptide indolicidin. Int J Nanomedicine 11:4199–4211. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S107752
Galdiero E, Falanga A, Siciliano A, Maselli V, Guida M, Carotenuto R, Tussellino M, Lombardi L, Benvenuto G, Galdiero S (2017) Daphnia magna and Xenopus laevis as in vivo models to probe toxicity and uptake of quantum dots functionalized with gH625. Int J Nanomedicine 12:2717–2731. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S127226
Gams W, Dingley JM (2006) Hypocrea and Trichoderma studies marking the 90th birthday of Joan M. Dingley. CBS, Centraalbureau voor Schimmelcultures, Utrecht
Giraud F, Guiraud P, Kadri M, Blake G, Steiman R (2001) Biodegradation of anthracene and fluoranthene by fungi isolated from an experimental constructed wetland for wastewater treatment. Water Res 35:4126–4136. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00137-3
Giri K, Rawat AP, Rawat M, Rai JPN (2014) Biodegradation of hexachlorocyclohexane by two species of Bacillus isolated from contaminated soil. Chem Ecol 30:97–109. https://doi.org/10.1080/02757540.2013.844795
Glass NL, Donaldson GC (1995) Development of primer sets designed for use with the PCR to amplify conserved genes from filamentous ascomycetes. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:1323–1330
Godoy P, Reina R, Calderón A, Wittich RM, García-Romera I, Aranda E (2016) Exploring the potential of fungi isolated from PAH-polluted soil as a source of xenobiotics-degrading fungi. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:20985–20996. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7257-1
Gonçalves MS (2012) Isolation of filamentous fungi present in swine wastewater that are resistant and with the ability to remove atrazine. Afr J Biotechnol 11:11074–11077. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB11.4018
Groudeva VI, Groudev SN, Doycheva AS (2001) Bioremediation of waters contaminated with crude oil and toxic heavy metals. Int J Miner Process 62:293–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-7516(00)00060-0
Gu B, Phelps TJ, Liang L, Dickey MJ, Roh Y, Kinsall BL, Palumbo AV, Jacobs GK (1999) Biogeochemical dynamics in zero-valent iron columns: implications for permeable reactive barriers. Environ Sci Technol 33:2170–2177. https://doi.org/10.1021/es981077e
Guillén-Jiménez F de M, Cristiani-Urbina E, Cancino-Díaz JC et al (2012) Lindane biodegradation by the Fusarium verticillioides AT-100 strain, isolated from Agave tequilana leaves: kinetic study and identification of metabolites. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 74:36–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2012.04.020
Gurung B, Race M, Fabbricino M, Komínková D, Libralato G, Siciliano A, Guida M (2018) Assessment of metal pollution in the Lambro Creek (Italy). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:754–762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.11.041
Gururajan K, Belur PD (2018) Screening and selection of indigenous metal tolerant fungal isolates for heavy metal removal. Environ Technol Innov 9:91–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2017.11.001
Harms H, Schlosser D, Wick LY (2011) Untapped potential: exploiting fungi in bioremediation of hazardous chemicals. Nat Rev Microbiol 9:177–192. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2519
Hoagland RE, Zablotowicz RM, Hall JC (2000) Pesticide metabolism in plants and microorganisms: an overview. In: Hall JC, Hoagland RE, Zablotowicz RM (eds) Pesticide biotransformation in plants and microorganisms: similarities and divergences, ACS Symposium Series, vol 777. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, pp 2–27. https://doi.org/10.1021/bk-2001-0777.ch001
Hu W, Wang T, Khim JS, Luo W, Jiao W, Lu Y, Naile JE, Chen C, Zhang X, Giesy JP (2010) HCH and DDT in sediments from marine and adjacent riverine areas of North Bohai Sea, China. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 59:71–79. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-009-9455-z
Hussain S, Arshad M, Springael D, SøRensen SR, Bending GD, Devers-Lamrani M, Maqbool Z, Martin-Laurent F (2015) Abiotic and biotic processes governing the fate of phenylurea herbicides in soils: a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 45:1947–1998. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2014.1001141
Jaklitsch WM, Komon M, Kubicek CP, Druzhinina IS (2005) Hypocrea voglmayrii sp. nov. from the Austrian Alps represents a new phylogenetic clade in Hypocrea/Trichoderma. Mycologia 97:1365–1378. https://doi.org/10.1080/15572536.2006.11832743
Kanissery RG, Sims GK (2011) Biostimulation for the enhanced degradation of herbicides in soil. Appl Environ Soil Sci 2011:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/843450
Karsch-Mizrachi I, Nakamura Y, Cochrane G, on behalf of the International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration (2012) The international nucleotide sequence database collaboration. Nucleic Acids Res 40:D33–D37. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr1006
Katayama A, Matsumura F (1993) Degradation of organochlorine pesticides, particularly endosulfan, by Trichoderma harzianum. Environ Toxicol Chem 12:1059–1065. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620120612
Kawasaki L, Aguirre J (2001) Multiple catalase genes are differentially regulated in Aspergillus nidulans. J Bacteriol 183:1434–1440. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.183.4.1434-1440.2001
Kim M-J, Lee H, Choi Y-S, Kim GH, Huh NY, Lee S, Lim YW, Lee SS, Kim JJ (2010) Diversity of fungi in creosote-treated crosstie wastes and their resistance to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 97:377–387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-010-9416-6
Kõljalg U, Larsson K-H, Abarenkov K, Nilsson RH, Alexander IJ, Eberhardt U, Erland S, Høiland K, Kjøller R, Larsson E, Pennanen T, Sen R, Taylor AF, Tedersoo L, Vrålstad T, Ursing BM (2005) UNITE: a database providing web-based methods for the molecular identification of ectomycorrhizal fungi: methods. New Phytol 166:1063–1068. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2005.01376.x
Komínková D, Fabbricino M, Gurung B, Race M, Tritto C, Ponzo A (2018) Sequential application of soil washing and phytoremediation in the land of fires. J Environ Manag 206:1081–1089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.11.080
Kreiner M, Harvey LM, McNeil B (2002) Oxidative stress response of a recombinant Aspergillus niger to exogenous menadione and H2O2 addition. Enzym Microb Technol 30:346–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0229(01)00517-8
Kulshreshtha S, Mathur N, Bhatnagar P (2014) Mushroom as a product and their role in mycoremediation. AMB Express 4:29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-014-0029-8
Leitão AL (2009) Potential of Penicillium species in the bioremediation field. Int J Environ Res Public Health 6:1393–1417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph6041393
Li Q, McNeil B, Harvey LM (2008) Adaptive response to oxidative stress in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus niger B1-D. Free Radic Biol Med 44:394–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.09.019
Lushchak VI (2011) Adaptive response to oxidative stress: bacteria, fungi, plants and animals. Comp Biochem Physiol Part C Toxicol Pharmacol 153:175–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2010.10.004
Maggi O, Persiani AM, Casado MA, Pineda FD (2005) Effects of elevation, slope position and livestock exclusion on microfungi isolated from soils of Mediterranean grasslands. Mycologia 97:984–995. https://doi.org/10.3852/mycologia.97.5.984
Malloch D, Cain RF (1971) New cleistothecial Sordariaceae and a new family, Coniochaetaceae. Can J Bot 49:869–880. https://doi.org/10.1139/b71-127
Maqbool Z, Hussain S, Imran M, Mahmood F, Shahzad T, Ahmed Z, Azeem F, Muzammil S (2016) Perspectives of using fungi as bioresource for bioremediation of pesticides in the environment: a critical review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:16904–16925. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7003-8
Marco-Urrea E, García-Romera I, Aranda E (2015) Potential of non-ligninolytic fungi in bioremediation of chlorinated and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. New Biotechnol 32:620–628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2015.01.005
Marr J, Kremer S, Sterner O, Anke H (1996) Transformation and mineralization of halophenols by Penicillium simplicissimum SK9117. Biodegradation 7:165–171. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00114628
Martens R (1976) Degradation of [8,9,-14C]endosulfan by soil microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol 31:853–858
Montibus M, Pinson-Gadais L, Richard-Forget F, Barreau C, Ponts N (2015) Coupling of transcriptional response to oxidative stress and secondary metabolism regulation in filamentous fungi. Crit Rev Microbiol 41:295–308. https://doi.org/10.3109/1040841X.2013.829416
Morillo E, Villaverde J (2017) Advanced technologies for the remediation of pesticide-contaminated soils. Sci Total Environ 586:576–597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.020
Mougin C, Pericaud C, Malosse C, Laugero C, Asther M (1996) Biotransformation of the insecticide lindane by the white rot basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Pestic Sci 47:51–59. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1096-9063(199605)47:1<51::AID-PS391>3.0.CO;2-V
Mrema EJ, Rubino FM, Brambilla G, Moretto A, Tsatsakis AM, Colosio C (2013) Persistent organochlorinated pesticides and mechanisms of their toxicity. Toxicology 307:74–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2012.11.015
Nadal M, Marquès M, Mari M, Domingo JL (2015) Climate change and environmental concentrations of POPs: a review. Environ Res 143:177–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2015.10.012
Nagata Y, Endo R, Ito M et al (2007) Aerobic degradation of lindane (γ-hexachlorocyclohexane) in bacteria and its biochemical and molecular basis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76:752. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-1066-x
Nawab A, Aleem A, Malik A (2003) Determination of organochlorine pesticides in agricultural soil with special reference to gamma-HCH degradation by Pseudomonas strains. Bioresour Technol 88:41–46
Persiani AM, Maggi O, Montalvo J, Casado MA, Pineda FD (2008) Mediterranean grassland soil fungi: patterns of biodiversity, functional redundancy and soil carbon storage. Plant Biosyst 142:111–119. https://doi.org/10.1080/11263500701872713
Phillips TM, Seech AG, Lee H, Trevors JT (2005) Biodegradation of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) by microorganisms. Biodegradation 16:363–392. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-004-2413-6
Pitt JI (1979) The genus Penicillium and its teleomorphic states Eupenicillium and Talaromyces. Academic Press, London
Prasad R (ed) (2017) Mycoremediation and environmental sustainability. Springer International Publishing, Cham
Råberg U, Terziev N, Daniel G (2013) Degradation of Scots pine and beech wood exposed in four test fields used for testing of wood preservatives. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 79:20–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2012.12.010
Ramirez C, Martinez AT (1982) Manual and atlas of the Penicillia. Elsevier Biomedical Press ; Sole distributors for the USA and Canada, Elsevier/North-Holland, Amsterdam ; New York : New York, N.Y
Roze LV, Chanda A, Linz JE (2011) Compartmentalization and molecular traffic in secondary metabolism: a new understanding of established cellular processes. Fungal Genet Biol 48:35–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2010.05.006
Russell JR, Huang J, Anand P, Kucera K, Sandoval AG, Dantzler KW, Hickman DS, Jee J, Kimovec FM, Koppstein D, Marks DH, Mittermiller PA, Núñez SJ, Santiago M, Townes MA, Vishnevetsky M, Williams NE, Vargas MPN, Boulanger LA, Bascom-Slack C, Strobel SA (2011) Biodegradation of polyester polyurethane by endophytic fungi. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:6076–6084. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00521-11
Russo D, Siciliano A, Guida M, Galdiero E, Amoresano A, Andreozzi R, Reis NM, Li Puma G, Marotta R (2017) Photodegradation and ecotoxicology of acyclovir in water under UV254 and UV254/H2O2 processes. Water Res 122:591–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.06.020
Saez JM, Alvarez A, Fuentes MS, Amoroso MJ, Benimeli CS (2017) An overview on microbial degradation of lindane. In: Singh SN (ed) Microbe-induced degradation of pesticides. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 191–212
Salam JA, Das N (2014) Lindane degradation by Candida VITJzN04, a newly isolated yeast strain from contaminated soil: kinetic study, enzyme analysis and biodegradation pathway. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30:1301–1313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-013-1551-6
Salam JA, Lakshmi V, Das D, Das N (2013) Biodegradation of lindane using a novel yeast strain, Rhodotorula sp. VITJzN03 isolated from agricultural soil. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 29:475–487. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-012-1201-4
Samuels GJ, Hebbar PK (2015) Trichoderma: identification and agricultural applications. APS Press, St. Paul, Minn
Scherer MM, Richter S, Valentine RL, Alvarez PJJ (2000) Chemistry and microbiology of permeable reactive barriers for in situ groundwater clean up. Crit Rev Microbiol 26:221–264. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408410091154237
Scheringer M (2004) Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in the focus of science and politics. Environ Sci Pollut Res 11:1–2. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02980278
Sheoran AS, Sheoran V (2006) Heavy metal removal mechanism of acid mine drainage in wetlands: acritical review. Miner Eng 19:105–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2005.08.006
Sherif A, Elhussein A (2011) Biodegradation of fungicide Thiram (TMTD) in soil under laboratory conditions. Am J Biotechnol Mol Sci 1:57–68. https://doi.org/10.5251/ajbms.2011.1.2.57.68
Siddique T, Okeke BC, Arshad M, Frankenberger WT (2003) Biodegradation kinetics of endosulfan by Fusarium ventricosum and a Pandoraea species. J Agric Food Chem 51:8015–8019. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf030503z
Singh H (2006) Mycoremediation: fungal bioremediation. Wiley, Hoboken
Singh SN (2017) Microbe-induced degradation of pesticides. Springer International Publishing, Cham
Singh BK, Kuhad RC (1999) Biodegradation of lindane (γ-hexachlorocyclohexane) by the white-rot fungus Trametes hirsutus. Lett Appl Microbiol 28:238–241. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2672.1999.00508.x
Singh BK, Kuhad RC (2000) Degradation of insecticide lindane (γ-HCH) by white-rot fungi Cyathus bulleri and Phanerochaete sordida. Pest Manag Sci 56:142–146. https://doi.org/10.1002/1526-4998(200002)56:2<142::AID-PS104>3.0.CO;2-I
Słaba M, Różalska S, Bernat P, Szewczyk R, Piątek MA, Długoński J (2015) Efficient alachlor degradation by the filamentous fungus Paecilomyces marquandii with simultaneous oxidative stress reduction. Bioresour Technol 197:404–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.08.045
Spina F, Cecchi G, Landinez-Torres A, Pecoraro L, Russo F, Wu B, Cai L, Liu XZ, Tosi S, Varese GC, Zotti M, Persiani AM (2018) Fungi as a toolbox for sustainable bioremediation of pesticides in soil and water. Plant Biosyst 152:474–488. https://doi.org/10.1080/11263504.2018.1445130
Srivastava S, Thakur IS (2006) Evaluation of bioremediation and detoxification potentiality of Aspergillus niger for removal of hexavalent chromium in soil microcosm. Soil Biol Biochem 38:1904–1911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.12.016
Szewczyk R, Kuśmierska A, Bernat P (2018) Ametryn removal by Metarhizium brunneum: biodegradation pathway proposal and metabolic background revealed. Chemosphere 190:174–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.10.011
Taşeli BK (2006) Dehalogenation of lindane by Penicillium camemberti. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 77:882–887. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-006-1226-1
Tripathi P, Singh PC, Mishra A, Chauhan PS, Dwivedi S, Bais RT, Tripathi RD (2013) Trichoderma: a potential bioremediator for environmental clean up. Clean Techn Environ Policy 15:541–550. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-012-0553-7
Tu CM (1994) Effects of herbicides and fumigants on microbial activities in soil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 53:12–17
Ulčnik A, Kralj Cigić I, Zupančič-Kralj L et al (2012) Bioremediation of lindane by wood-decaying fungi. Drv Ind 63:271–276
Verdin A, Sahraoui AL-H, Durand R (2004) Degradation of benzo[a]pyrene by mitosporic fungi and extracellular oxidative enzymes. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 53:65–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2003.12.001
Vidali M (2001) Bioremediation. An overview. Pure Appl Chem 73:1163–1172. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac200173071163
Vijgen J, Abhilash PC, Li Y et al (2011) Hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) as new Stockholm Convention POPs—a global perspective on the management of lindane and its waste isomers. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18:152–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-010-0417-9
von Arx JA, Müller E (1975) A re-evaluation of the bitunicate ascomycetes with keys to families and genera. Stud Mycol 9:1–159
Wacławek S, Antoš V, Hrabák P, Černík M, Elliott D (2016) Remediation of hexachlorocyclohexanes by electrochemically activated persulfates. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:765–773. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5312-y
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ (eds) PCR Protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Academic Press, New York, pp 315–322
Yu KSH, Wong AHY, Yau KWY, Wong YS, Tam NFY (2005) Natural attenuation, biostimulation and bioaugmentation on biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in mangrove sediments. Mar Pollut Bull 51:1071–1077. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2005.06.006
Zabielska-Matejuk J, Czaczyk K (2006) Biodegradation of new quaternary ammonium compounds in treated wood by mould fungi. Wood Sci Technol 40:461–475. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-005-0065-2
Zhao R, Bao H, Liu Y (2010) Isolation and characterization of Penicillium oxalicum ZHJ6 for biodegradation of methamidophos. Agric Sci China 9:695–703. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1671-2927(09)60145-0
Acknowledgements
We greatly thank Dr. Flavia Pinzari for her precious support in the genetic analysis and bioinformatics. M. Cernik thanks the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic and the European Union - European Structural and Investment Funds in the frames of Operational Programme Research, Development and Education - project Hybrid Materials for Hierarchical Structures (HyHi, Reg. No. CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/16_019/0000843).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Russo, F., Ceci, A., Maggi, O. et al. Understanding fungal potential in the mitigation of contaminated areas in the Czech Republic: tolerance, biotransformation of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) and oxidative stress analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 24445–24461 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05679-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05679-w