Abstract
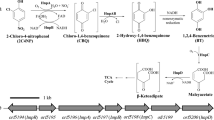
γ-Hexachlorocyclohexane (γ-HCH, also called γ-BHC and lindane) is a halogenated organic insecticide that causes serious environmental problems. The aerobic degradation pathway of γ-HCH was extensively revealed in bacterial strain Sphingobium japonicum (formerly Sphingomonas paucimobilis) UT26. γ-HCH is transformed to 2,5-dichlorohydroquinone through sequential reactions catalyzed by LinA, LinB, and LinC, and then 2,5-dichlorohydroquinone is further metabolized by LinD, LinE, LinF, LinGH, and LinJ to succinyl-CoA and acetyl-CoA, which are metabolized in the citrate/tricarboxylic acid cycle. In addition to these catalytic enzymes, a putative ABC-type transporter system encoded by linKLMN is also essential for the γ-HCH utilization in UT26. Preliminary examination of the complete genome sequence of UT26 clearly demonstrated that lin genes for the γ-HCH utilization are dispersed on three large circular replicons with sizes of 3.5 Mb, 682 kb, and 191 kb. Nearly identical lin genes were also found in other HCH-degrading bacterial strains, and it has been suggested that the distribution of lin genes is mainly mediated by insertion sequence IS6100 and plasmids. Recently, it was revealed that two dehalogenases, LinA and LinB, have variants with small number of amino acid differences, and they showed dramatic functional differences for the degradation of HCH isomers, indicating these enzymes are still evolving at high speed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basta T, Keck A, Klein J, Stolz A (2004) Detection and characterization of conjugative degradative plasmids in xenobiotic-degrading Sphingomonas strains. J Bacteriol 186:3862–3872
Bohac M, Nagata Y, Prokop Z, Prokop M, Monincova M, Tsuda M, Koca J, Damborsky J (2002) Halide-stabilizing residues of haloalkane dehalogenases studied by quantum mechanic calculations and site-directed mutagenesis. Biochemistry 41:14272–14280
Boltner D, Moreno-Morillas S, Ramos JL (2005) 16S rDNA phylogeny and distribution of lin genes in novel hexachlorocyclohexane-degrading Sphingomonas strains. Environ Microbiol 7:1329–1338
Boubakri H, Beuf M, Simonet P, Vogel TM (2006) Development of metagenomic DNA shuffling for the construction of a xenobiotic gene. Gene 375:87–94
Cai M, Xun L (2002) Organization and regulation of pentachlorophenol-degrading genes in Sphingobium chlorophenolicum ATCC 39723. J Bacteriol 184:4672–4680
Ceremonie H, Boubakri H, Mavingui P, Simonet P, Vogel TM (2006) Plasmid-encoded gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane degradation genes and insertion sequences in Sphingobium francense (ex-Sphingomonas paucimobilis Sp+). FEMS Microbiol Lett 257:243–252
Chaloupkova R, Sykorova J, Prokop Z, Jesenska A, Monincova M, Pavlova M, Tsuda M, Nagata Y, Damborsky J (2003) Modification of activity and specificity of haloalkane dehalogenase from Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26 by engineering of its entrance tunnel. J Biol Chem 278:52622–52628
Damborsky J, Rorije E, Jesenska A, Nagata Y, Klopman G, Peijnenburg WJGM (2001) Structure-specificity relationships for haloalkane dehalogenases. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:2681–2689
Dogra C, Raina V, Pal R, Suar M, Lal S, Gartemann KH, Holliger C, van der Meer JR, Lal R (2004) Organization of lin genes and IS6100 among different strains of hexachlorocyclohexane-degrading Sphingomonas paucimobilis: evidence for horizontal gene transfer. J Bacteriol 186:2225–2235
Endo T, Ikeo K, Gojobori T (1996) Large-scale search for genes on which positive selection may operate. Mol Biol Evol 13:685–690
Endo R, Kamakura M, Miyauchi K, Fukuda M, Ohtsubo Y, Tsuda M, Nagata Y (2005) Identification and characterization of genes involved in the downstream degradation pathway of γ-hexachlorocyclohexane in Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26. J Bacteriol 187:847–853
Endo R, Ohtsubo Y, Tsuda M, Nagata Y (2006) Growth inhibition by metabolites of γ-hexachlorocyclohexane in Sphingobium japonicum UT26. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 70:1029–1032
Endo R, Ohtsubo Y, Tsuda M, Nagata Y (2007) Identification and characterization of genes encoding a putative ABC-type transporter essential for the utilization of γ-hexachlorocyclohexane in Sphingobium japonicum UT26. J Bacteriol 189:3712–3720
Gil R, Silva FJ, Pereto J, Moya A (2004) Determination of the core of a minimal bacterial gene set. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 68:518–537
Hynkova K, Nagata Y, Takagi M, Damborsky J (1999) Identification of the catalytic triad in the haloalkane dehalogenase from Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26. FEBS Lett 446:177–181
Imai R, Nagata Y, Senoo K, Wada H, Fukuda M, Takagi M, Yano K (1989) Dehydrochlorination of γ-Hexachlorocyclohexane (γ-BHC) by γ-BHC-assimilating Pseudomonas paucimobilis. Agric Biol Chem 53:2015–2017
Imai R, Nagata Y, Fukuda M, Takagi M, Yano K (1991) Molecular cloning of a Pseudomonas paucimobilis gene encoding a 17-kilodalton polypeptide that eliminates HCl molecules from γ-Hexachlorocyclohexane. J Bacteriol 173:6811–6819
Ito M, Prokop Z, Klvana M, Ohtsubo Y, Tsuda M, Damborsky J, Nagata Y (2007) Degradation of β-hexachlorocyclohexane by haloalkane dehalogenase LinB from γ-hexachlorocyclohexane-utilizing bacterium Sphingobium sp. MI1205. Arch Microbiol (in press) DOI https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-007-0251-8
Iwata H, Tanabe S, Sakai N, Tatsukawa R (1993) Distribution of persistent organochlorines in the Oceanic air and surface seawater and the role of ocean on their global transport and fate. Environ Sci Technol 27:1080–1098
Janssen DB (2004) Evolving haloalkane dehalogenases. Curr Opin Chem Biol 8:150–159
Janssen DB, Dinkla IJ, Poelarends GJ, Terpstra P (2005) Bacterial degradation of xenobiotic compounds: evolution and distribution of novel enzyme activities. Environ Microbiol 7:1868–1882
Jesenska A, Sedlacek I, Damborsky J (2000) Dehalogenation of haloalkanes by Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv and other mycobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:219–222
Jesenska A, Bartos M, Czernekova V, Rychlik I, Pavlik I, Damborsky J (2002) Cloning and expression of the haloalkane dehalogenase gene dhmA from Mycobacterium avium N85 and preliminary characterization of DhmA. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:3724–3730
Jesenska A, Pavlova M, Strouhal M, Chaloupkova R, Tesinska I, Monincova M, Prokop Z, Bartos M, Pavlik I, Rychlik I et al (2005) Cloning, biochemical properties, and distribution of mycobacterial haloalkane dehalogenases. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:6736–6745
Kmunicek J, Hynkova K, Jedlicka T, Nagata Y, Negri A, Gago F, Wade RC, Damborsky J (2005) Quantitative analysis of substrate specificity of haloalkane dehalogenase LinB from Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26. Biochemistry 44:3390–3401
Kumari R, Subudhi S, Suar M, Dhingra G, Raina V, Dogra C, Lal S, van der Meer JR, Holliger C, Lal R (2002) Cloning and characterization of lin genes responsible for the degradation of hexachlorocyclohexane isomers by Sphingomonas paucimobilis strain B90. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:6021–6028
Lal R, Dogra C, Malhotra S, Sharma P, Pal R (2006) Diversity, distribution and divergence of lin genes in hexachlorocyclohexane-degrading sphingomonads. Trends Biotechnol 24:121–130
Li YF, Scholtz MT, Van Heyst BJ (2003) Global gridded emission inventories of beta-hexachlorocyclohexane. Environ Sci Technol 37:3493–3498
Mahillon J, Chandler M (1998) Insertion sequences. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:725–774
Marek J, Vevodova J, Smatanova IK, Nagata Y, Svensson LA, Newman J, Takagi M, Damborsky J (2000) Crystal structure of the haloalkane dehalogenase from Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26. Biochemistry 39:14082–14086
Martin C, Timm J, Rauzier J, Gomez-Lus R, Davies J, Gicquel B (1990) Transposition of an antibiotic resistance element in mycobacteria. Nature 345:739–743
Miyauchi K, Suh S-K, Nagata Y, Takagi M (1998) Cloning and sequencing of a 2,5-dichlorohydroquinone reductive dehalogenase gene whose product is involved in degradation of γ-Hexachlorocyclohexane by Sphingomonas paucimobilis. J Bacteriol 180:1354–1359
Miyauchi K, Adachi Y, Nagata Y, Takagi M (1999) Cloning and sequencing of a novel type of meta-cleavage dioxygenase gene whose product is involved in the degradation of γ-hexachlorocyclohexane in Sphingomonas paucimobilis. J Bacteriol 181:6712–6719
Miyauchi K, Lee HS, Fukuda M, Takagi M, Nagata Y (2002) Cloning and characterization of linR, involved in regulation of the downstream pathway for γ-hexachlorocyclohexane degradation in Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1803–1807
Miyauchi K, Fukuda M, Tsuda M, Takagi M, Nagata Y (2005) Identification of insertion sequence from a γ-hexachlorocyclohexane degrading bacterium, Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 69:216–219
Miyazaki R, Sato Y, Ito M, Ohtsubo Y, Nagata Y, Tsuda M (2006) Complete nucleotide sequence of an exogenously isolated plasmid, pLB1, involved in γ-hexachlorocyclohexane degradation. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:6923–6933
Mohn WW, Mertens B, Neufeld JD, Verstraete W, de Lorenzo V (2006a) Distribution and phylogeny of hexachlorocyclohexane-degrading bacteria in soils from Spain. Environ Microbiol 8:60–68
Mohn WW, Garmendia J, Galvao TC, de Lorenzo V (2006b) Surveying biotransformations with a la carte genetic traps: translating dehydrochlorination of lindane (γ-hexachlorocyclohexane) into lacZ-based phenotypes. Environ Microbiol 8:546–555
Monincova M, Prokop Z, Vevodova J, Nagata Y, Damborsky J (2007) Weak activity of haloalkane dehalogenase LinB with 1,2,3-trichloropropane revealed by X-ray crystallography and microcalorimetry. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(6):2005–2008
Nagasawa S, Kikuchi R, Nagata Y, Takagi M, Matsuo M (1993a) Stereochemical analysis of γ-HCH degradation by Pseudomonas paucimobilis UT26. Chemosphere 26:1187–1201
Nagasawa S, Kikuchi R, Nagata Y, Takagi M, Matsuo M (1993b) Aerobic mineralization of γ-HCH by Pseudomonas paucimobilis UT26. Chemosphere 26:1719–1728
Nagata Y, Nariya T, Ohtomo R, Fukuda M, Yano K, Takagi M (1993a) Cloning and sequencing of a dehalogenase gene encoding an enzyme with hydrolase activity involved in the degradation of γ-hexachlorocyclohexane (γ-HCH) in Pseudomonas paucimobilis. J Bacteriol 175:6403–6410
Nagata Y, Hatta T, Imai R, Kimbara K, Fukuda M, Yano K, Takagi M (1993b) Purification and characterization of γ-hexachlorocyclohexane (γ-HCH) dehydrochlorinase (LinA) from Pseudomonas paucimobilis. Biosci Biotech Biochem 57:1582–1583
Nagata Y, Ohtomo R, Miyauchi K, Fukuda M, Yano K, Takagi M (1994) Cloning and Sequencing of a 2,5-dichloro-2,5-cyclohexadiene-1,4-diol dehydrogenase gene involved in the degradation of γ-hexachlorocyclohexane in Pseudomonas paucimobilis. J Bacteriol 176:3117–3125
Nagata Y, Miyauchi K, Damborsky J, Manova K, Ansorgova A, Takagi M (1997) Purification and characterization of haloalkane dehalogenase of a new substrate class from a γ-hexachlorocyclohexane-degrading bacterium, Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26. Appl Environ Micobiol 63:3707–3710
Nagata Y, Futamura A, Miyauchi K, Takagi M (1999a) Two different types of dehalogenase, LinA and LinB, which are involved in the γ-HCH degradation in Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26, are localized in periplasmic space without molecular processing. J Bacteriol 181:5409–5413
Nagata Y, Miyauchi K, Takagi M (1999b) Complete analysis of genes and enzymes for γ-hexachlorocyclohexane degradation in Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 23:380–390
Nagata Y, Mori K, Takagi M, Murzin AG, Damborsky J (2001) Identification of protein fold and catalytic residues of γ-hexachlorocyclohexane dehydrochlorinase LinA. Proteins 45:471–477
Nagata Y, Prokop Z, Marvanova S, Sykorova J, Monincova M, Tsuda M, Damborsky J (2003) Reconstruction of mycobacterial dehalogenase Rv2579 by cumulative mutagenesis of haloalkane dehalogenase LinB. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:2349–2355
Nagata Y, Prokop Z, Sato Y, Jerabek P, Kumar A, Ohtsubo Y, Tsuda M, Damborsky J (2005) Degradation of β-hexachlorocyclohexane by haloalkane dehalogenase LinB from Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:2183–2185
Nagata Y, Kamakura M, Endo R, Miyazaki R, Ohtsubo Y, Tsuda M (2006) Distribution of γ-hexachlorocyclohexane-degrading genes on three replicons in Sphingobium japonicum UT26. FEMS Microbiol Lett 256:112–118
Oakley AJ, Prokop Z, Bohac M, Kmunicek J, Jedlicka T, Monincova M, Kuta-Smatanova I, Nagata Y, Damborsky J, Wilce MC (2002) Exploring the structure and activity of haloalkane dehalogenase from Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26: evidence for product- and water-mediated inhibition. Biochemistry 41:4847–4855
Oakley AJ, Klvana M, Otyepka M, Nagata Y, Wilce MC, Damborsky J (2004) Crystal structure of haloalkane dehalogenase LinB from Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26 at 0.95 Å resolution: dynamics of catalytic residues. Biochemistry 43:870–878
Pavlova M, Klvana M, Jesenska A, Prokop Z, Konecna H, Sato T, Tsuda M, Nagata Y, Damborsky J (2007) The identification of catalytic pentad in the haloalkane dehalogenase DhmA from Mycobacterium avium N85: reaction mechanism and molecular evolution. J Struct Biol 157:384–392
Peisajovich SG, Rockah L, Tawfik DS (2006) Evolution of new protein topologies through multistep gene rearrangements. Nat Genet 38:168–174
Phillips TM, Seech AG, Lee H, Trevors JT (2005) Biodegradation of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) by microorganisms. Biodegradation 16:363–392
Prokop Z, Monincova M, Chaloupkova R, Klvana M, Nagata Y, Janssen DB, Damborsky J (2003) Catalytic mechanism of the haloalkane dehalogenase LinB from Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26. J Biol Chem 278:45094–45100
Prokop Z, Damborsky J, Oplustil F, Jesenska A, Nagata Y (2005) Method of detoxification of yperite by using haloalkane dehalogenases. Patent, Czech Republic, Application number: CZ 2005-352 A1
Sahu SK, Patnaik KK, Sharmila M, Sethunathan N (1990) Degradation of alpha-, beta-, and gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane by a soil bacterium under aerobic conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:3620–3622
Sato Y, Monincova M, Chaloupkova R, Prokop Z, Ohtsubo Y, Minamisawa K, Tsuda M, Damborsky J, Nagata Y (2005) Two rhizobial strains, Mesorhizobium loti MAFF303099 and Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA110, encode haloalkane dehalogenases with novel structures and substrate specificities. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:4372–4379
Sato Y, Natsume R, Tsuda M, Damborsky J, Nagata Y, Senda T (2007) Crystallization and preliminary crystallographic analysis of a haloalkane dehalogenase, DbjA, from Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA110. Acta Crystallogr F 63:294–296
Senoo K, Wada H (1989) Isolation and identification of an aerobic γ-HCH-decomposing bacterium from soil. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 35:79–87
Sharma P, Raina V, Kumari R, Malhotra S, Dogra C, Kumari H, Kohler HP, Buser HR, Holliger C, Lal R (2006) Haloalkane dehalogenase LinB is responsible for β- and δ-hexachlorocyclohexane transformation in Sphingobium indicum B90A. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:5720–5727
Streltsov VA, Prokop Z, Damborsky J, Nagata Y, Oakley A, Wilce MCJ (2003) Haloalkane dehalogenase LinB from Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26: X-ray crystallographic studies of dehalogenation of brominated substrates. Biochemistry 42:10104–10112
Suar M, Hauser A, Poiger T, Buser HR, Muller MD, Dogra C, Raina V, Holliger C, van der Meer JR, Lal R, Kohler HP (2005) Enantioselective transformation of alpha-hexachlorocyclohexane by the dehydrochlorinases LinA1 and LinA2 from the soil bacterium Sphingomonas paucimobilis B90A. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:8514–8518
Trantirek L, Hynkova K, Nagata Y, Murzin A, Ansorgova A, Sklenar V, Damborsky J (2001) Reaction mechanism and stereochemistry of γ-hexachlorocyclohexane dehydrochlorinase LinA. J Biol Chem 276:7734–7740
Vacquier VD, Lee YH (1993) Abalone sperm lysin: unusual mode of evolution of a gamete recognition protein. Zygote 1:181–196
Walker K (1999) Factors influencing the distribution of lindane and other hexachlorocyclohexanes in the environment. Environ Sci Technol 33:4373–4378
Willett K, Ulrich E, Hites R (1998) Differential toxicity and environmental fates of hexachlorocyclohexane isomers. Environ Sci Technol 32:2197–2207
Wu J, Hong Q, Han P, He J, Li S (2007) A gene linB2 responsible for the conversion of beta-HCH and 2,3,4,5,6-pentachlorocyclohexanol in Sphingomonas sp. BHC-A. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73:1097–1105
Acknowledgments
The UT26 genome sequence has been determined by National Institute of Technology and Evaluation (NITE). This work includes collaborative works with Dr. Yukari Sato and Dr. Jiri Damborsky and his colleagues. This work was supported by Grant-in-Aids from Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology and The Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries (HC-07-2323), Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagata, Y., Endo, R., Ito, M. et al. Aerobic degradation of lindane (γ-hexachlorocyclohexane) in bacteria and its biochemical and molecular basis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76, 741–752 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-1066-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-1066-x