Abstract
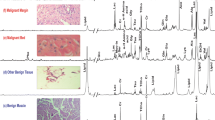
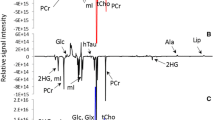
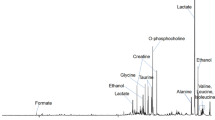
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) represents more than 90% of all head and neck cancers as reported by Hermans (Cancer Imaging, 5(Spec No A), S52–S57, 2005), which draws attention of investigative research for novel predictive metabolic biomarkers to understand the malignancy induced biochemical perturbations occurring at molecular level. In the present work, proton HR-MAS NMR spectroscopic studies have been performed on resected human oral SCC tumor tissues, its neighboring margins and bed tissues (n = 159), obtained from 36 patients (n = 27 training set; n = 9 unknown test set), for the identification of metabolic fingerprints. The proton NMR spectra were then subjected to chemometric unsupervised PCA and supervised OSC-filtered PCA and PLS-DA multivariate analysis. Application of PLS-DA on orthogonally signal corrected training data-set (n = 120 tissue specimens; 27 patients) allowed >95% correct classification of malignant tissues from benign samples with >98% specificity and sensitivity. The OSC-PLS-DA model thus constructed was used to predict the class membership of unknown tissue specimens (n = 39) obtained from nine patients. These tissue samples were correctly predicted in its respective histological categories with 97.4% diagnostic accuracy. The regression coefficients obtained from OSC-filtered PLS-DA model indicated that malignant tissues had higher levels of glutamate, choline, phosphocholine, lactate, acetate, taurine, glycine, leucine, lysine, isoleucine and alanine, and lower levels of creatine and PUFA, representing altered metabolic processes (lipidogenesis, protein synthesis, and volume regulation) during tumor progression. Thus proton HR-MAS MR spectroscopy could efficiently identify the metabolic perturbations of malignant tumor from non-malignant bed and margins tissue specimens, which may be helpful in understanding the extent of tumor penetration in neighboring tissues.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HR-MAS:
-
High resolution magic angle spinning
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- OSC:
-
Orthogonal signal correction
- PLS:
-
Partial least square
- NOESY:
-
Nuclear overhauser enhancement spectroscopy
- COSY:
-
Correlation spectroscopy
- CPMG:
-
Carr Purcell Meiboom Gill sequence
- HSQC:
-
Heteronuclear single quantum coherence
- SCC:
-
Squamous cell carcinoma
References
Baracos, V. E., & Mackenzie, M. L. (2006). Investigations of branched-chain amino acids and their metabolites in animal models of cancer. Journal of Nutrition, 136(1 Suppl), 237S–242S.
Beckwith-Hall, B. M., Brindle, J. T., Barton, R. H., et al. (2002). Application of orthogonal signal correction to minimise the effects of physical and biological variation in high resolution 1H NMR spectra of biofluids. Analyst, 127(10), 1283–1288.
Bezabeh, T., Odlum, O., Nason, R., et al. (2005). Prediction of treatment response in head and neck cancer by magnetic resonance spectroscopy. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 26(2), 2108–2113.
Bisbal, M. C. M., Bonmati, L., Piquer, J., et al. (2004). 1H and 13C HRMAS spectroscopy of intact biopsy samples ex vivo and in vivo 1H MRS study of human high grade gliomas. NMR in Biomedicine, 17(2), 191–205.
Bollard, M. E., Garrod, S., Holmes, E., et al. (2000). High-resolution (1)H and (1)H-(13)C magic angle spinning NMR spectroscopy of rat liver. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 44(2), 201–207.
Boyle, J. O., & Strong, E. W. (2001). Oral cavity cancer. London: BC Decker Inc.
Brandizzi, D., Gandolfo, M., Velazco, M. L., Cabrini, R. L., & Lanfranchi, H. E. (2008). Clinical features and evolution of oral cancer: A study of 274 cases in Buenos Aires, Argentina. Medicinia Oral, Patologia Oral y Cirugia Bucal, 13(9), E544–E548.
Brennan, J. A., Mao, L., Hruban, R. H., et al. (1995). Molecular assessment of histopathological staging in squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. New England Journal of Medicine, 332(7), 429–435.
Brindle, J. T., Antti, H., Holmes, E., et al. (2002). Rapid and noninvasive diagnosis of the presence and severity of coronary heart disease using 1H-NMR-based metabonomics. Nature Medicine, 8(12), 1439–1444.
Chan, E. C., Koh, P. K., Mal, M., et al. (2009). Metabolic profiling of human colorectal cancer using high-resolution magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance (HR-MAS NMR) spectroscopy and gas chromatography mass spectrometry (GC/MS). Journal of Proteome Research, 8(1), 352–361.
Cheng, L. L., Ma, M. J., Becerra, L., et al. (1997a). Quantitative neuropathology by high resolution magic angle spinning proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 94(12), 6408–6413.
Cheng, L. L., Ma, M. J., Becerra, L., et al. (1997b). Quantitative neuropathy by high resolution magic angle spinning proton mgnetic resonance spectroscopy. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 94, 6408–6413.
Cheng, L. L., Chang, W. I., Louis, D. N., & Gonzalez, R. G. (1998). Correlation of High-Resolution Magic Angle Spinning Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy with histopathology of Intact Human Brain Tumor Specimens. Cancer Research, 58, 1825–1832.
Cheng, L. L., Anthony, D. C., Comite, A. R., et al. (2000). Quantification of microheterogeneity in glioblastoma multiforme with ex vivo high resolution magic-angle spinning (HRMAS) proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Neuro-Oncology, 2(2), 87–95.
Cheng, L. L., Burns, M. A., Taylor, J. L., et al. (2005). Metabolic characterization of human prostate cancer with tissue magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Cancer Research, 65(8), 3030–3034.
Cohan, D. M., Popat, S., Kaplan, S. E., et al. (2009). Oropharyngeal cancer: current understanding and management. Current Opinion in Otolaryngology & Head and Neck Surgery, 17(2), 88–94.
Crain, R. C., Clark, R. W., & Harvey, B. E. (1983). Role of lipid transfer proteins in the abnormal lipid content of Morris hepatoma mitochondria and microsomes. Cancer Research, 43(7), 3197–3202.
Donnell, A., Jin, S., & Zavras, A. I. (2008). Delay in diagnosis of oral cancer. Journal of Stomatological Investigation, 2(1), 15–26.
Duarte, I. F., Stanley, E. G., Holmes, E., et al. (2005). Metabolic assessment of human liver transplants from biopsy samples at the donor and recipient stages using high-resolution magic angle spinning 1H NMR spectroscopy. Analytical Chemistry, 77(17), 5570–5578.
Facchinetti, M. M., Gandini, N. A., Fermento, M. E., et al. (2010). The expression of sphingosine kinase-1 in head and neck carcinoma. Cells, Tissues, Organs, 192(5), 314–324.
Fisher, R. A., & Yates, F. (1957). In statistical tables for biological, agricultural and medical research. London: Oliver and Boyd.
Garrod, S., Humpher, E., Connor, S. C., et al. (2001). High-resolution 1H NMR and magic angle spinning NMR spectroscopic investigation of the biochemical effects of 2-bromoethanamine in intact renal and hepatic tissue. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 45(5), 781–790.
Gavaghan, C. L., Wilson, I. D., & Nicholson, J. K. (2002). Physiological variation in metabolic phenotyping and functional genomic studies: Use of orthogonal signal correction and PLS-DA. FEBS Letters, 530(1–3), 191–196.
Green, S. B. (1991). How many subjects does it take to do a regression analysis. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 26(3), 499–510.
Griffin, J. L., & Shockcor, J. P. (2004). Metabolic profiles of cancer cells. Nature Reviews Cancer, 4(7), 551–561.
Hashibe, M., Brennan, P., Benhamou, S., et al. (2007). Alcohol drinking in never users of tobacco, cigarette, smoking in non-drinkers and the risk of head and neck cancer: pooled analysis in the International Head and Neck Cancer. Journal of the National Cancer Institiute, 99, 777–789.
Hermans, R. (2005). Oropharyngeal cancer. Cancer Imaging, 5(Spec No A), S52–S57.
Jordan, K. W., & Cheng, L. L. (2007). NMR-based metabolomics approach to target biomarkers for human prostate cancer. Expert Review of Proteomics, 4(3), 389–400.
Kao, S. Y., Chen, Y. P., Tu, H. F., et al. (2010). Nuclear STK15 expression is associated with aggressive behaviour of oral carcinoma cells in vivo and in vitro. Journal of Pathology, 222(1), 99–109.
Khandekar, S. P., Bagdey, P. S., & Tiwari, R. R. (2006). Oral cancer and some epidemiological factors: A hospital based study. Indian Journal of Community Medicine, 31(3), 157–159.
Mashberg, A., & Samit, A. (1995). Early diagnosis of asymptomatic oral and oropharyngeal squamous cancers. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 45, 328–351.
McFate, T., Mohyeldin, A., Lu, H., et al. (2008). Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex activity controls metabolic and malignant phenotype in cancer cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 283(33), 22700–22708.
Morton, R., Waite, M., Hartz, J. W., Cunningham, C., & Morris, H. P. (1977). The composition and metabolism of microsomal and mitochondrial membrane lipids in the Morris 7777 hepatoma. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 92, 381–403.
Mukherji, S. K., Schiro, S., Castillo, M., et al. (1996). Proton MR spectroscopy of squamous cell carcinoma of the upper aerodigestive tract: In vitro characteristics. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 17, 1485–1490.
Mukherji, S. K., Schiro, S., Castillo, M., et al. (1997). Proton MR spectroscopy of squamous cell carcinoma of the extracranial head and neck: in vitro and in vivo studies. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 18, 1057–1072.
Ng, S. H., Yen, T. C., Chang, J. T., et al. (2006). Prospective study of [18F] fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography and computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma with palpably negative neck. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 24(27), 4371–4376.
Norton, J. A., Shamberger, R., Stein, T. P., Milne, G. W., & Brennan, M. F. (1981). The influence of tumor-bearing on protein metabolism in the rat. Journal of Surgical Research, 30(5), 456–462.
Partridge, M., Li, S. R., Pateromichelakis, S., et al. (2000). Detection of minimal residual cancer to investigate why oral tumors recur despite seemingly adequate treatment. Clinical Cancer Research, 6(7), 2718–2725.
Podo, F. (1999). Tumor phospholipid metabolism. NMR in Biomedicine, 12, 413–439.
Rocha, C. M., Barros, A. S., Gil, A. M., et al. (2010). Metabolic profiling of human lung cancer tissue by 1H high resolution magic angle spinning (HRMAS) NMR spectroscopy. Journal of Proteome Research, 9(1), 319–332.
Rosado, J. O., Salvado, M., & Bonatto, D. (2007). Importance of the trans-sulfuration pathway in cancer prevention and promotion. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 301(1–2), 1–12.
Rzeski, W., Turski, L., & Ikonomidou, C. (2001). Glutamate antagonists limit tumor growth. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 98(11), 6372–6377.
Sayed, S. E., Bezabeh, T., Odlum, O., et al. (2002). An ex vivo study exploring the diagnostic potential of 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck region. MRS of Head and Neck Tumors, 24, 766–772.
Shen, M. R., Chou, C. Y., & Ellory, J. C. (2001). Swelling-activated taurine and K + transport in human cervical cancer cells: association with cell cycle progression. Pflugers Archiv: European Journal of Physiology, 441(6), 787–795.
Sinha, R., Anderson, D. E., McDonald, S. S., & Greenwald, P. (2003). Cancer risk and diet in India. Journal of Postgraduate Medicine, 49, 222–228.
Sitter, B., Sonnewald, U., Spraul, M., Fjosne, H. E., & Gribbestad, I. S. (2002). High-resolution magic angle spinning MRS of breast cancer tissue. NMR in Biomedicine, 15(5), 327–337.
Srivastava, S., Roy, R., Singh, S., et al. (2010). Taurine—a possible fingerprint biomarker in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: A pilot study by 1H NMR spectroscopy. Cancer Biomarkers: Section A of Disease Markers, 6(1), 11–20.
Tessem, M. B., Swanson, M. G., Keshari, K. R., et al. (2008). Evaluation of lactate and alanine as metabolic biomarkers of prostate cancer using 1H HR-MAS spectroscopy of biopsy tissues. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 60(3), 510–516.
Tugnoli, V., Mucci, A., Schenetti, L., et al. (2004). Molecular characterization of human gatric mucosa by HRMAS magnetic resonance spectroscopy. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 14, 1065–1071.
Tzika, A. A., Cheng, L. L., Goumnerova, L., et al. (2002). Biochemical characterization of pediatric brain tumors by using in vivo and ex vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Journal of Neurosurgery, 96(6), 1023–1031.
van Houten, V. M., Leemans, C. R., Kummer, J. A., et al. (2004). Molecular diagnosis of surgical margins and local recurrence in head and neck cancer patients: A prospective study. Clinical Cancer Research, 10(11), 3614–3620.
Voorhis, C. R. W. V., & Morgan, B. L. (2007). Understanding power and rules of thumb for determining sample sizes. Tutorials in Quantitative Methods for Psychology, 3(2), 43–50.
Wang, Y., Bollard, M. E., Keun, H., et al. (2003). Spectral editing and pattern recognition methods applied to high-resolution magic-angle spinning 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of liver tissues. Analytical Biochemistry, 323(1), 26–32.
Wang, Y., Bollard, M. E., Nicholson, J. K., & Holmes, E. (2006). Exploration of the direct metabolic effects of mercury II chloride on the kidney of Sprague-Dawley rats using high-resolution magic angle spinning 1H NMR spectroscopy of intact tissue and pattern recognition. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 40(2), 375–381.
Warburg, O. (1956). On the origin of cancer cells. Science, 123(3191), 309–314.
Waridel, F., Estreicher, A., Bron, L., et al. (1997). Field cancerisation and polyclonal p53 mutation in the upper aero-digestive tract. Oncogene, 14(2), 163–169.
Wilson, M., Davies, N. P., Grundy, R. G., & Peet, A. C. (2009). A quantitative comparison of metabolite signals as detected by in vivo MRS with ex vivo 1H HR-MAS for childhood brain tumours. NMR in Biomedicine, 22(2), 213–219.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge division of SAIF at Central Drug Research Institute (CDRI), Lucknow, for offering lab facilities to acquire NMR data. The Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi is thanked for providing SRF fellowship to Shatakshi Srivastava. The authors gratefully acknowledge Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi for providing a fellowship and NMR facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srivastava, S., Roy, R., Gupta, V. et al. Proton HR-MAS MR spectroscopy of oral squamous cell carcinoma tissues: an ex vivo study to identify malignancy induced metabolic fingerprints. Metabolomics 7, 278–288 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-010-0253-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-010-0253-4