Abstract
Introduction
Changes in skin phenotypic characteristics are based on skin tissue. The study of the metabolic changes in skin tissue can help understand the causes of skin diseases and identify effective therapeutic interventions.
Objectives
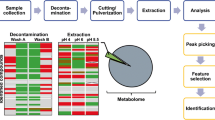
We aimed to establish and optimize a non-targeted skin metabolome extraction system for skin tissue metabolomics with high metabolite coverage, recovery, and reproducibility using gas chromatography/mass spectrometry.
Methods
The metabolites in skin tissues were extracted using eleven different extraction systems, which were designed using reagents with different polarities based on sequential solid-liquid extraction employing a two-step strategy and analyzed using gas chromatograph/mass spectrometry. The extraction efficiency of diverse solvents was evaluated by coefficient of variation (CV), multivariate analysis, metabolites coverage, and relative peak area analysis.
Results
We identified 119 metabolites and the metabolite profiles differed significantly between the eleven extraction systems. Metabolites with high abundances in the organic extraction systems, followed by aqueous extraction, were involved in the biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids, while metabolites with high abundances in the aqueous extraction systems, followed by organic extraction, were involved in amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism, and glycerolipid metabolism. MeOH/chloroform-H2O and MeOH/H2O-chloroform were the extraction systems that yielded the highest number of metabolites, while MeOH/acetonitrile (ACN)-H2O and ACN/H2O-IPA exhibited superior metabolite recoveries.
Conclusion
Our results demonstrated that our research facilitates the selection of an appropriate metabolite extraction approach based on the experimental purpose for the metabolomics study of skin tissue.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Aa, J., Wang, G., Hao, H., Huang, Q., Lu, Y., Yan, B., Zh, W., Liu, L., & Kang, A. (2010). Differential regulations of blood pressure and perturbed metabolism by total ginsenosides and conventional antihypertensive agents in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 31, 930–937. https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2010.86.
Abel, J., & Haarmann-Stemmann, T. (2010). An introduction to the molecular basics of aryl hydrocarbon receptor biology. https://doi.org/10.1515/bc.2010.128.
Anwar, M. A., Vorkas, P. A., Li, J. V., Shalhoub, J., Want, E. J., Davies, A. H., & Holmes, E. (2015). Optimization of metabolite extraction of human vein tissue for ultra performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance-based untargeted metabolic profiling. The Analyst, 140, 7586–7597. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5an01041a.
Benson, H. A. (2012). Skin structure, function, and permeation. Topical and Transdermal Drug Delivery: Principles and Practice, 1st ed.; Benson, HAE, Watkinson, AC, Eds, 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118140505.
Bu, T., Zhng, M., Lee, S. H., Cheong, Y. E., Park, Y., Kim, K. H., Kim, D., & Kim, S. (2022). GC-TOF/MS-based metabolomics for comparison of volar and non-volar skin types. Metabolites, 12, 717. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12080717.
Buszewska-Forajta, M., Patejko, M., Macioszek, S., Sigorski, D., Iżycka-Świeszewska, E., & Markuszewski, M. J. (2019). Paraffin-embedded tissue as a novel matrix in metabolomics study: Optimization of metabolite extraction method. Chromatographia, 82, 1501–1513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-019-03769-y.
Cai, Y., & Dong, Q. (2021). Metabonomics research accelerates discovery of medical biomarkers. E3S Web of Conferences, 03048. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202124503048.
Davies, T. (1998). The new automated mass spectrometry deconvolution and identification system (AMDIS). Spectroscopy Europe, 10, 24–27.
Dettmer, K., Nürnberger, N., Kaspar, H., Gruber, M. A., Almstetter, M. F., & Oefner, P. J. (2011). Metabolite extraction from adherently growing mammalian cells for metabolomics studies: Optimization of harvesting and extraction protocols. Analytical & Bioanalytical Chemistry, 399, 1127–1139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-4425-x.
Dupont, E., Gomez, J., & Bilodeau, D. (2013). Beyond UV radiation: A skin under challenge. International Journal of Cosmetic Science, 35, 224–232. https://doi.org/10.1111/ics.12036.
Foroutan, A., Fitzsimmons, C., Mandal, R., Piri-Moghadam, H., Zheng, J., Guo, A., Li, C., Guan, L. L., & Wishart, D. S. (2020). The bovine metabolome. Metabolites, 10, 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10060233.
Fritsche-Guenther, R., Bauer, A., Gloaguen, Y., Lorenz, M., & Kirwan, J. A. (2020). Modified protocol of harvesting, extraction, and normalization approaches for gas chromatography mass spectrometry-based metabolomics analysis of adherent cells grown under high fetal calf serum conditions. Metabolites, 10, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10010002.
García-Cañaveras, J. C., López, S., Castell, J. V., Donato, M. T., & Lahoz, A. (2016). Extending metabolome coverage for untargeted metabolite profiling of adherent cultured hepatic cells. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 408, 1217–1230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-9227-8.
Hu, Z. P., Kim, Y. M., Sowa, M. B., Robinson, R. J., Gao, X., Metz, T. O., Morgan, W. F., & Zhang, Q. (2012). Metabolomic response of human skin tissue to low dose ionizing radiation. Molecular BioSystems, 8, 1979–1986. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2mb25061f.
Ima, B., Song, Z. C., Iv, C., & Mvi, A. (2019). Kidney harvesting and metabolite extraction for metabolomics studies in rodents - ScienceDirect. Methods in Cell Biology, 154, 15–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.mcb.2019.05.009.
Johansson, J. A., & Headon, D. J. (2014). Regionalisation of the skin. Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology, 25–26, 3–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2013.12.007.
Kapoore, R. V., Coyle, R., Staton, C. A., Brown, N. J., & Vaidyanathan, S. (2015). Cell line dependence of metabolite leakage in metabolome analyses of adherent normal and cancer cell lines. Metabolomics, 11, 1743–1755. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-015-0833-4.
Kim, S., Lee, H., & Kim, K. H. (2018). Metabolomic elucidation of recovery of Melissa officinalis from UV-B irradiation stress. Industrial Crops and Products, 121, 428–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.05.002.
Li, B., He, X., Jia, W., & Li, H. (2017). Novel applications of metabolomics in personalized medicine: A mini-review. Molecules, 22, 1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22071173.
Lorenz, M., Fritsche-Guenther, R., Bartsch, C., Vietzke, A., Eisenberger, A., Stangl, K., Stangl, V., & Kirwan, J. A. (2023). J.I.J.o.M.S. Serum starvation accelerates intracellular metabolism in endothelial cells. 24, 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021189.
Masson, P., Alves, A. C., Ebbels, T. M., Nicholson, J. K., & Want, E. J. (2010). Optimization and evaluation of metabolite extraction protocols for untargeted metabolic profiling of liver samples by UPLC-MS. Analytical Chemistry, 82, 7779–7786. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac101722e.
Masson, P., Spagou, K., Nicholson, J. K., & Want, E. J. (2011). Technical and Biological Variation in UPLC – MS-Based untargeted metabolic profiling of liver extracts: Application in an experimental toxicity study on Galactosamine. Analytical Chemistry, 83, 1116–1123. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac103011b.
Misra, B. B., Upadhayay, R. P., Cox, L. A., & Olivier, M. (2018). Optimized GC–MS metabolomics for the analysis of kidney tissue metabolites. Metabolomics, 14, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-018-1373-5.
Morita, A., Torii, K., Maeda, A., & Yamaguchi, Y. (2009). Molecular basis of tobacco smoke-induced premature skin aging. Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings, 53–55. https://doi.org/10.1038/jidsymp.2009.13.
Naz, S., Moreira dos Santos, D. C., Garcia, A., & Barbas, C. (2014). Analytical protocols based on LC–MS, GC–MS and CE–MS for nontargeted metabolomics of biological tissues. Bioanalysis, 6, 1657–1677. https://doi.org/10.4155/bio.14.119.
Nizioł, J., Copié, V., Tripet, B. P., Nogueira, L. B., Nogueira, K. O., Ossoliński, K., Arendowski, A., & Ruman, T. (2021). Metabolomic and elemental profiling of human tissue in kidney cancer. Metabolomics, 17, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-021-01779-2.
Pasikanti, K. K., Ho, P. C., & Chan, E. C. (2008). Development and validation of a gas chromatography/mass spectrometry metabonomic platform for the global profiling of urinary metabolites. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry: An International Journal devoted to the Rapid Dissemination of Up-to‐the‐minute. Research in Mass Spectrometry, 22, 2984–2992. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcm.3699.
Peterson, A. L., Walker, A. K., Sloan, E. K., & Creek, D. J. (2016). Optimized method for untargeted metabolomics analysis of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Metabolites, 6, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo6040030.
Rinn, J. L., Bondre, C., Gladstone, H. B., Brown, P. O., & Chang, H. Y. (2006). Anatomic demarcation by positional variation in fibroblast gene expression programs. PLoS Genetics, 2, e119. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.0020119.
Rinn, J. L., Wang, J. K., Liu, H., Montgomery, K., Van De Rijn, M., & Chang, H. Y. (2008). A systems biology approach to anatomic diversity of skin. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 128, 776–782. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jid.5700986.
Salek, R., Cheng, K. K., & Griffin, J. (2011). The study of mammalian metabolism through NMR-based metabolomics, Methods in enzymology, Elsevier. pp. 337–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-385118-5.00017-7.
Sengel, P. (1990). Pattern formation in skin development. The International Journal of Developmental Biology, 34, 33–50. https://doi.org/10.1387/IJDB.2203463.
Ser, Z., Liu, X., Tang, N. N., & Locasale, J. W. (2015). Extraction parameters for metabolomics from cultured cells. Analytical Biochemistry, 475, 22–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2015.01.003.
Sévin, D. C., Kuehne, A., Zamboni, N., & Sauer, U. (2015). Biological insights through nontargeted metabolomics. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 34, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2014.10.001.
Styczynski, M. P., Moxley, J. F., Tong, L. V., Walther, J. L., Jensen, K. L., & Stephanopoulos, G. N. (2007). Systematic identification of conserved metabolites in GC/MS data for metabolomics and biomarker discovery. Analytical Chemistry, 79, 966–973. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac0614846.
Tarentini, E., Odorici, G., Righi, V., Paganelli, A., Giacomelli, L., Mirisola, V., Mucci, A., Benassi, L., D’Aversa, E., Lasagni, C., Kaleci, S., Reali, E., & Magnoni, C. (2021). Integrated metabolomic analysis and cytokine profiling define clusters of immuno-metabolic correlation in new-onset psoriasis. Scientific Reports, 11, 10472. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-89925-7.
Tsugawa, H., Tsujimoto, Y., Arita, M., Bamba, T., & Fukusaki, E. (2011). GC/MS based metabolomics: Development of a data mining system for metabolite identification by using soft independent modeling of class analogy (SIMCA). BMC Bioinformatics, 12, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-12-131.
Vierkötter, A., Schikowski, T., Ranft, U., Sugiri, D., Matsui, M., Krämer, U., & Krutmann, J. (2010). Airborne particle exposure and extrinsic skin aging. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 130, 2719–2726. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2010.204.
Vorkas, P. A., Isaac, G., Anwar, M. A., Davies, A. H., Want, E. J., Nicholson, J. K., & Holmes, E. (2015). Untargeted UPLC-MS profiling pipeline to expand tissue metabolome coverage: Application to cardiovascular disease. Analytical Chemistry, 87, 4184–4193. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac503775m.
Vorkas, P. A., Abellona, U. M., & Li, J. V. (2018). Tissue multiplatform-based Metabolomics/Metabonomics for enhanced Metabolome Coverage. Methods in Molecular Biology, 1738, 239–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7643-0_17.
Wedge, D. C., Allwood, J. W., Dunn, W., Vaughan, A. A., Simpson, K., Brown, M., Priest, L., Blackhall, F. H., Whetton, A. D., Dive, C., & Goodacre, R. (2011). Is serum or plasma more appropriate for intersubject comparisons in metabolomic studies? An assessment in patients with small-cell lung cancer. Analytical Chemistry, 83, 6689–6697. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac2012224.
Wold, S., & Sjöström, M. (1977). SIMCA: A method for analyzing chemical data in terms of similarity and analogy. ACS Publications. https://doi.org/10.1021/bk-1977-0052.ch012.
Wu, H., Southam, A. D., Hines, A., & Viant, M. R. (2008). High-throughput tissue extraction protocol for NMR-and MS-based metabolomics. Analytical Biochemistry, 372, 204–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2007.10.002.
Xu, X., Zang, Q., Zhang, R., Liu, J., He, J., Zhang, R., & Abliz, Z. (2019). Systematic optimization and evaluation of sample pretreatment methods for LC-MS-based metabolomics analysis of adherent mammalian cancer cells. Analytical Methods, 11, 3014–3022. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9AY00792J.
Xu, F., Song, C., Liu, W., & Chen, G. (2021). Protocol for intracellular and extracellular metabolite detection in human embryonic stem cells. STAR Protocols, 2, 100740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xpro.2021.100740.
Yamaguchi, Y., Itami, S., Tarutani, M., Hosokawa, K., Miura, H., & Yoshikawa, K. (1999). Regulation of keratin 9 in nonpalmoplantar keratinocytes by palmoplantar fibroblasts through epithelial-mesenchymal interactions. The Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 112, 483–488. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1747.1999.00544.x.
Yamaguchi, Y., Itami, S., Watabe, H., Yasumoto, K., Abdel-Malek, Z. A., Kubo, T., Rouzaud, F., Tanemura, A., Yoshikawa, K., & Hearing, V. J. (2004). Mesenchymal-epithelial interactions in the skin: Increased expression of dickkopf1 by palmoplantar fibroblasts inhibits melanocyte growth and differentiation. Journal of Cell Biology, 165, 275–285. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200311122.
Yamaguchi, Y., Passeron, T., Hoashi, T., Watabe, H., Rouzaud, F., Yasumoto, K., Hara, T., Tohyama, C., Katayama, I., Miki, T., & Hearing, V. J. (2008). Dickkopf 1 (DKK1) regulates skin pigmentation and thickness by affecting Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in keratinocytes. The Faseb Journal, 22, 1009–1020. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.07-9475com.
Yamaguchi, Y., Morita, A., Maeda, A., & Hearing, V. J. (2009). Regulation of skin pigmentation and thickness by Dickkopf 1 (DKK1). The Journal of Investigative Dermatology. Symposium Proceedings / the Society for Investigative Dermatology, Inc. [And] European Society for Dermatological Research, 14, 73–75. https://doi.org/10.1038/jidsymp.2009.4.
Yang, K., Lv, T., Wu, J., Zhang, X., Xue, Y., Yu, P., & Liu, Q. (2022). The Protective Effect of Electroacupuncture on the renal cortex of SHR: A metabonomic analysis. Biomedical Chromatography, e5338. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.5338.
Zarate, E., Boyle, V., Rupprecht, U., Green, S., Villas-Boas, S. G., Baker, P., & Pinu, F. R. (2016). Fully automated trimethylsilyl (TMS) derivatisation protocol for metabolite profiling by GC-MS. Metabolites, 7, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo7010001.
Zhang, T., Xu, J., Liu, Y., & Liu, J. (2019). Metabolomic profiling for identification of potential biomarkers in patients with dermatomyositis. Metabolomics, 15, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-019-1539-9.
Zhao, X., Psarianos, P., Ghoraie, L. S., Yip, K., Goldstein, D., Gilbert, R., Witterick, I., Pang, H., Hussain, A., & Lee, J. H. (2019). Metabolic regulation of dermal fibroblasts contributes to skin extracellular matrix homeostasis and fibrosis. Nature Metabolism, 1, 147–157. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-018-0008-5.
Zukunft, S., Prehn, C., Röhring, C., Möller, G., Hrabě de Angelis, M., Adamski, J., & Tokarz, J. (2018). High-throughput extraction and quantification method for targeted metabolomics in murine tissues. Metabolomics, 14, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-017-1312-x.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) for funding this work by the Young Researcher Program (number 2020R1G1A100826811).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TB and SK: conception and design, investigation, collection and assembly of data, data analysis and interpretation, writing-original draft preparation, writing-review and editing, and final approval of the manuscript. SK: project administration. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The animal experiments were conducted according to ethical guidelines for the care and use of animals, with approval from the Jeonju University Animal Experimental Ethics Committee (jjIACUC-20220610-2022-0405-B1).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bu, T., Kim, S. Development of metabolome extraction strategy for metabolite profiling of skin tissue. Metabolomics 20, 48 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-024-02120-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-024-02120-3