Abstract
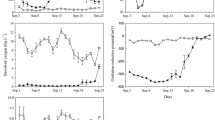
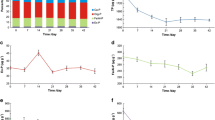
The phosphorus (P) release from bloom-cyanobacterium during its decline period is one of the most important parts involved in lake P-biogeochemical cycle, which is an important nutrient self-regulating process to sustain eutrophic status in lakes. An in situ experiment was set up to study the phosphorus release mechanisms of cyanobacterial blooms in Dianchi Lake during its decline period. In the enclosure, the cyanobacteria were dying out gradually and this process further affected the water quality parameters and lead to P release from bloom-cyanobacteria. The pH and electric conductivity (EC) increased substantially, while the redox potential (ORP) decreased during the whole experimental period. Among all the released P forms, the orthophosphate (ortho-P) was the main released P form and accounted for 96.7 and 67.8% of the total phosphorus (TP) increment in the water and the TP reduction in algae respectively. According to the TP in sediment and lost P of overlying water column, it could be concluded that the ortho-P released from algae was absorbed by sediment as well. The release of TP, organic P (OP), and ortho-P from bloom-cyanobacteria all followed the first-order kinetics, and the release rate of ortho-P was much higher than that of OP (p < 0.05). Furthermore, according to the total extracellular polysaccharide (EPS) determination and related Pearson’s correlation analysis, the release of TP and ortho-P from bloom-cyanobacteria would probably depend on the reduction of capsular polysaccharide (CPS) and colonial sheath disaggregation. In conclusion, a large amount of ortho-P was released and adsorbed by sediment gradually during cyanobacterial bloom decline period, and these bioavailable P could provide the sufficient nutrient for newborn cyanobacteria and could contribute to the construction of a new internal P cycle among sediment, water, and cyanobacterial bloom.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlgren J, Tranvik L, Gogool A et al (2005) Depth attenuation of biogenic phosphorus compounds in lake sediment measured by 31PNMR. Environ Sci Technol 39:867–872
Alam MGM, Jahan N, Thalib L, Wei B, Maekawa T (2001) Effects of environ-mental factors on the seasonally change of phytoplankton population in a closed freshwater pond. Environ Int 27:363–371
Andrieux-Loyer F, Aminot A (2001) Phosphorus forms related to sediment grain size and geochemieal characteristics in French coastal areas. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 52:617–629
Cao X, Wang YQ, He J, Luo X, Zheng Z (2016) Phosphorus mobility among sediments, water and cyanobacteria enhanced by cyanobacteria blooms in eutrophic Dianchi Lake. Environ Pollut 219:580–587
Chen WM, Cai HJ (1996) Study on the aerobic decomposition of Microcystis in Taihu Lake. J Lake Sci 8:248–252 (in Chinese)
Chuai X, Ding W, Chen X, Wang X, Miao A, Xi B, He L, Yang L (2011) Phosphorus release from cyanobacterial blooms in Meiliang Bay of Lake Taihu, China. Ecol Eng 37:842–849
Eaton AD, Clesceri LS, Rice EW et al (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. American Public Health Association, Washington
Fang T, Ao H, Chai QH et al (2004) The spatio-temporal of water environmental status in Dianchi Lake. Acta Hydrobiol Sin 28:124–130 (in Chinese)
Feng W, Zhu Y, Wu F, Meng W, Giesy JP, He Z, Song L, Fan M (2016) Characterization of phosphorus forms in lake macrophytes and algae by solution 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:7288–7297
Foree EG, McCarty PL (1970) Anaerobic decomposition of algae. Environ Sci Technol 4:842–849
Golterman H, Paing J, Serrano L, Gomez E (1998) Presence of and phosphate release from polyphosphates or phytate phosphate in lake sediments. Hydrobiologia 364:99–104
He XB, Ren LL, Lin YH, Tian X, Zhang P, Li X, Han G, Huang F (2009) Dynamics of water-extractable phosphorus during the degradation of Microcystis aeruginosa by four bacteria species. Ecol Eng 35:570–575
Hecky RE, Kilham P (1988) Nutrient limitation of phytoplankton in freshwater and marine environments: a review of recent evidence on the effects of enrichment. Limnol Oceanogr 33:796–822
Hellebust J, Craigie J (1978) Handbook of phycological methods. Physiological and Biochemical Methods. Cambridge University, Cambridge
Hu J, Shen Q, Liu YD, Liu J (2007) Mobility of different phosphorus pools in the sediment of Dianchi Lake during cyanobacterial blooms. Environ Monit Assess 132:141–153
Jewell WJ, McMarty PL (1971) Aerobic decomposition of algae. Environ Sci Technol 5:1023–1031
Liu JZ, Luo XX, Zhang NM, Wu Y (2016) Phosphorus released from sediment of Dianchi lake and its effect on growth of Microcystis aeruginosa. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:16321–16328
Liu YM, Chen W, Li DH, Shen Y, Li G, Liu Y (2006) First report of aphantoxins in China—waterblooms of toxigenic Aphanizomenon flos-aquae in Dianchi Lake. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 65:84–92
Lu R (2000) Methods of soil and agro-chemical analysis. China Agricultural Scientech Press, Beijing
Monbet P, Mckelvie I, Saefumillah A (2007) Aprotocol to assess the enzymatic release of dissolved organic phosphorus species in waters under environmentally relevant conditions. Environ Sci Technol 41:7479–7485
Murrell MC, Lores EM (2004) Phytoplankton and zooplankton seasonal dynamics in a subtropical estuary: importance of cyanobacteria. J Plankton Res 26:371–382
Osgood RA (1998) A hypothesis on the role of aphanizomenon in translocating phosphorus. Hydrobiologia 169:69–76
Otsuka S, Suda S, Li R, Matsumoto S, Watanabe MM (2000) Morphological variability of colonies of Microcystis morphospecies in culture. J Gen Appl Microbiol 46:39–50
Pereira S, Zille A, Micheletti E, Moradas-Ferreira P, de Philippis R, Tamagnini P (2009) Complexity of cyanobacterial exopolysaccharides: composition, structures, inducing factors and putative genes involved in their biosynthesis and assembly. FEMS Microbiol Rev 33:917–941
Pettersson K, Herlitz E, Istvanovics V (1993) The role of gloeotrichia-echinulata in the transfer of phosphorus from sediments to water in lake erken. Hydrobiologia 253:123–129
Reynolds CS, Jaworski GHM, Cmiech HA et al (1981) On the annual cycle of the blue-green alga Microcystis aeruginosa Kutz emend Elenkin. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 293:419–477
Rodrigues M, Oliveira A, Queiroga H, Fortunato AB, Zhang YJ (2009) Three-dimensional modeling of the lower trophic levels in the Ria de Averio (Portugal). Ecol Model 220:1274–1290
Shi X, Yang L, Niu X, Xiao L, Kong Z, Qin B, Gao G (2003) Intracellular phosphorus metabolism of Microcystis aeruginosa under various redox potential in darkness. Microbiol Res 158:345–352
Shi L, Cai Y, Kong F et al (2016) Changes in structure and element composition of mucilage sheath of Microcystis colony during the bloom decline period. J Lake Sci 28:944–950 (In Chinese)
Solidoro C, Pencenik G, Pastres R et al (1997) Modelling macroal-gae (Ulva rigida) in the Venice lagoon: model structure identification and first parameters estimation. Ecol Model 94:191–206
Spears BM, Carvalho L, Perkins R, Kirika A, Paterson DM (2012) Long-term variation and regulation of internal phosphorus loading in Loch Lenen. Hydrobiologia 681:23–33
Staats N, De Winder B, Stal LJ et al (1999) Isolation and characterization of extracellular polysaccharides from the epipelic diatoms Cylindrotheca closterium and Navicula salinarum. Eur J Phycol 34:161–169
State Environmental Protection Administration (SEPA) of China (2002) Monitor and analysis method of water and wastewater, 4th edn. Chinese Environmental Science Publication House, Beijing, pp 246–248
Sun XJ, Qin BQ, Zhu GG (2007) Release of colloidal phosphorus, nitrogen and organic carbon in the course of dying decomposing of cyanobacteria. China Environ Sci 27:341–345 (in Chinese)
Vövös L, Balogh KV, Koncz E, Konvács A (2003) Phytoplankton and bacterioplank-ton production in a reed-covered water body. Aquat Bot 77:99–110
Wu Z, Wang S, Zhang L (2016) DGT induced fluxes in sediments model for the simulation of phosphorus process and the assessment of phosphorus release risk. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:14608–14620
Xie LQ, Xie P, Tang HJ (2003) Enhancement of dissolved phosphorus release from sediment to lake water by Microcystis blooms—an enclosure experiment in a hyper-eutrophic, subtropical Chinese lake. Environ Pollut 112:391–339
Zeng S, Yuan X, Shi X, Qiu Y (2010) Effect of inoculum/substrate ratio on methane yield and orthophosphate release from anaerobic digestion of Microcystis spp. J Hazard Mater 178:89–93
Zhang R, Wang L, Wu F (2015a) Phosphorus speciation in surface sediments of a hypertrophic lake, southwestern China: insights from fractionation and 31P NMR. Chin J Geochem 34:167–176
Zhang Z, Wang H, Zhou J, Li H, He Z, van Nostrand JD, Wang Z, Xu X (2015b) Redox potential and microbial functional gene diversity in wetland sediments under simulated warming conditions: implications for phosphorus mobilization. Hydrobiologia 743:221–235
Zhu Y, Wu F, He Z, Guo J, Qu X, Xie F, Giesy JP, Liao H, Guo F (2013) Characterization of organic phosphorus in lake sediments by sequential fractionation and enzymatic hydrolysis. Environ Sci Technol 47:7679–7687
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Science Fund of China (51468066) and Project of Science and Technology Program of Yunnan Province, China (2014FB105). We appreciate Dr. Limei Shi, Nanjing Institute of Geography and Limnology, Chinese Academy of Science, for the help with providing the scanning electron micrographs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Wang, W., Zhang, K. et al. Phosphorus release from cyanobacterial blooms during their decline period in eutrophic Dianchi Lake, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 13579–13588 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1517-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1517-1