Abstract
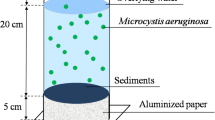
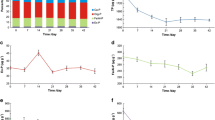
Taihu Lake, the third largest freshwater lake, is typical of many eutrophic lakes in China. In recent years, Taihu Lake is frequently suffering from extensive algal blooms which dramatically change the environmental conditions (e.g., oxygen concentration and pH) and thereafter may influence phosphorus (P) exchanges at the sediment–water interface. Here, we used the repeated ANOVA to compare the water P concentration either with or without algae addition by a mimic experiment. Over a period of 20 days of incubation, chlorophyll a (Chl-a), water temperature, dissolved oxygen (DO), oxidation–reduction potential (ORP), pH, nitrate (NO3 −), as well as the P fractions of overlying water and sediments were monitored. Results showed that compared with the Control treatment algal bloom significantly decreased DO, ORP, and pH and increased P concentration of overlying water. The first 7 days of incubation could be considered as a period of algal decomposition for the Algae treatment based on the decreased Chl-a concentration, as well as the black and smelly water. The increased total P (TP), dissolved total P (DTP), and soluble reactive P (SRP) during the initial 7 days mainly resulted from the P release from the decomposing algae when DO concentration was lower than 0.5 mg L−1, and NO3 − having a potential to suppress iron (Fe) reduction was up to 1.1 mg L−1. Subsequently, Chl-a concentration dramatically increased and reached at a maximum value on September 17, which indicated that algal growth became the dominant process. The increased P level during algal growth might result from the sediment Fe-bound P release when DO and NO3 − concentration was kept at low levels, which could be further confirmed by the lowest NaOH-extractable P (NaOH-P) in the sediments on September 19. The results indicate that influence of algal blooms on sediments P release cannot be neglected during algal decomposition as well as the followed period of algal growth in Meiliang Bay, the highly polluted region of Taihu Lake.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen JM (1982) Effect of nitrate concentration in lake water on phosphate release from the sediment. Water Res 16(7):1119–1126
Boers P (1991) The influence of pH on phosphate release from lake sediments. Water Res 25(3):309–311
Chen Y, Fan C, Teubner K, Dokulil M (2003) Changes of nutrients and phytoplankton chlorophyll-a in a large shallow lake, Taihu, China: an 8-year investigation. Hydrobiologia 506(1–3):273–279
Christophoridis C, Fytianos K (2006) Conditions affecting the release of phosphorus from surface lake sediments. J Environ Qual 35(4):1181–1192
Chuai X, Ding W, Chen X, Wang X, Miao A, Xi B, He L, Yang L (2011) Phosphorus release from cyanobacterial blooms in Meiliang Bay of Lake Taihu, China. Ecol Eng 37(6):842–849
Gao L, Zhang L, Hou J, Wei Q, Fu F, Shao H (2013) Decomposition of macroalgal blooms influences phosphorus release from the sediments and implications for coastal restoration in Swan Lake, Shandong, China. Ecol Eng 60:19–28
Garcia-Robledo E, Corzo A, Garcia de Lomas J, Van Bergeijk S (2008) Biogeochemical effects of macroalgae decomposition on intertidal microbenthos: a microcosm experiment. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 356:139–151
Gillan DC, Pede A, Sabbe K, Gao Y, Leermakers M, Baeyens W, Louriño Cabana B, Billon G (2012) Effect of bacterial mineralization of phytoplankton-derived phytodetritus on the release of arsenic, cobalt and manganese from muddy sediments in the Southern North Sea. A microcosm study. Sci Total Environ 419:98–108
Gubelit YI, Berezina NA (2010) The causes and consequences of algal blooms: the Cladophora glomerata bloom and the Neva estuary (eastern Baltic Sea). Mar Pollut Bull 61(4):183–188
Hemond HF, Lin K (2010) Nitrate suppresses internal phosphorus loading in an eutrophic lake. Water Res 44(12):3645–3650
Huang C, Li Y, Yang H, Sun D, Yu Z, Zhang Z, Chen X, Xu L (2014a) Detection of algal bloom and factors influencing its formation in Taihu Lake from 2000 to 2011 by MODIS. Environ Earth Sci 71(8):3705–3714
Huang J, Gao J, Hoermann G, Fohrer N (2014b) Modeling the effects of environmental variables on short-term spatial changes in phytoplankton biomass in a large shallow lake, Lake Taihu. Environ Earth Sci 72(9):3609–3621
Jiang X, Jin X, Yao Y, Li L, Wu F (2006) Effects of oxygen on the release and distribution of phosphorus in the sediments under the light condition. Environ Pollut 141(3):482–487
Jin X, Tu Q (1990) Standard of Lake Eutrophication Survey of China. China Environmental Science Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese)
Jin X, Wang S, Pang Y, Wu FC (2006) Phosphorus fractions and the effect of pH on the phosphorus release of the sediments from different trophic areas in Taihu Lake, China. Environ Pollut 139(2):288–295
Kim L-H, Choi E, Stenstrom MK (2003) Sediment characteristics, phosphorus types and phosphorus release rates between river and lake sediments. Chemosphere 50(1):53–61
Malhi SS, McGill WB (1982) Nitrification in three Alberta soils: effect of temperature, moisture and substrate concentration. Soil Biol Biochem 14(4):393–399
Paalme T, Kukk H, Kotta J, Orav H (2002) ‘In vitro’and ‘in situ’ decomposition of nuisance macroalgae Cladophora glomerata and Pilayella littoralis. In: Nutrients and eutrophication in estuaries and coastal waters. Springer, pp 469–476
Paerl HW, Xu H, McCarthy MJ, Zhu G, Qin B, Li Y, Gardner WS (2011) Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a hyper-eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China): the need for a dual nutrient (N & P) management strategy. Water Res 45(5):1973–1983
Qin B, Xu P, Wu Q, Luo L, Zhang Y (2007) Environmental issues of lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 581(1):3–14
Qin B, Zhu G, Gao G, Zhang Y, Li W, Paerl HW, Carmichael WW (2010) A drinking water crisis in Lake Taihu, China: linkage to climatic variability and lake management. Environ Manag 45(1):105–112
Redshaw C, Mason C, Hayes C, Roberts R (1990) Factors influencing phosphate exchange across the sediment–water interface of eutrophic reservoirs. Hydrobiologia 192(2–3):233–245
Ruban V, López-Sánchez JF, Pardo P, Rauret G, Muntau H, Quevauviller P (2001) Harmonized protocol and certified reference material for the determination of extractable contents of phosphorus in freshwater sediments—a synthesis of recent works. Fresenius J Anal Chem 370(2–3):224–228
Smith L, Watzin MC, Druschel G (2011) Relating sediment phosphorus mobility to seasonal and diel redox fluctuations at the sediment–water interface in a eutrophic freshwater lake. Limnol Oceanogr 56(6):2251–2264
Smolders A, Lamers L, Moonen M, Zwaga K, Roelofs J (2001) Controlling phosphate release from phosphate-enriched sediments by adding various iron compounds. Biogeochemistry 54(2):219–228
Søndergaard M, Jensen JP, Jeppesen E (1999) Internal phosphorus loading in shallow Danish lakes. In: Shallow Lakes’ 98. Springer, pp 145–152
Søndergaard M, Jensen JP, Jeppesen E (2003) Role of sediment and internal loading of phosphorus in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 506(1):135–145
Sørensen J (1982) Reduction of ferric iron in anaerobic, marine sediment and interaction with reduction of nitrate and sulfate. Appl Environ Microbiol 43(2):319–324
Viaroli P, Bartoli M, Bondavalli C, Christian R, Giordani G, Naldi M (1996) Macrophyte communities and their impact on benthic fluxes of oxygen, sulphide and nutrients in shallow eutrophic environments. Hydrobiologia 329(1–3):105–119
Wauer G, Gonsiorczyk T, Kretschmer K, Casper P, Koschel R (2005) Sediment treatment with a nitrate-storing compound to reduce phosphorus release. Water Res 39:494–500
Wu X, Kong F (2009) Effects of light and wind speed on the vertical distribution of Microcystis aeruginosa colonies of different sizes during a summer bloom. Int Rev Hydrobiol 94(3):258–266
Xie L, Xie P, Tang H (2003) Enhancement of dissolved phosphorus release from sediment to lake water by Microcystis blooms—an enclosure experiment in a hyper-eutrophic, subtropical Chinese lake. Environ Pollut 122(3):391–399
Xu H, Paerl HW, Qin B, Zhu G, Gao G (2010) Nitrogen and phosphorus inputs control phytoplankton growth in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Limnol Oceanogr 55(1):420–432
Yuan H, An S, Shen J, Liu E (2014) The characteristic and environmental pollution records of phosphorus species in different trophic regions of Taihu Lake, China. Environ Earth Sci 71(2):783–792
Zhang X, Chen Q (2011) Spatial-temporal characteristic of water quality in Lake Taihu and its relationship with algal bloom. J Lake Sci 23(3):339–347 (in Chinese)
Zhang X, Chen C, Ding J, Hou A, Li Y, Niu Z, Su X, Xu Y, Laws EA (2010) The 2007 water crisis in Wuxi, China: analysis of the origin. J Hazard Mater 182(1–3):130–135
Zhu M, Zhu G, Zhao L, Yao X, Zhang Y, Gao G, Qin B (2013) Influence of algal bloom degradation on nutrient release at the sediment–water interface in Lake Taihu, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 20(3):1803–1811
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation for Youth (41403102) and the National Water Pollution Control and Management Technology Major Project (2012ZX07101-013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Jiang, X., Zheng, B. et al. Effect of algal bloom on phosphorus exchange at the sediment–water interface in Meiliang Bay of Taihu Lake, China. Environ Earth Sci 75, 57 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4810-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4810-z