Abstract
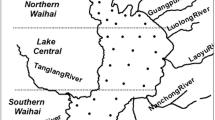
By the method of P fractionation, we examined sedimentary P fractions in Lake Dianchi before and during cyanobacterial blooms, namely in April 2004 and August 2004, respectively. In this study, the whole lake is divided into four areas to discuss P fractions in sediment and the relationship between them and water quality or the nutrient status. The results show that where the water body was much more eutrophic (higher levels of total phosphorus, total nitrogen, chlorophyll and trophic status index) in Lake Dianchi, there can be more potentially available phosphorus (BD–P and NaOH–P) and less no available phosphorus (HCl–P and residual P) in the corresponding sediments. Statistical analysis and statistical plots are used to compare the distribution of every P fraction during cyanobacterial blooms with that before cyanobacterial blooms, and the results indicate that the different P fractions had the different mobility. HCl–P and residual P were relatively stable, while NaOH–P, BD–P and NH4Cl–P were more mobile. BD–P can intensively be released from sediment to water and consequently promote cyanobacterial blooms, and at the same time the NaOH–P concentration increased in sediment, which can result from that BD–P released can be partly immobilized to NaOH–P. During cyanobacterial blooms BD–P can be as a source, but NaOH–P as a sink. Besides, total phosphorus in sediment had no significant differences between two samplings.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldock, J. A., & Skjemstad, J. O. (1999). Soil organic carbon/soil organic matter. In K. I. Peverill, L. A. Sparrow & D. J. Reuter (Eds.), Soil analysis: An interpretation manual (pp.159–170). Collingwood: CSIRO Publishing.
Boström, B., Andersen, J. M., Fleischer, S., & Jasson, M. (1988). Exchange of phosphorus across the sediment–water interface. Hydrobiologia, 170, 229–244.
Boström, B., & Pettersson, K. (1982). Different patterns of phosphorus release from lake sediments in laboratory experiments. Hydrobiologia, 92, 415–429.
Butkus, S. R., Welch, E. B., Horner, R. R., & Spyridakis, D. E. (1988). Lake response modeling using biologically available phosphorus. Journal of Water Pollution Control Federation, 60, 1663–1669.
Dorich, R. A., Nelson, D. W., & Sommers, L. E. (1980). Algal availability of sediment phosphorus in drainage water of the Black Creek watershed. Journal of Environmental Quality, 9, 557–563.
Dorich, R. A., Nelson, D. W., & Sommers, L. E. (1984). Availability of phosphorus to algal from eroded soil fraction. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 11, 253–264.
Einsele, W. (1936). ‘Über die beziehungen der Eisenkreislaufes zum Phosphorkreislauf im eutrophen See.’ Archiv fur Hydrobiologie, 29, 664–686.
Fang, T, Ao, H., Chai, Q. H., & Liu, J. T. (2004). The spatio–temporal of water environmental status in Lake Dianchi. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 28, 124–130.
Gomez, E., Fillit, M., Ximenes, M. C., & Picot, B. (1998). Phosphate mobility at the sediment–water interface of a Mediterranean lagoon (etang du Mèjean), seasonal phosphate variation. Hydrobiologia, 373, 203–216.
Gonsiorczyk, T., Casper, P., & Koschel, R. (2001). Mechanisms of phosphorus release from the bottom sediment of the oligotrophic Lake Stechlin: Importance of the permanently oxic sediment surface. Archiv fur Hydrobiologie, 151, 203–219.
Hansen, J., Reitzel, K., Jensen, H. S., & Andersen, F. Ø. (2003). Effects of aluminum, iron, oxygen and nitrate additions on phosphorus release from the sediment of a Danish softwater lake. Hydrobiologia, 492, 139–149.
Hazelton, P. A., & Murphy, B. W. (Eds.) (1992). What do all the numbers mean: A guide for the interpretation of soil test results. Sydney: NSW Department of Conservation and Land Management (incorporating the Soil Conservation Service of NSW).
Heidenreich, M., & Kleeberg, A. (2003). Phosphorus-binding in iron-rich sediments of a shallow reservoir: Spatial characterization based on sonar data. Hydrobiologia, 506, 147–153.
Holtan, H., Kamp-Nielsen, L., & Stuanes, A. D. (1988). Phosphorus in soil, water and sediment, an overview. Hydrobiologia, 170, 19–34.
Hu, J., Liu, Y. D., & Liu, J. T. (2006). The comparison of phosphorus pools from the sediment in two bays of lake Dianchi for cyanobacterial bloom assessment. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 121(1–3), 1–14.
Hupfer, M., Gächter, R., & Giovanoli, R. (1995). Transformation of phosphorus species in settling seston and during early sediment diagenesis. Aquatic Sciences, 57, 305–324.
Kaiserli, A., Voutsa, D., & Samara, C. (2002). Phosphorus fractionation in lake sediments – Lakes Volvi and Koronia, N. Greece. Chemosphere, 46, 1147–1155.
Kann, J., & Walker, W., Jr. (1999). Nutrient and hydrological loading to Upper Klamath Lake, Oregon, 1991–1998: Ashland, Oregon, Aquatic Ecosystem Sciences LLC, prepared for Klamath Tribes Natural Resources Department and the Bureau of Reclamation Cooperative Studies, 47 p. plus appendices.
Lijklema, L. (1977). The role of iron in the exchange of phosphate between water and sediments. In H. L. Golterman (Ed.), Interactions between sediments and fresh water. Proceedings of International Symposium, Amsterdam, the Netherlands. 6–10 Sept. 1976. Dr W. Junk B. V., The Hague: 313–317.
Mitchell, S. F. (1989). Primary production in a shallow eutrophic lake dominated alternately by phytoplankton and by submerged macrophytes. Aquatic Botany, 33, 101–110.
Mortimer, C. H. (1941). The exchange of dissolved substances between mud and water in lakes. Journal of Ecology, 29, 280–329.
Mortimer, C. H. (1942). The exchange of dissolved substances between mud and water in lakes. Journal of Ecology, 30, 147–201.
Paludan, C., & Jensen, H. S. (1995). Sequential extraction of phosphorus in freshwater wetland and lake sediments: Significance of humic acids. Wetlands, 15, 365–373.
Paludan, C., & Morris, J. T. (1999). Distribution and speciation of phosphorus along a salinity gradient in intertidal marsh sediments. Biogeochemistry, 45, 197–221.
Pettersson, K. (1998). Mechanisms for internal loading of phosphorus in lakes. Hydrobiologia, 373/374, 21–25.
Pettersson, K. (2001). Phosphorus characteristics of settling and suspended particles in Lake Erken. The Science of the Total Environment, 266, 79–86.
Pettersson, K., Boström, B., & Jacobsen, O. S. (1988). Phosphorus in sediments – Speciation and analysis. Hydrobiologia, 170, 91–101.
Psenner, R., Boström, B., Dinka, M., Petterson, K., Pucsko, R., & Sager, M. (1988). Fractionation of P in suspended matter and sediments. Archiv fur Hydrobiologie Beihefte Ergebnisse Limnologie, 30, 98–109.
Psenner, R., Pucsko, R., & Sager, M. (1985). Fraktionierung organischer und anorganischer Phosphorverbindungen von Sediment. Versuch einer Definition oekologisch wichtiger Fraktionen. Archives Hydrobiologia, (/Suppl.70), 111–115.
Ramm, K., & Scheps, V. (1997). Phosphorus balance of a polytropic shallow lake with consideration of phosphorus release. Hydrobiologia, 342/343, 45–53.
Rydin, E. (2000). Potentially mobile phosphorus in Lake Erken sediment. Water Research, 34, 2037–2042.
Rydin, E., & Welch, R. (1998). Aluminum dose required to inactivate P in lake sediments. Water Research, 32, 2969–2976.
Rydin, E., & Welch, R. (1999). Dosing alum to Wisconsin Lake sediments based on in vitro formation on aluminum bound phosphate. Lake and Reservoir Management, 15, 324–331.
Sharpley, A. N. (1991). Soil phosphorus extracted by iron–aluminum–oxide-impregnated filter paper. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 55, 1038–1041.
Thomas, E. A. (1973). Phosphorus and eutrophication. In E. J. Griffith, A. Beeton, J. M. Spencer, & D. T. Mitchell (Eds.), Environmental phosphorus handbook (p 630). New York, New York: Wiley.
Van Der Molen, D. T., Portielje, R., Boers, P. C. M., & Lijklema, L. (1998). Changes in sediment phosphorus as a result of eutrophication and oligotrophication in Lake Veluwe, the Netherlands. Water Research, 32, 3281–3288.
Zhou, Y. Y, Li, J. Q, Fu, Y. Q., Zhang, M. (2001). Kinetics of alkaline phosphatase in lake sediment associated with cage culture of Oreochromis niloticus. Aquaculture, 203, 23–32.
Zhou, Y. Y, Li, J. Q, Zhang, M. (2002). Temporal and spatial variations in kinetics of alkaline phosphatase in sediments of a shallow Chinese eutrophic lake (Lake Donghu). Water Research, 36, 2084–2090.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, J., Shen, Q., Liu, Y. et al. Mobility of Different Phosphorus Pools in the Sediment of Lake Dianchi during Cyanobacterial Blooms. Environ Monit Assess 132, 141–153 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-9509-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-9509-x