Abstract
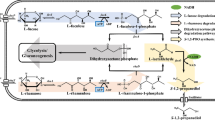
1,2,4-butanetriol (BT) is a polyol with unique chemical properties, which has a stereocenter and can be divided into D-BT (the S-enantiomer) and L-BT (the R-enantiomer). BT can be used for the synthesis of 1,2,4-butanetriol trinitrate, 3-hydroxytetrahydrofuran, polyurethane, and other chemicals. It is widely used in the military industry, medicine, tobacco, polymer. At present, the BT is mainly synthesized by chemical methods, which are accompanied by harsh reaction conditions, poor selectivity, many by-products, and environmental pollution. Therefore, BT biosynthesis methods with the advantages of mild reaction conditions and green sustainability have become a current research hotspot. In this paper, the research status of microbial synthesis of BT was summarized from the following three aspects: (1) the biosynthetic pathway establishment for BT from xylose; (2) metabolic engineering strategies employed for improving BT production from xylose; (3) other substrates for BT production. Finally, the challenges and prospects of biosynthetic BT were discussed for future methods to improve competitiveness for industrial production.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Abdel-Ghany SE, Day I, Heuberger AL, Broeckling CD, Reddy AS (2013) Metabolic engineering of Arabidopsis for butanetriol production using bacterial genes. Metab Eng 20:109–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2013.10.003
Bamba T, Yukawa T, Guirimand G, Inokuma K, Sasaki K, Hasunuma T, Kondo A (2019) Production of 1,2,4-butanetriol from xylose by Saccharomyces cerevisiae through Fe metabolic engineering. Metab Eng 56:17–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2019.08.012
Bañares AB, Valdehuesa KNG, Ramos KRM, Nisola GM, Lee WK, Chung WJ (2019) Discovering a novel D-xylonate-responsive promoter: the PyjhI-driven genetic switch towards better 1,2,4-butanetriol production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103(19):8063–8074. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10073-0
Bañares AB, Nisola GM, Valdehuesa KNG, Lee WK, Chung WJ (2021) Understanding D-xylonic acid accumulation: a cornerstone for better metabolic engineering approaches. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105(13):5309–5324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11410-y
Bera AK, Ho NWY, Khan A, Sedlak M (2011) A genetic overhaul of Saccharomyces cerevisiae 424A(LNH-ST) to improve xylose fermentation. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 38(5):617–626. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-010-0806-6
Bilal M, Asgher M, Iqbal HMN, Hu H, Zhang X (2017) Biotransformation of lignocellulosic materials into value-added products—A review. Int J Biol Macromol 98:447–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.01.133
Bondar M, da Fonseca MMR, Cesário MT (2021) Xylonic acid production from xylose by Paraburkholderia Sacchari. Biochem Eng J 170:107982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2021.107982
Bornscheuer UT, Huisman GW, Kazlauskas RJ, Lutz S, Moore JC, Robins K (2012) Engineering the third wave of biocatalysis. Nature 485(7397):185–194. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11117
Cao Y, Niu W, Guo J, Xian M, Liu H (2015) Biotechnological production of 1,2,4-butanetriol: an efficient process to synthesize energetic material precursor from renewable biomass. Sci Rep-UK 5:18149. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep18149
Chistoserdova L, Kalyuzhnaya MG (2018) Current trends in methylotrophy. Trends Microbiol 26(8):703–714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2018.01.011
Cunha JT, Romani A, Inokuma K, Johansson B, Hasunuma T, Kondo A, Domingues L (2020) Consolidated bioprocessing of corn cob-derived hemicellulose: engineered industrial Saccharomyces cerevisiaeas efficient whole cell biocatalysts. Biotechnol Biofuels 13:138. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-020-01780-2
Dagley S, Trudgill PW (1965) Metabolism of galactarate, D-glucarate and various pentoses by species of Pseudomonas. Biochem J 95(1):48–58. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj0950048
De la Plaza M, Fernández de Palencia P, Peláez C, Requena T (2004) Biochemical and molecular characterization of α-ketoisovalerate decarboxylase, an enzyme involved in the formation of aldehydes from amino acids by Lactococcus lactis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 238(2):367–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.femsle.2004.07.057
Desmons S, Fauré R, Bontemps S (2019) Formaldehyde as a promising C1 source: the instrumental role of biocatalysis for stereocontrolled reactions. ACS Catal 9(10):9575–9588. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.9b03128
Deutscher J, Francke C, Postma PW (2006) How phosphotransferase system-related protein phosphorylation regulates carbohydrate metabolism in bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 70(4):939–1031. https://doi.org/10.1128/mmbr.00024-06
Di Y, Wang X, Feng A, Lu X, Zong H, Zhuge B (2021) Improved 1,2,4-butanetriol production by weaken acetate pathway in a recombinant Escherichia coli. Food and Fermentation Industries 47(19):29–34. https://doi.org/10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.026826(in Chinese)
Dong X, Sun C, Guo J, Ma X, Xian M, Zhang R (2023) Highly efficient biosynthesis of 2,4-dihydroxybutyric acid by a methanol assimilation pathway in engineered Escherichia coli. Green Chem 25(19):7662–7672. https://doi.org/10.1039/d3gc02083e
Gao H, Gao Y, Dong R (2017) Enhanced biosynthesis of 3,4-dihydroxybutyric acid by engineered Escherichia coli in a dual-substrate system. Bioresour Technol 245:794–800. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.09.017
Ghosh D (2017) Synthetic and systems biology approach towards designing metabolic bypass and identifying novel enzymes for cholesterol lowering drug precursor (BTO) biosynthesis from crude glycerol. J Appl Pharm Sci 7(10):48–57. https://doi.org/10.7324/JAPS.2017.71007
Ghosh AK, Bilcer G, Schiltz G (2001) Syntheses of FDA approved HIV protease inhibitors. Synthesis 2001(15):2203–2229. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2001-18434
Gosset G (2005) Improvement of Escherichia coli production strains by modification of the phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system. Microb Cell Fact 4:14. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-4-14
Gouranlou F, Kohsary I (2010) Synthesis and characterization of 1,2,4-butanetrioltrinitrate. Asian J Chem 22(6):4221–4228
Hanessian S, Ugolini A, Dube D, Glamyan A (1984) Facile access to (S)-1,2,4-butanetriol and its derivatives. Can J Chem-Rev Can Chim 62(11):2146–2147. https://doi.org/10.1139/v84-367
He S, Zhuge B, Lu X, Zong H, Chen W, Song J (2017) Influence of the deficiency of by-product pathways on biosynthesis of D-1,2,4-butanetriol in Escherichia coli. Microbiol China 44(1):30–37. https://doi.org/10.13344/j.microbiol.china.160140(in Chinese)
Hu S, Gao Q, Wang X, Yang J, Xu N, Chen K, Xu S, Ouyang P (2018) Efficient production of D-1,2,4-butanetriol from D-xylose by engineered Escherichia coli whole-cell biocatalysts. Front Chem Sci Eng 12(4):772–779. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-018-1731-x
Jarboe LR (2011) YqhD: a broad-substrate range aldehyde reductase with various applications in production of biorenewable fuels and chemicals. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89(2):249–257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2912-9
Jiang Y, Liu W, Cheng T, Cao Y, Zhang R, Xian M (2015) Characterization of D-xylonate dehydratase YjhG from Escherichia coli. Bioengineered 6(4):227–232. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2015.1040208
Jing P, Cao X, Lu X, Zong H, Zhuge B (2018) Modification of an engineered Escherichia coli by a combined strategy of deleting branch pathway, fine-tuning xylose isomerase expression, and substituting decarboxylase to improve 1,2,4-butanetriol production. J Biosci Bioeng 126(5):547–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2018.05.019
Johnsen U, Schonheit P (2004) Novel xylose dehydrogenase in the halophilic archaeon Haloarcula Matismortui. J Bacteriol 186(18):6198–6207. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.186.18.6198-6207.2004
Kim SM, Choi BY, Ryu YS, Jung SH, Park JM, Kim GH, Lee SK (2015) Simultaneous utilization of glucose and xylose via novel mechanisms in engineered Escherichia coli. Metab Eng 30:141–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2015.05.002
Kumar P, Park H, Yuk Y, Kim H, Jang J, Pagolu R, Park S, Yeo C, Choi KY (2023) Developed and emerging 1,4-butanediol commercial production strategies: forecasting the current status and future possibility. Crit Rev Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1080/07388551.2023.2176740
Kwak BS (2005) Applications of heterogeneous catalytic processes to the environmentally friendly synthesis of fine chemicals. Catal Surv Asia 9(2):103–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10563-005-5996-y
Lau MK (2007) Syntheses and downstream purification of 1,2,4-butanetriol. Dissertation, Michigan State University
Lee C, Kim I, Lee J, Lee KL, Min B, Park C (2010) Transcriptional activation of the aldehyde reductase YqhD by YqhC and its implication in glyoxal metabolism of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol 192(16):4205–4214. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.01127-09
Li X, Cai Z, Li Y, Zhang Y (2014) Design and construction of a non-natural malate to 1,2,4-butanetriol pathway creates possibility to produce 1,2,4-butanetriol from glucose. Sci Rep-UK 4:5541. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep05541
Li Y, Liu Y, Yang C, Lu X, Zong H, Zhuge B (2020) Production of D-1,2,4-butanetriol by engineering Klebsiella pneumoniae. Microbiol China 47(8):2505–2515. https://doi.org/10.13344/j.microbiol.china.200015(in Chinese)
Li N, Shan XY, Zhou JW, Yu SQ (2022a) Identification of key genes through the constructed CRISPR-dcas9 to facilitate the efficient production of O-acetylhomoserine in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 10:978686. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2022.978686
Li Y, Yao P, Zhang S, Feng J, Su H, Liu X, Sheng X, Wu Q, Zhu D, Ma Y (2023b) Creating a new benzaldehyde lyase for atom-economic synthesis of chiral 1,2,4-butanetriol and 2-aminobutane-1,4-diol from formaldehyde. Chem Catal 3(1):100467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.checat.2022.11.006
Liu H, Valdehuesa KN, Nisola GM, Ramos KR, Chung WJ (2012) High yield production of D-xylonic acid from D-xylose using engineered Escherichia coli. Bioresour Technol 115:244–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.08.065
Liu H, Ramos KR, Valdehuesa KN, Nisola GM, Lee WK, Chung WJ (2013a) Biosynthesis of ethylene glycol in Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(8):3409–3417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4618-7
Liu R, Liang L, Li F, Wu M, Chen K, Ma J, Jiang M, Wei P, Ouyang P (2013b) Efficient succinic acid production from lignocellulosic biomass by simultaneous utilization of glucose and xylose in engineered Escherichia coli. Bioresour Technol 149:84–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.09.052
Liu J, Li H, Zhao G, Caiyin Q, Qiao J (2018) Redox cofactor engineering in industrial microorganisms: strategies, recent applications and future directions. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 45(5):313–327. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-018-2031-7
Liu D, Zhang Y, Li J, Sun W, Yao Y, Tian C (2023) The Weimberg pathway: an alternative for Myceliophthora Thermophila to utilize D-xylose. Biotechnol Biofuels 16:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-023-02266-7
Lu X, He S, Zong H, Song J, Chen W, Zhuge B (2016) Improved 1,2,4-butanetriol production from an engineered Escherichia coli by co-expression of different chaperone proteins. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 32(9):149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-016-2085-5
Lu X, Ren S, Lu J, Zong H, Song J, Zhuge B (2018) Enhanced 1,3-propanediol production in Klebsiella pneumoniae by a combined strategy of strengthening the TCA cycle and weakening the glucose effect. J Appl Microbiol 124(3):682–690. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.13685
Mak WS, Tran S, Marcheschi R, Bertolani S, Thompson J, Baker D, Liao JC, Siegel JB (2015) Integrative genomic mining for enzyme function to enable engineering of a unnatural biosynthetic pathway. Nat Commun 6:10005. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10005
Mangaloglu L, Van-Iderstine S, Chen B, Taghibiglou C, Cheung R, Adeli K (2000) Effect of atorvastatin (Lipitor) on VLDL-APOB and VLDL-triglyceride overproduction in vivo in an insulin resistant hamster model. Atherosclerosis 151(1):45. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9150(00)80202-6
Mao X, Qian X, Lin J, Wei D (2023) Engineering Gluconobacter oxydans for efficient production of 3,4-dihydroxybutunate or 1,2,4-butanetriol from D-xylose. Biochem Eng J 195:108936. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2023.108936
Milne N, van Maris AJA, Pronk JT, Daran JM (2015) Comparative assessment of native and heterologous 2-oxo acid decarboxylases for application in isobutanol production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Biofuels 8:204. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-015-0374-0
Nguyen LT, Phan D-P, Sarwar A, Tran MH, Lee OK, Lee EY (2021) Valorization of industrial lignin to value-added chemicals by chemical depolymerization and biological conversion. Ind Crop Prod 161:113219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.113219
Niu W, Molefe MN, Frost JW (2003) Microbial synthesis of the energetic material precursor 1,2,4-butanetriol. J Am Chem Soc 125(43):12998–12999. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja036391+
Nunez MF, Pellicer MT, Badia J, Aguilar J, Baldoma L (2001) Biochemical characterization of the 2-ketoacid reductases encoded by ycdW and yiaE genes in Escherichia coli. Biochem J 354:707–715. https://doi.org/10.1042/0264-6021:3540707
Petroll K, Kopp D, Care A, Bergquist PL, Sunna A (2019) Tools and strategies for constructing cell-free enzyme pathways. Biotechnol Adv 37(1):91–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2018.11.007
Pisacane FJ (1982) 1,2,4-Butanetriol: analysis and synthesis. Technology report, Naval Surface Weapons Center, US
Polsinelli I, Salomone-Stagni M, Benini S (2022) Erwinia tasmaniensis levansucrase shows enantiomer selection for (S)-1,2,4-butanetriol. Acta Crystallogr F 78:289–296. https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053230x2200680x
Ren T, Liu DX (1999) Synthesis of cationic lipids from 1,2,4-butanetriol. Tetrahedron Lett 40(2):209–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0040-4039(98)02381-8
Serna-Loaiza S, Miltner A, Miltner M, Friedl A (2019) A review on the feedstocks for the sustainable production of bioactive compounds in biorefineries. Sustainability 11(23):6765. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11236765
Stephens C, Christen B, Fuchs T, Sundaram V, Watanabe K, Jenal U (2007) Genetic analysis of a novel pathway for D-xylose metabolism in Caulobacter crescentus. J Bacteriol 189(5):2181–2185. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.01438-06
Sulzenbacher G, Alvarez K, van den Heuvel RHH, Versluis C, Spinelli M, Campanacci V, Valencia C, Cambillau C, Eklund H, Tegoni M (2004) Crystal structure of E-coli alcohol dehydrogenase YqhD: evidence of a covalently modified NADP coenzyme. J Mol Biol 342(2):489–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2004.07.034
Sun W, Lu X, Zong H, Fang H, Zhu G, Song J (2014) Biosynthesis of D-1,2,4-butanetriol by an engineered Escherichia coli. Microbiol China 41(10):1948–1954. https://doi.org/10.13344/j.microbiol.china.130901(in Chinese)
Sun L, Yang F, Sun H, Zhu T, Li X, Li Y, Xu Z, Zhang Y (2016) Synthetic pathway optimization for improved 1,2,4-butanetriol production. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 43(1):67–78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-015-1693-7
Sutiono S, Zachos I, Paschalidis L, Pick A, Burger J, Sieber V (2023) Biocatalytic production of 1,2,4-butanetriol beyond a titer of 100 g/L: boosting by intermediates. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 11:6592–6599. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.2c07418
Turner PC, Miller EN, Jarboe LR, Baggett CL, Shanmugam KT, Ingram LO (2011) YqhC regulates transcription of the adjacent Escherichia coli genes yqhD and dkgA that are involved in furfural tolerance. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 38(3):431–439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-010-0787-5
Valdehuesa KNG, Liu H, Ramos KRM, Park SJ, Nisola GM, Lee WK, Chung WJ (2014) Direct bioconversion of D-xylose to 1,2,4-butanetriol in an engineered Escherichia coli. Process Biochem 49(1):25–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2013.10.002
Valdehuesa KN, Lee WK, Ramos KR, Cabulong RB, Choi J, Liu H, Nisola GM, Chung WJ (2015) Identification of aldehyde reductase catalyzing the terminal step for conversion of xylose to butanetriol in engineered Escherichia coli. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 38(9):1761–1772. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-015-1417-4
Van Dien S (2013) From the first drop to the first truckload: commercialization of microbial processes for renewable chemicals. Curr Opin Biotechnol 24(6):1061–1068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2013.03.002
Walther T, Topham CM, Irague R, Auriol C, Baylac A, Cordier H, Dressaire C, Lozano-Huguet L, Tarrat N, Martineau N, Stodel M, Malbert Y, Maestracci M, Huet R, Andre I, Remaud-Simeon M, Francois JM (2017) Construction of a synthetic metabolic pathway for biosynthesis of the unnatural methionine precursor 2,4-dihydroxybutyric acid. Nat Commun 8:15828. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15828
Wang M, Chen B, Fang Y, Tan T (2017) Cofactor engineering for more efficient production of chemicals and biofuels. Biotechnol Adv 35(8):1032–1039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2017.09.008
Wang X, Xu N, Hu S, Yang J, Gao Q, Xu S, Chen K, Ouyang P (2018) D-1,2,4-Butanetriol production from renewable biomass with optimization of synthetic pathway in engineered Escherichia coli. Bioresour Technol 250:406–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.11.062
Wang J, Chen Q, Wang X, Chen K, Ouyang P (2022a) The biosynthesis of D-1,2,4-butanetriol from D-arabinose with an engineered Escherichia coli. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 10:844517. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2022.844517
Wang J, Jiang T, Milligan S, Zhang J, Li C, Yan Y (2022b) Improving isoprenol production via systematic CRISPRi screening in engineered Escherichia coli. Green Chem 24(18):6955–6964. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2gc02255a
Yamada-Onodera K, Norimoto A, Kawada N, Furuya R, Yamamoto H, Tani Y (2007) Production of optically active 1,2,4-butanetriol from corresponding racemate by microbial stereoinversion. J Biosci Bioeng 103(5):494–496. https://doi.org/10.1263/jbb.103.494
Yamaguchi A, Hiyoshi N, Sato O, Bando KK, Shirai M (2009) Enhancement of cyclic ether formation from polyalcohol compounds in high temperature liquid water by high pressure carbon dioxide. Green Chem 11(1):48–52. https://doi.org/10.1039/b812318g
Yang Q, Guo X, Liu Y, Jiang H (2021) Biocatalytic C-C bond formation for one carbon resource utilization. Int J Mol Sci 22(4):1890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041890
Yep A, Kenyon GL, McLeish MJ (2008) Saturation mutagenesis of putative catalytic residues of benzoylformate decarboxylase provides a challenge to the accepted mechanism. P Natl Acad Sci USA 105(15):5733–5738. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0709657105
Yim H, Haselbeck R, Niu W, Pujol-Baxley C, Burgard A, Boldt J, Khandurina J, Trawick JD, Osterhout RE, Stephen R, Estadilla J, Teisan S, Schreyer HB, Andrae S, Yang TH, Lee SY, Burk MJ, Van Dien S (2011) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for direct production of 1,4-butanediol. Nat Chem Biol 7(7):445–452. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.580
Yin W, Cao Y, Jin M, Xian M, Liu W (2021) Metabolic engineering of E. coli for xylose production from glucose as the sole carbon source. ACS Synth Biol 10(9):2266–2275. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.1c00184
Yu P, Jiang J, Chen C, Wang Z, Wang D, Li G, Li X (2022a) Ru/SiO2 catalyst for highly selective hydrogenation of dimethyl malate to 1,2,4-butanetriol at low temperatures in aqueous solvent. Catal Lett 152(10):3046–3057. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-021-03877-1
Yu T, Liu Q, Wang X, Liu X, Chen Y, Nielsen J (2022b) Metabolic reconfiguration enables synthetic reductive metabolism in yeast. Nat Metab 4(11):1551–1559. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-022-00654-1
Yuan T, Liu B, Yuan X, Feng L, Xu X, Zhu J, Chen Z, Xu R, Chen J, Xu G, Lin J, Yang L, Li M, Lian J, Wu M (2023) Multisite mutation of the Escherichia coli cAMP receptor protein: enhancing xylitol biosynthesis by activating xylose catabolism and improving strain tolerance. J Agric Food Chem 71(45):17226–17234. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.3c05445
Yukawa T, Bamba T, Guirimand G, Matsuda M, Hasunuma T, Kondo A (2021) Optimization of 1,2,4-butanetriol production from xylose in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by metabolic engineering of NADH/NADPH balance. Biotechnol Bioeng 118(1):175–185. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.27560
Zhang HS, Liu G, Zhang J, Bao J (2016a) Fermentative production of high titer gluconic and xylonic acids from corn stover feedstock by Gluconobacter oxydans and techno-economic analysis. Bioresour Technol 219:123–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.07.068
Zhang N, Wang J, Zhang Y, Gao H (2016b) Metabolic pathway optimization for biosynthesis of 1,2,4-butanetriol from xylose by engineered Escherichia coli. Enzyme Microb Technol 93–94:51–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2016.07.007
Zhang H, Han X, Wei C, Bao J (2017) Oxidative production of xylonic acid using xylose in distillation stillage of cellulosic ethanol fermentation broth by Gluconobacter oxydans. Bioresour Technol 224:573–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.11.039
Zhao M, Shi D, Lu X, Zong H, Zhuge B (2019) Co-production of 1,2,4-butantriol and ethanol from lignocellulose hydrolysates. Bioresour Technol 282:433–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.03.057
Zu J, Xu S, Lu X, Zong H, Zhuge B (2019) Construction of a 1,2,4-butanetriol-integrated strain and fermentation of its co-substrate. Chin J Appl Environ Biology 25(4):966–971. https://doi.org/10.19675/j.cnki.1006-687x.2018.11006
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Key R&D Program of Shandong Province, China (No. 2023JMRH0201), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 22007091).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XM, JG and RZ designed and wrote the manuscript. CS revised the manuscript. RZ and MX funded this manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have any potential financial conflicts of interest associated with this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, X., Sun, C., Xian, M. et al. Progress in research on the biosynthesis of 1,2,4-butanetriol by engineered microbes. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 40, 68 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-024-03885-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-024-03885-4