Abstract
In recent years, immunotherapy has produced many unexpected breakthroughs in oncological therapy; however, it still has many deficiencies. For example, the number of patients who are unresponsive to anti-programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), anti-cytotoxic T-like antigen-4 (CTLA4), and anti-programmed death-1 (PD1) therapies cannot be ignored, and the search for an undiscovered immunosuppressive pathway is imminent. Five decades ago, researchers found that activation of the adenosinergic pathway was negatively correlated with prognosis in many cancers. This review describes the entire process of the adenosinergic pathway in the tumor microenvironment and the mechanism of immunosuppression, which promotes tumor metastasis and drug resistance. Additionally, the review explores factors that regulate this pathway, including signaling factors secreted by the tumor microenvironment and certain anti-tumor drugs. Additionally, the combination of adenosinergic pathway inhibitors with chemotherapy, checkpoint blockade therapy, and immune cell-based therapy is summarized. Finally, certain issues regarding treatment via inhibition of this pathway and the use of targeted nanoparticles to reduce adverse reactions in patients are put forward in this review.

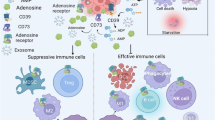
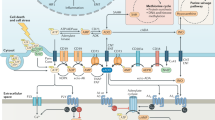
The inhibitors of adenosinergic pathway loaded nanoparticles enter tumor tissue through EPR effect, and inhibit adenosinergic pathway to enhance or restore the effect of immune checkpoint blockade therapy, chemotherapies and immune cell-based therapy. Note: EPR means enhanced penetration and retention, × means blockade

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrett J, Blazar B (2009) Genetic trickery—escape of leukemia from immune attack. N Engl J Med 361:524–525
Eltzschig HK, Sitkovsky MV, Robson SC (2012) Purinergic signaling during inflammation. N Engl J Med 367:2322–2333
Gil Del Alcazar CR, Huh SJ, Ekram MB, Trinh A, Liu LL, Beca F, Zi X, Kwak M, Bergholtz H, Su Y, Ding L, Russnes HG, Richardson AL, Babski K, Min Hui Kim E, McDonnell CH III, Wagner J, Rowberry R, Freeman GJ, Dillon D, Sorlie T, Coussens LM, Garber JE, Fan R, Bobolis K, Allred DC, Jeong J, Park SY, Michor F, Polyak K (2017) Immune escape in breast cancer during in situ to invasive carcinoma transition. Cancer Discov 7:1098–1115
Young A, Mittal D, Stagg J, Smyth MJ (2014) Targeting cancer-derived adenosine: new therapeutic approaches. Cancer Discov 4:879–888
Hodi FS, O’Day SJ, McDermott DF, Weber RW, Sosman JA (2010) Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med 363:711–723
Topalian SL, Smith DC, Brahmer JR, Gettinger SN (2012) Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. N Engl J Med 366:2443–2454
Wolchok JD, Kluger H, Callahan MK, Postow MA, Rizvi NA, Lesokhin AM, Segal NH, Ariyan CE, Gordon RA, Reed K, Burke MM, Caldwell A, Kronenberg SA, Agunwamba BU, Zhang X, Lowy I, Inzunza HD, Feely W, Horak CE, Hong Q, Korman AJ, Wigginton JM, Gupta A, Sznol M (2013) Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med 369:122–133
Allard B, Longhi MS, Robson SC, Stagg J (2017) The ectonucleotidases CD39 and CD73: novel checkpoint inhibitor targets. Immunol Rev 276:121–144
Maj T, Wang W, Crespo J, Zhang H, Wang W, Wei S, Zhao L, Vatan L, Shao I, Szeliga W, Lyssiotis C, Liu JR, Kryczek I, Zou W (2017) Oxidative stress controls regulatory T cell apoptosis and suppressor activity and PD-L1-blockade resistance in tumor. Nat Immunol 18:1332–1341
Di Virgilio F, Adinolfi E (2017) Extracellular purines, purinergic receptors and tumor growth. Oncogene 36:293–303
Beavis PA, Stagg J, Darcy PK, Smyth MJ (2012) CD73: a potent suppressor of antitumor immune responses. Trends Immunol 33:231–237
Young A, Ngiow SF, Madore J, Reinhardt J, Landsberg J, Chitsazan A, Rautela J, Bald T, Barkauskas DS, Ahern E, Huntington ND, Schadendorf D, Long GV, Boyle GM, Holzel M, Scolyer RA, Smyth MJ (2017) Targeting adenosine in BRAF-mutant melanoma reduces tumor growth and metastasis. Cancer Res 77:4684–4696
Turcotte M, Spring K, Pommey S, Chouinard G, Cousineau I, George J, Chen GM, Gendoo DM, Haibe-Kains B, Karn T, Rahimi K, Le Page C, Provencher D, Mes-Masson AM, Stagg J (2015) CD73 is associated with poor prognosis in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Cancer Res 75:4494–4503
Leclerc BG, Charlebois R, Chouinard G, Allard B, Pommey S, Saad F, Stagg J (2016) CD73 expression is an independent prognostic factor in prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 22:158–166
Gaudreau PO, Allard B, Turcotte M, Stagg J (2016) CD73-adenosine reduces immune responses and survival in ovarian cancer patients. Oncoimmunology 5:1–10
Inoue Y, Yoshimura K, Kurabe N, Kahyo T, Kawase A, Tanahashi M, Ogawa H, Inui N, Funai K, Shinmura K (2017) Prognostic impact of CD73 and A2A adenosine receptor expression in non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 8:8738–8751
Limagne E, Euvrard R, Thibaudin M, Rebe C, Derangere V, Chevriaux A, Boidot R, Vegran F, Bonnefoy N, Vincent J, Bengrine-Lefevre L, Ladoire S, Delmas D, Apetoh L, Ghiringhelli F (2016) Accumulation of MDSC and Th17 cells in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer predicts the efficacy of a FOLFOX-bevacizumab drug treatment regimen. Cancer Res 76:5241–5252
Wu XR, He XS, Chen YF, Yuan RX, Zeng Y, Lian L, Zou YF, Lan N, Wu XJ, Lan P (2012) High expression of CD73 as a poor prognostic biomarker in human colorectal cancer. J Surg Oncol 106:130–137
Allard B, Turcotte M, Stagg J (2012) CD73-generated adenosine: orchestrating the tumor-stroma interplay to promote cancer growth. J Biomed Biotechnol 2012:1–8
Leth-Larsen R, Lund R, Hansen H, Laenkholm A, Tarin D, Jensen O, Ditzel H (2009) Metastasis-related plasma membrane proteins of human breast cancer cells identified by comparative quantitative mass spectrometry. Mol Cell Proteomics 8:1436–1449
Serra S, Horenstein AL, Vaisitti T, Brusa D, Rossi D, Laurenti L, D’Arena G, Coscia M, Tripodo C, Inghirami G, Robson SC, Gaidano G, Malavasi F, Deaglio S (2011) CD73-generated extracellular adenosine in chronic lymphocytic leukemia creates local conditions counteracting drug-induced cell death. Blood 118:6141–6152
Loi S, Pommey S, Haibe-Kains B, Beavis PA, Darcy PK, Smyth MJ, Stagg J (2013) CD73 promotes anthracycline resistance and poor prognosis in triple negative breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:11091–11096
Allard B, Pommey S, Smyth MJ, Stagg J (2013) Targeting CD73 enhances the antitumor activity of anti-PD-1 and anti-CTLA-4 mAbs. Clin Cancer Res 19:5626–5635
Mittal D, Sinha D, Barkauskas D, Young A, Kalimutho M, Stannard K, Caramia F, Haibe-Kains B, Stagg J, Khanna KK, Loi S, Smyth MJ (2016) Adenosine 2B receptor expression on cancer cells promotes metastasis. Cancer Res 76:4372–4382
June 15, 2018. https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02503774
June 15, 2018. https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03267589
June 15, 2018. https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03454451
June 15, 2018. https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03207867
June 15, 2018. https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02403193
June 15, 2018. https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02655822
June 15, 2018. https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02740985
June 15, 2018. https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03274479
Schuler PJ, Harasymczuk M, Schilling B, Saze Z, Strauss L, Lang S, Johnson JT, Whiteside TL (2013) Effects of adjuvant chemoradiotherapy on the frequency and function of regulatory T cells in patients with head and neck cancer. Clin Cancer Res 19:6585–6596
Jie HB, Schuler PJ, Lee SC, Srivastava RM, Argiris A, Ferrone S, Whiteside TL, Ferris RL (2015) CTLA-4(+) regulatory T cells increased in cetuximab-treated head and neck cancer patients suppress NK cell cytotoxicity and correlate with poor prognosis. Cancer Res 75:2200–2210
Benci JL, Xu B, Qiu Y, Wu TJ, Dada H, Twyman-Saint Victor C, Cucolo L, Lee DSM, Pauken KE, Huang AC, Gangadhar TC, Amaravadi RK, Schuchter LM, Feldman MD, Ishwaran H, Vonderheide RH, Maity A, Wherry EJ, Minn AJ (2016) Tumor interferon signaling regulates a multigenic resistance program to immune checkpoint blockade. Cell 167:1540–1554
Turcotte M, Allard D, Mittal D, Bareche Y, Buisseret L, Jose V, Pommey S, Delisle V, Loi S, Joensuu H, Kellokumpu-Lehtinen PL, Sotiriou C, Smyth MJ, Stagg J (2017) CD73 promotes resistance to HER2/ErbB2 antibody therapy. Cancer Res 77:5652–5663
Mikhailov A, Sokolovskaya A, Yegutkin GG, Amdahl H, West A, Yagita H, Lahesmaa R, Thompson LF, Jalkanen S, Blokhin D, Eriksson JE (2008) CD73 participates in cellular multiresistance program and protects against TRAIL-induced apoptosis. J Immunol 181:464–475
Stagg J, Divisekera U, McLaughlin N, Sharkey J, Pommey S, Denoyer D, Dwyer KM, Smyth MJ (2010) Anti-CD73 antibody therapy inhibits breast tumor growth and metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:1547–1552
Vijayan D, Young A, Teng MWL, Smyth MJ (2017) Targeting immunosuppressive adenosine in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 17:709–724
Saze Z, Schuler PJ, Hong CS, Cheng D, Jackson EK, Whiteside TL (2013) Adenosine production by human B cells and B cell-mediated suppression of activated T cells. Blood 122:9–18
Cannons JL, Lu KT, Schwartzberg PL (2012) Lymph node choreography: B cells take the lead. Nat Immunol 13:630–632
Rittiner JE, Korboukh I, Hull-Ryde EA, Jin J, Janzen WP, Frye SV, Zylka MJ (2012) AMP is an adenosine A1 receptor agonist. J Biol Chem 287:5301–5309
Iwata Y, Matsushita T, Horikawa M, DiLillo D, Yanaba K, Venturi G, Szabolcs P, Bernstein S, Magro C, Williams A (2011) Characterization of a rare IL-10-competent B-cell subset in humans that parallels mouse regulatory B10 cells. Blood 117:530–541
Reinhardt J, Landsberg J, Schmid-Burgk JL, Ramis BB, Bald T, Glodde N, Lopez-Ramos D, Young A, Ngiow SF, Nettersheim D, Schorle H, Quast T, Kolanus W, Schadendorf D, Long GV, Madore J, Scolyer RA, Ribas A, Smyth MJ, Tumeh PC, Tuting T, Holzel M (2017) MAPK signaling and inflammation link melanoma phenotype switching to induction of CD73 during immunotherapy. Cancer Res 77:4697–4709
Sorrentino C, Miele L, Porta A, Pinto A, Morello S (2015) Myeloid-derived suppressor cells contribute to A2B adenosine receptor-induced VEGF production and angiogenesis in a mouse melanoma model. Oncotarget 6:27478–27489
Takenaka MC, Robson S, Quintana FJ (2016) Regulation of the T cell response by CD39. Trends Immunol 37:427–439
Chalmin F, Mignot G, Bruchard M, Chevriaux A, Vegran F, Hichami A, Ladoire S, Derangere V, Vincent J, Masson D, Robson SC, Eberl G, Pallandre JR, Borg C, Ryffel B, Apetoh L, Rebe C, Ghiringhelli F (2012) Stat3 and Gfi-1 transcription factors control Th17 cell immunosuppressive activity via the regulation of ectonucleotidase expression. Immunity 36:362–373
Regateiro FS, Howie D, Nolan KF, Agorogiannis EI, Greaves DR, Cobbold SP, Waldmann H (2011) Generation of anti-inflammatory adenosine by leukocytes is regulated by TGF-beta. Eur J Immunol 41:2955–2965
Deaglio S, Dwyer KM, Gao W, Friedman D, Usheva A, Erat A, Chen JF, Enjyoji K, Linden J, Oukka M, Kuchroo VK, Strom TB, Robson SC (2007) Adenosine generation catalyzed by CD39 and CD73 expressed on regulatory T cells mediates immune suppression. J Exp Med 204:1257–1265
Chatterjee S, Thyagarajan K, Kesarwani P, Song JH, Soloshchenko M, Fu J, Bailey SR, Vasu C, Kraft AS, Paulos CM, Yu XZ, Mehrotra S (2014) Reducing CD73 expression by IL1beta-programmed Th17 cells improves immunotherapeutic control of tumors. Cancer Res 74:6048–6059
Cekic C, Day YJ, Sag D, Linden J (2014) Myeloid expression of adenosine A2A receptor suppresses T and NK cell responses in the solid tumor microenvironment. Cancer Res 74:7250–7259
Trautmann A (2009) Extracellular ATP in the immune system: more than just a “danger signal”. Sci Signal 2:1–3
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Zitvogel L (2013) Immunogenic cell death in cancer therapy. Annu Rev Immunol 31:51–72
Yegutkin GG (2008) Nucleotide- and nucleoside-converting ectoenzymes: important modulators of purinergic signalling cascade. Biochim Biophys Acta 1783:673–694
Resta R, Yamashita Y, Thompson L (1998) Ecto-enzyme and signaling functions of lymphocyte CD73. Immunol Rev 161:95–109
Luca Antonioli RC, Federico Da Settimo CB, C.L.M., Fornai M, Tuccori M, Awwad O (2012) Adenosine deaminase in the modulation of immune system and its potential as a novel target for treatment of inflammatory disorders. Curr Drug Targets 13:842–862
Papanikolaou A, Papafotika A, Murphy C, Papamarcaki T, Tsolas O, Drab M, Kurzchalia TV, Kasper M, Christoforidis S (2005) Cholesterol-dependent lipid assemblies regulate the activity of the ecto-nucleotidase CD39. J Biol Chem 280:26406–26414
Kirley TL, Crawford PA, Smith TM (2006) The structure of the nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolases (NTPDases) as revealed by mutagenic and computational modeling analyses. Purinergic Signal 2:379–389
Grinthal A, Guidotti G (2006) CD39, NTPDase 1, is attached to the plasma membrane by two transmembrane domains. Why? Purinergic Signal 2:391–398
Grinthal A, Guidotti G (2002) Transmembrane domains confer different substrate specificities and adenosine diphosphate hydrolysis mechanisms on CD39, CD39L1, and chimeras. Biochemistry 41:1947–1956
Stagg J, Smyth MJ (2010) Extracellular adenosine triphosphate and adenosine in cancer. Oncogene 29:5346–5358
Laura Airas JN, Salmi M, Puurunen T, Smith DJ, Jalkanen S (1997) Differential regulation and function of CD73, a glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-linked 70-kD adhesion molecule, on lymphocytes and endothelial cells. J Cell Biol 136:421–431
Gennady Yegutkin PB, Burnstock G (2000) Effect of shear stress on the release of soluble ecto-enzymes ATPase and 5′-nucleotidase along with endogenous ATP from vascular endothelial cells. Brit J Pharmacol 129:921–926
Heuts DP, Weissenborn MJ, Olkhov RV, Shaw AM, Gummadova J, Levy C, Scrutton NS (2012) Crystal structure of a soluble form of human CD73 with ecto-5′-nucleotidase activity. Chembiochem 13:2384–2391
Knapp K, Zebisch M, Pippel J, El-Tayeb A, Muller CE, Strater N (2012) Crystal structure of the human ecto-5′-nucleotidase (CD73): insights into the regulation of purinergic signaling. Structure 20:2161–2173
Zhong X, Malhotra R, Woodruff R, Guidotti G (2001) Mammalian plasma membrane ecto-nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 1, CD39, is not active intracellularly. The N-glycosylation state of CD39 correlates with surface activity and localization. J Biol Chem 276:41518–41525
Faas MM, Saez T, de Vos P (2017) Extracellular ATP and adenosine: the Yin and Yang in immune responses? Mol Asp Med 55:9–19
Beavis PA, Divisekera U, Paget C, Chow MT, John LB, Devaud C, Dwyer K, Stagg J, Smyth MJ, Darcy PK (2013) Blockade of A2A receptors potently suppresses the metastasis of CD73+ tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:14711–14716
Ohta ASM (2001) Role of G-protein-coupled adenosine receptors in downregulation of inflammation and protection from tissue damage. Nature 414:916–920
Ohta A, Gorelik E, Prasad SJ, Ronchese F, Lukashev D, Wong MK, Huang X, Caldwell S, Liu K, Smith P, Chen JF, Jackson EK, Apasov S, Abrams S, Sitkovsky M (2006) A2A adenosine receptor protects tumors from antitumor T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:13132–13137
Vecchio EA, Tan CY, Gregory KJ, Christopoulos A, White PJ, May LT (2016) Ligand-independent adenosine A2B receptor constitutive activity as a promoter of prostate cancer cell proliferation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 357:36–44
Cronstein BNLR, Philips M, Hirschhorn R, Abramson SB, Weissmann G (1992) Neutrophil adherence to endothelium is enhanced via adenosine A1 receptors and inhibited via adenosine A2 receptors. J Immunol 148:2201–2206
Butler M, Sanmugalingam D, Burton VJ, Wilson T, Pearson R, Watson RP, Smith P, Parkinson SJ (2012) Impairment of adenosine A3 receptor activity disrupts neutrophil migratory capacity and impacts innate immune function in vivo. Eur J Immunol 42:3358–3368
Bastid J, Regairaz A, Bonnefoy N, Dejou C, Giustiniani J, Laheurte C, Cochaud S, Laprevotte E, Funck-Brentano E, Hemon P, Gros L, Bec N, Larroque C, Alberici G, Bensussan A, Eliaou JF (2015) Inhibition of CD39 enzymatic function at the surface of tumor cells alleviates their immunosuppressive activity. Cancer Immunol Res 3:254–265
Jin D, Fan J, Wang L, Thompson LF, Liu A, Daniel BJ, Shin T, Curiel TJ, Zhang B (2010) CD73 on tumor cells impairs antitumor T-cell responses: a novel mechanism of tumor-induced immune suppression. Cancer Res 70:2245–2255
Zhi X, Chen S, Zhou P, Shao Z, Wang L, Ou Z, Yin L (2007) RNA interference of ecto-5′-nucleotidase (CD73) inhibits human breast cancer cell growth and invasion. Clin Exp Metastasis 24:439–448
Antonioli L, Blandizzi C, Pacher P, Hasko G (2013) Immunity, inflammation and cancer: a leading role for adenosine. Nat Rev Cancer 13:842–857
Sorrentino C, Miele L, Porta A, Pinto A, Morello S (2016) Activation of the A2B adenosine receptor in B16 melanomas induces CXCL12 expression in FAP-positive tumor stromal cells, enhancing tumor progression. Oncotarget 7:64274–64288
Zhou X, Zhi X, Zhou P, Chen S, Zhao F, Shao Z, Ou Z, Yin L (2007) Effects of ecto-5′-nucleotidase on human breast cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Oncol Rep 17:1341–1346
Terp MG, Olesen KA, Arnspang EC, Lund RR, Lagerholm BC, Ditzel HJ, Leth-Larsen R (2013) Anti-human CD73 monoclonal antibody inhibits metastasis formation in human breast cancer by inducing clustering and internalization of CD73 expressed on the surface of cancer cells. J Immunol 191:4165–4173
Fletcher JM, Lonergan R, Costelloe L, Kinsella K, Moran B, O’Farrelly C, Tubridy N, Mills KH (2009) CD39+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells suppress pathogenic Th17 cells and are impaired in multiple sclerosis. J Immunol 183:7602–7610
Grant CR, Liberal R, Holder BS, Cardone J, Ma Y, Robson SC, Mieli-Vergani G, Vergani D, Longhi MS (2014) Dysfunctional CD39(POS) regulatory T cells and aberrant control of T-helper type 17 cells in autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology 59:1007–1015
Dwyer KM, Hanidziar D, Putheti P, Hill PA, Pommey S, McRae JL, Winterhalter A, Doherty G, Deaglio S, Koulmanda M, Gao W, Robson SC, Strom TB (2010) Expression of CD39 by human peripheral blood CD4+ CD25+ T cells denotes a regulatory memory phenotype. Am J Transplant 10:2410–2420
Zhou Q, Yan J, Putheti P, Wu Y, Sun X, Toxavidis V, Tigges J, Kassam N, Enjyoji K, Robson SC, Strom TB, Gao W (2009) Isolated CD39 expression on CD4+ T cells denotes both regulatory and memory populations. Am J Transplant 9:2303–2311
Hilchey SP, Kobie JJ, Cochran MR, Secor-Socha S, Wang JC, Hyrien O, Burack WR, Mosmann TR, Quataert SA, Bernstein SH (2009) Human follicular lymphoma CD39+-infiltrating T cells contribute to adenosine-mediated T cell hyporesponsiveness. J Immunol 183:6157–6166
Ngiow SF, Young A, Blake SJ, Hill GR, Yagita H, Teng MW, Korman AJ, Smyth MJ (2016) Agonistic CD40 mAb-driven IL12 reverses resistance to anti-PD1 in a T-cell-rich tumor. Cancer Res 76:6266–6277
Raskovalova T, Lokshin A, Huang X, Jackson EK, Gorelik E (2006) Adenosine-mediated inhibition of cytotoxic activity and cytokine production by IL-2/NKp46-activated NK cells. Immunol Res 36:91–99
Kalekar LA, Schmiel SE, Nandiwada SL, Lam WY, Barsness LO, Zhang N, Stritesky GL, Malhotra D, Pauken KE, Linehan JL, O’Sullivan MG, Fife BT, Hogquist KA, Jenkins MK, Mueller DL (2016) CD4(+) T cell anergy prevents autoimmunity and generates regulatory T cell precursors. Nat Immunol 17:304–314
Saito T, Nishikawa H, Wada H, Nagano Y, Sugiyama D, Atarashi K (2016) Two FOXP3 + CD4 + T cell subpopulations distinctly control the prognosis of colorectal cancers. Nat Med 22:679–684
Gourdin N, Bossennec M, Rodriguez C, Vigano S, Machon C, Jandus C, Bauche D, Faget J, Durand I, Chopin N, Tredan O, Marie JC, Dubois B, Guitton J, Romero P, Caux C, Menetrier-Caux C (2018) Autocrine adenosine regulates tumor polyfunctional CD73+CD4+ effector T cells devoid of immune checkpoints. Cancer Res 78(13):3604–3618
Michael Romio BR, Bongardt S, Hüls S, Burghoff S, Schrader J (2011) Extracellular purine metabolism and signaling of CD73-derived adenosine in murine Treg and Teff cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 301:530–539
Figueiro F, Muller L, Funk S, Jackson EK, Battastini AM, Whiteside TL (2016) Phenotypic and functional characteristics of CD39(high) human regulatory B cells (Breg). Oncoimmunology 5:e1082703
Kaku H, Cheng KF, Al-Abed Y, Rothstein TL (2014) A novel mechanism of B cell-mediated immune suppression through CD73 expression and adenosine production. J Immunol 193:5904–5913
Flores-Santibanez F, Fernandez D, Meza D, Tejon G, Vargas L, Varela-Nallar L, Arredondo S, Guixe V, Rosemblatt M, Bono MR, Sauma D (2015) CD73-mediated adenosine production promotes stem cell-like properties in mouse Tc17 cells. Immunology 146:582–594
Bono MR, Fernandez D, Flores-Santibanez F, Rosemblatt M, Sauma D (2015) CD73 and CD39 ectonucleotidases in T cell differentiation: beyond immunosuppression. FEBS Lett 589:3454–3460
Sitkovsky MV, Kjaergaard J, Lukashev D, Ohta A (2008) Hypoxia-adenosinergic immunosuppression: tumor protection by T regulatory cells and cancerous tissue hypoxia. Clin Cancer Res 14:5947–5952
Cekic C, Linden J (2014) Adenosine A2A receptors intrinsically regulate CD8+ T cells in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Res 74:7239–7249
Chatterjee D, Tufa DM, Baehre H, Hass R, Schmidt RE, Jacobs R (2014) Natural killer cells acquire CD73 expression upon exposure to mesenchymal stem cells. Blood 123:594–595
Wallace KL, Linden J (2010) Adenosine A2A receptors induced on iNKT and NK cells reduce pulmonary inflammation and injury in mice with sickle cell disease. Blood 116:5010–5020
Morello S, Sorrentino R, Montinaro A, Luciano A, Maiolino P, Ngkelo A, Arra C, Adcock IM, Pinto A (2011) NK1.1+ cells and CD8+ T cells mediate the antitumor activity of Cl-IB-MECA in a mouse melanoma model. Neoplasia 13:365–IN320
Young A, Ngiow SF, Gao Y, Patch AM, Barkauskas DS, Messaoudene M, Lin G, Coudert JD, Stannard KA, Zitvogel L, Degli-Esposti MA, Vivier E, Waddell N, Linden J, Huntington ND, Souza-Fonseca-Guimaraes F, Smyth MJ (2018) A2AR adenosine signaling suppresses natural killer cell maturation in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Res 78:1003–1016
Hyman MC, Petrovic-Djergovic D, Visovatti SH, Liao H, Yanamadala S, Bouis D, Su EJ, Lawrence DA, Broekman MJ, Marcus AJ, Pinsky DJ (2009) Self-regulation of inflammatory cell trafficking in mice by the leukocyte surface apyrase CD39. J Clin Invest 119:1136–1149
Zanin RF, Braganhol E, Bergamin LS, Campesato LF, Filho AZ, Moreira JC, Morrone FB, Sevigny J, Schetinger MR, de Souza Wyse AT, Battastini AM (2012) Differential macrophage activation alters the expression profile of NTPDase and ecto-5′-nucleotidase. PLoS One 7:e31205
Ponce NE, Sanmarco LM, Eberhardt N, Garcia MC, Rivarola HW, Cano RC, Aoki MP (2016) CD73 inhibition shifts cardiac macrophage polarization toward a microbicidal phenotype and ameliorates the outcome of experimental Chagas cardiomyopathy. J Immunol 197:814–823
Yegutkin GG, Marttila-Ichihara F, Karikoski M, Niemela J, Laurila JP, Elima K, Jalkanen S, Salmi M (2011) Altered purinergic signaling in CD73-deficient mice inhibits tumor progression. Eur J Immunol 41:1231–1241
Csoka B, Selmeczy Z, Koscso B, Nemeth ZH, Pacher P, Murray PJ, Kepka-Lenhart D, Morris SM Jr, Gause WC, Leibovich SJ, Hasko G (2012) Adenosine promotes alternative macrophage activation via A2A and A2B receptors. FASEB J 26:376–386
Koscso B, Csoka B, Kokai E, Nemeth ZH, Pacher P, Virag L, Leibovich SJ, Hasko G (2013) Adenosine augments IL-10-induced STAT3 signaling in M2c macrophages. J Leukoc Biol 94:1309–1315
Montalban Del Barrio I, Penski C, Schlahsa L, Stein RG, Diessner J, Wockel A, Dietl J, Lutz MB, Mittelbronn M, Wischhusen J, Hausler SFM (2016) Adenosine-generating ovarian cancer cells attract myeloid cells which differentiate into adenosine-generating tumor associated macrophages—a self-amplifying, CD39- and CD73-dependent mechanism for tumor immune escape. J Immunother Cancer 4:49
Vasquez-Dunddel D, Pan F, Zeng Q, Gorbounov M, Albesiano E, Fu J, Blosser RL, Tam AJ, Bruno T, Zhang H, Pardoll D, Kim Y (2013) STAT3 regulates arginase-I in myeloid-derived suppressor cells from cancer patients. J Clin Invest 123:1580–1589
Ryzhov S, Novitskiy SV, Goldstein AE, Biktasova A, Blackburn MR, Biaggioni I, Dikov MM, Feoktistov I (2011) Adenosinergic regulation of the expansion and immunosuppressive activity of CD11b+Gr1+ cells. J Immunol 187:6120–6129
Olivier M, Hollstein M, Hainaut P (2010) TP53 mutations in human cancers: origins, consequences, and clinical use. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2:a001008
Morello S, Ito K, Yamamura S, Lee KY, Jazrawi E, DeSouza P, Barnes P, Cicala C, Adcock IM (2006) IL-1 beta and TNF-alpha regulation of the adenosine receptor (A2A) expression: differential requirement for NF-kappa B binding to the proximal promoter. J Immunol 177:7173–7183
Kolachala V, Asamoah V, Wang L, Obertone TS, Ziegler TR, Merlin D, Sitaraman SV (2005) TNF-alpha upregulates adenosine 2b (A2b) receptor expression and signaling in intestinal epithelial cells: a basis for A2bR overexpression in colitis. Cell Mol Life Sci 62:2647–2657
Ahmad A, Ahmad S, Glover L, Miller SM, Shannon JM, Guo X, Franklin WA, Bridges JP, Schaack JB, Colgan SP, White CW (2009) Adenosine A2A receptor is a unique angiogenic target of HIF-2alpha in pulmonary endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:10684–10689
Chavez-Valdez R, Ahlawat R, Wills-Karp M, Gauda EB (2016) Mechanisms of modulation of cytokine release by human cord blood monocytes exposed to high concentrations of caffeine. Pediatr Res 80:101–109
Li L, Wang L, Li J, Fan Z, Yang L, Zhang Z, Zhang C, Yue D, Qin G, Zhang T, Li F, Chen X, Ping Y, Wang D, Gao Q, He Q, Huang L, Li H, Huang J, Zhao X, Xue W, Sun Z, Lu J, Yu JJ, Zhao J, Zhang B, Zhang Y (2018) Metformin-induced reduction of CD39 and CD73 blocks myeloid-derived suppressor cell activity in patients with ovarian cancer. Cancer Res 78:1779–1791
Samanta D, Park Y, Ni X, Li H, Zahnow CA, Gabrielson E, Pan F, Semenza GL (2018) Chemotherapy induces enrichment of CD47(+)/CD73(+)/PDL1(+) immune evasive triple-negative breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115:E1239–E1248
Wink MR, Tamajusuku ASK, Braganhol E, Casali EA, Barreto-Chaves MLM, Sarkis JJF, Battastini AMO (2003) Thyroid hormone upregulates ecto-5′-nucleotidase/CD73 in C6 rat glioma cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 205:107–114
Tamajusuku AS, Carrillo-Sepulveda MA, Braganhol E, Wink MR, Sarkis JJ, Barreto-Chaves ML, Battastini AM (2006) Activity and expression of ecto-5′-nucleotidase/CD73 are increased by thyroid hormones in vascular smooth muscle cells. Mol Cell Biochem 289:65–72
Bastomsky C, Zakarija M, Mckenzie J (1971) Thyroid hydrolysis of cyclic amp as influenced by thyroid gland activity. Biochim Biophys Acta 230:286
Murphy PS, Wang J, Bhagwat SP, Munger JC, Janssen WJ, Wright TW, Elliott MR (2017) CD73 regulates anti-inflammatory signaling between apoptotic cells and endotoxin-conditioned tissue macrophages. Cell Death Differ 24:559–570
Mittal D, Young A, Stannard K, Yong M, Teng MW, Allard B, Stagg J, Smyth MJ (2014) Antimetastatic effects of blocking PD-1 and the adenosine A2A receptor. Cancer Res 74:3652–3658
Hay CM, Sult E, Huang Q, Mulgrew K, Fuhrmann SR, McGlinchey KA, Hammond SA, Rothstein R, Rios-Doria J, Poon E, Holoweckyj N, Durham NM, Leow CC, Diedrich G, Damschroder M, Herbst R, Hollingsworth RE, Sachsenmeier KF (2016) Targeting CD73 in the tumor microenvironment with MEDI9447. Oncoimmunology 5:e1208875
Raffaella Iannone LM, Maiolino P, Pinto A, Morello S (2014) Adenosine limits the therapeutic effectiveness of anti-CTLA4 mAb in a mouse melanoma model. Am J Cancer Res 4:172–181
Waickman AT, Alme A, Senaldi L, Zarek PE, Horton M, Powell JD (2012) Enhancement of tumor immunotherapy by deletion of the A2A adenosine receptor. Cancer Immunol Immunother 61:917–926
Iannone R, Miele L, Maiolino P, Pinto A, Morello S (2013) Blockade of A2b adenosine receptor reduces tumor growth and immune suppression mediated by myeloid-derived suppressor cells in a mouse model of melanoma. Neoplasia 15:1400–IN1410
Michaud M, Martins I, Sukkurwala AQ, Adjemian S, Ma Y, Pellegatti P, Shen S, Kepp O, Scoazec M, Mignot G, Rello-Varona S, Tailler M, Menger L, Vacchelli E, Galluzzi L, Ghiringhelli F, di Virgilio F, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G (2011) Autophagy-dependent anticancer immune responses induced by chemotherapeutic agents in mice. Science 334:1573–1577
Long Wang JF, Thompson LF, Yi Z, Shin T, Curiel TJ, Zhang B (2011) CD73 has distinct roles in nonhematopoietic and hematopoietic cells to promote tumor growth in mice. J Clin Investig 121:2371–2382
Beavis PA, Henderson MA, Giuffrida L, Mills JK, Sek K, Cross RS, Davenport AJ, John LB, Mardiana S, Slaney CY, Johnstone RW, Trapani JA, Stagg J, Loi S, Kats L, Gyorki D, Kershaw MH, Darcy PK (2017) Targeting the adenosine 2A receptor enhances chimeric antigen receptor T cell efficacy. J Clin Invest 127:929–941
Kim DG, Bynoe MS (2016) A2A adenosine receptor modulates drug efflux transporter P-glycoprotein at the blood-brain barrier. J Clin Invest 126:1717–1733
Colgan SP, Eltzschig HK, Eckle T, Thompson LF (2006) Physiological roles for ecto-5′-nucleotidase (CD73). Purinergic Signal 2:351–360
Gao ZW, Dong K, Zhang HZ (2014) The roles of CD73 in cancer. Biomed Res Int 2014:460654
Giron MC, Bin A, Brun P, Etteri S, Bolego C, Florio C, Gaion RM (2008) Cyclic AMP in rat ileum: evidence for the presence of an extracellular cyclic AMP-adenosine pathway. Gastroenterology 134:1116–1126
Synnestvedt K, Furuta GT, Comerford KM, Louis N, Karhausen J, Eltzschig HK, Hansen KR, Thompson LF, Colgan SP (2002) Ecto-5′-nucleotidase (CD73) regulation by hypoxia-inducible factor-1 mediates permeability changes in intestinal epithelia. J Clin Investig 110:993–1002
Eckle T, Krahn T, Grenz A, Kohler D, Mittelbronn M, Ledent C, Jacobson MA, Osswald H, Thompson LF, Unertl K, Eltzschig HK (2007) Cardioprotection by ecto-5′-nucleotidase (CD73) and A2B adenosine receptors. Circulation 115:1581–1590
Grenz A, Zhang H, Eckle T, Mittelbronn M, Wehrmann M, Kohle C, Kloor D, Thompson LF, Osswald H, Eltzschig HK (2007) Protective role of ecto-5′-nucleotidase (CD73) in renal ischemia. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:833–845
Thompson LF, Eltzschig HK, Ibla JC, Van De Wiele CJ, Resta R, Morote-Garcia JC, Colgan SP (2004) Crucial role for ecto-5′-nucleotidase (CD73) in vascular leakage during hypoxia. J Exp Med 200:1395–1405
Castrop H, Huang Y, Hashimoto S, Mizel D, Hansen P, Theilig F, Bachmann S, Deng C, Briggs J, Schnermann J (2004) Impairment of tubuloglomerular feedback regulation of GFR in ecto-5′-nucleotidase/CD73–deficient mice. J Clin Investig 114:634–642
Annika Ålgars MK, Yegutkin GG, Stoitzner P, Niemelä J, Salmi M, Jalkanen S (2011) Different role of CD73 in leukocyte trafficking via blood and lymph vessels. Blood 117:4387–4393
Mills JH, Thompson LF, Mueller C, Waickman AT, Jalkanen S, Niemela J, Airas L, Bynoe MS (2008) CD73 is required for efficient entry of lymphocytes into the central nervous system during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:9325–9330
Hasko G, Pacher P, Vizi ES, Illes P (2005) Adenosine receptor signaling in the brain immune system. Trends Pharmacol Sci 26:511–516
Stagg J, Divisekera U, Duret H, Sparwasser T, Teng MW, Darcy PK, Smyth MJ (2011) CD73-deficient mice have increased antitumor immunity and are resistant to experimental metastasis. Cancer Res 71:2892–2900
Lennon PF, Taylor CT, Stahl GL, Colgan SP (1998) Neutrophil-derived 5′-adenosine monophosphate promotes endothelial barrier function via CD73-mediated conversion to adenosine and endothelial A(2B) receptor activation. J Exp Med 188:1433–1443
Brannon-Peppas L, Blanchette JO (2012) Nanoparticle and targeted systems for cancer therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 64:206–212
Lim SB, Banerjee A, Onyuksel H (2012) Improvement of drug safety by the use of lipid-based nanocarriers. J Control Release 163:34–45
Ibrahim BM, Park S, Han B, Yeo Y (2011) A strategy to deliver genes to cystic fibrosis lungs: a battle with environment. J Control Release 155:289–295
Omid C, Farokhzad RL (2009) Impact of nanotechnology on drug delivery. ACS Nano 3:16–20
Petros RA, DeSimone JM (2010) Strategies in the design of nanoparticles for therapeutic applications. Nat Rev Drug Discov 9:615–627
Guo S, Huang L (2014) Nanoparticles containing insoluble drug for cancer therapy. Biotechnol Adv 32:778–788
Wicki A, Witzigmann D, Balasubramanian V, Huwyler J (2015) Nanomedicine in cancer therapy: challenges, opportunities, and clinical applications. J Control Release 200:138–157
Hawkins MJ, Soon-Shiong P, Desai N (2008) Protein nanoparticles as drug carriers in clinical medicine. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 60:876–885
Di Bei JM, Youan B-BC (2010) Engineering nanomedicines for improved melanoma therapy: progress and promises. Nanomedicine 5:1385–1399
Dai Y, Xu C, Sun X, Chen X (2017) Nanoparticle design strategies for enhanced anticancer therapy by exploiting the tumour microenvironment. Chem Soc Rev 46:3830–3852
Shi J, Votruba AR, Farokhzad OC, Langer R (2010) Nanotechnology in drug delivery and tissue engineering: from discovery to applications. Nano Lett 10:3223–3230
Aggarwal P, Hall JB, McLeland CB, Dobrovolskaia MA, McNeil SE (2009) Nanoparticle interaction with plasma proteins as it relates to particle biodistribution, biocompatibility and therapeutic efficacy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 61:428–437
Wang J, Lu Z, Yeung BZ, Wientjes MG, Cole DJ, Au JL (2014) Tumor priming enhances siRNA delivery and transfection in intraperitoneal tumors. J Control Release 178:79–85
Jadidi-Niaragh F, Atyabi F, Rastegari A, Kheshtchin N, Arab S, Hassannia H, Ajami M, Mirsanei Z, Habibi S, Masoumi F, Noorbakhsh F, Shokri F, Hadjati J (2017) CD73 specific siRNA loaded chitosan lactate nanoparticles potentiate the antitumor effect of a dendritic cell vaccine in 4T1 breast cancer bearing mice. J Control Release 246:46–59
Zhang L, Radovic-Moreno AF, Alexis F, Gu FX, Basto PA, Bagalkot V, Jon S, Langer RS, Farokhzad OC (2007) Co-delivery of hydrophobic and hydrophilic drugs from nanoparticle-aptamer bioconjugates. ChemMedChem 2:1268–1271
Jack C-M, Hu LZ (2009) Therapeutic nanoparticles to combat cancer drug resistance. Curr Drug Metab 10:836–841
Li J, Wang Y, Zhu Y, Oupicky D (2013) Recent advances in delivery of drug-nucleic acid combinations for cancer treatment. J Control Release 172:589–600
Bertrand N, Wu J, Xu X, Kamaly N, Farokhzad OC (2014) Cancer nanotechnology: the impact of passive and active targeting in the era of modern cancer biology. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 66:2–25
Braganhol E, Tamajusuku AS, Bernardi A, Wink MR, Battastini AM (2007) Ecto-5′-nucleotidase/CD73 inhibition by quercetin in the human U138MG glioma cell line. Biochim Biophys Acta 1770:1352–1359
Allard B, Turcotte M, Stagg J (2014) Targeting CD73 and downstream adenosine receptor signaling in triple-negative breast cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets 18:863–881
Iqbal J, Saeed A, Raza R, Matin A, Hameed A, Furtmann N, Lecka J, Sevigny J, Bajorath J (2013) Identification of sulfonic acids as efficient ecto-5′-nucleotidase inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 70:685–691
Rafal Sadej JS, Andrzej C, Skladanowski (2006) Expression of ecto-5′-nucleotidase (eN, CD73) in cell lines from various stages of human melanoma. Melanoma Res 16:213–222
Sadej R, Inai K, Rajfur Z, Ostapkowicz A, Kohler J, Skladanowski AC, Mitchell BS, Spychala J (2008) Tenascin C interacts with ecto-5′-nucleotidase (eN) and regulates adenosine generation in cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1782:35–40
Thomson LF, Ruedi JM, Glass A, Moldenhauer G, Moller P, Low MG, Klemens MR, Massaia M, Lucas AH (1990) Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to the glycosyl phosphatidylinositol-anchored lymphocyte differentiation antigen ecto-5′-nucleotidase (CD73). HLA 35:9–19
L Airas MS, Jalkanen S (1993) Lymphocyte-vascular adhesion protein-2 is a novel 70-KDA molecule involved in lymphocyte adhesion to vascular endothelium. J Immunol 151:4228–4238
Stagg J, Beavis PA, Divisekera U, Liu MC, Moller A, Darcy PK, Smyth MJ (2012) CD73-deficient mice are resistant to carcinogenesis. Cancer Res 72:2190–2196
Zhan C, Li C, Wei X, Lu W, Lu W (2015) Toxins and derivatives in molecular pharmaceutics: drug delivery and targeted therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 90:101–118
Moriyama K, Sitkovsky MV (2010) Adenosine A2A receptor is involved in cell surface expression of A2B receptor. J Biol Chem 285:39271–39288
Hajiahmadi S, Panjehpour M, Aghaei M, Shabani M (2015) Activation of A2b adenosine receptor regulates ovarian cancer cell growth: involvement of Bax/Bcl-2 and caspase-3. Biochem Cell Biol 93:321–329
Long JS, Schoonen PM, Graczyk D, O’Prey J, Ryan KM (2015) p73 engages A2B receptor signalling to prime cancer cells to chemotherapy-induced death. Oncogene 34:5152–5162
Wei Q, Costanzi S, Balasubramanian R, Gao ZG, Jacobson KA (2013) A2B adenosine receptor blockade inhibits growth of prostate cancer cells. Purinergic Signal 9:271–280
Liu TZ, Wang X, Bai YF, Liao HZ, Qiu SC, Yang YQ, Yan XH, Chen J, Guo HB, Zhang SZ (2014) The HIF-2alpha dependent induction of PAP and adenosine synthesis regulates glioblastoma stem cell function through the A2B adenosine receptor. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 49:8–16
Abousamra NK, Salah El-Din M, Hamza Elzahaf E, Esmael ME (2015) Ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase-1 (E-NTPDase1/CD39) as a new prognostic marker in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma 56:113–119
Cai XY, Wang XF, Li J, Dong JN, Liu JQ, Li NP, Yun B, Xia RL (2015) Overexpression of CD39 and high tumoral CD39(+)/CD8(+) ratio are associated with adverse prognosis in resectable gastric cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:14757–14764
Antonioli L, Yegutkin GG, Pacher P, Blandizzi C, Haskó G (2016) Anti-CD73 in cancer immunotherapy: awakening new opportunities. Trends in Cancer 2(2):95–109
Wang H, Lee S, Nigro CL, Lattanzio L, Merlano M, Monteverde M, Matin R, Purdie K, Mladkova N, Bergamaschi D, Harwood C, Syed N, Szlosarek P, Briasoulis E, McHugh A, Thompson A, Evans A, Leigh I, Fleming C, Inman GJ, Hatzimichael E, Proby C, Crook T (2012) NT5E (CD73) is epigenetically regulated in malignant melanoma and associated with metastatic site specificity. Br J Cancer 106:1446–1452
Zhang B, Song B, Wang X, Chang XS, Pang T, Zhang X, Yin K, Fang GE (2015) The expression and clinical significance of CD73 molecule in human rectal adenocarcinoma. Tumour Biol 36:5459–5466
Liu N, Fang XD, Vadis Q (2012) CD73 as a novel prognostic biomarker for human colorectal cancer. J Surg Oncol 106:918–919
Xiong L, Wen Y, Miao X, Yang Z (2014) NT5E and FcGBP as key regulators of TGF-1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) are associated with tumor progression and survival of patients with gallbladder cancer. Cell Tissue Res 355:365–374
Ren ZH, Yuan YX, Ji T, Zhang CP (2016) CD73 as a novel marker for poor prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett 12:556–562
Yang Q, Du J, Zu L (2013) Overexpression of CD73 in prostate cancer is associated with lymph node metastasis. Pathol Oncol Res 19:811–814
Funding
This work was supported by The Fundamental Research Funds of Shandong University (No. 2018JC006) and Jiangxi Province Outstanding Young Talents Program (20162BCB23034).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Yi Huang declares that he/she has no competing interest.
Zili Gu declares that he/she has no competing interest.
Yang Fan declares that he/she has no competing interest.
Guangxi Zhai declares that he/she has no competing interest.
Xiaogang Zhao declares that he/she has no competing interest.
Qifeng Sun declares that he/she has no competing interest.
Yanbin Shi declares that he/she has no competing interest.
Guimei Lin declares that he/she has no competing interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Gu, Z., Fan, Y. et al. Inhibition of the adenosinergic pathway: the indispensable part of oncological therapy in the future. Purinergic Signalling 15, 53–67 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-018-9641-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-018-9641-4