Abstract
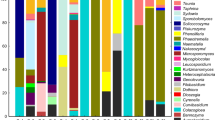
Antarctic environments can sustain a great diversity of well-adapted microorganisms known as psychrophiles or psychrotrophs. The potential of these microorganisms as a resource of enzymes able to maintain their activity and stability at low temperature for technological applications has stimulated interest in exploration and isolation of microbes from this extreme environment. Enzymes produced by these organisms have a considerable potential for technological applications because they are known to have higher enzymatic activities at lower temperatures than their mesophilic and thermophilic counterparts. A total of 518 Antarctic microorganisms, were isolated during Antarctic expeditions organized by the Instituto Antártico Uruguayo. Samples of particules suspended in air, ice, sea and freshwater, soil, sediment, bird and marine animal faeces, dead animals, algae, plants, rocks and microbial mats were collected from different sites in maritime Antarctica. We report enzymatic activities present in 161 microorganisms (120 bacteria, 31 yeasts and 10 filamentous fungi) isolated from these locations. Enzymatic performance was evaluated at 4 and 20°C. Most of yeasts and bacteria grew better at 20°C than at 4°C, however the opposite was observed with the fungi. Amylase, lipase and protease activities were frequently found in bacterial strains. Yeasts and fungal isolates typically exhibited lipase, celullase and gelatinase activities. Bacterial isolates with highest enzymatic activities were identified by 16S rDNA sequence analysis as Pseudomonas spp., Psychrobacter sp., Arthrobacter spp., Bacillus sp. and Carnobacterium sp. Yeasts and fungal strains, with multiple enzymatic activities, belonged to Cryptococcus victoriae, Trichosporon pullulans and Geomyces pannorum.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghajari N, Feller G, Gerday C, Haser R (1996) Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction studies of α-amylase from the Antarctic psychrophile Alteromonas halplanctis A23. Protein Sci 5(10):2128–2129. doi:10.1002/pro.5560051021
Alippi AM, Aguilar OM (1998) Characterization of isolates of Paenibacillus larvae subsp. larvae from diverse geographical origin by the polymerase chain reaction and Box primers. J Invertebr Pathol 72:21–27. doi:10.1006/jipa.1998.4748
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410. doi:10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2
Antranikian G, Vorgias CE, Bertoldo C (2005) Extreme environments as a resource for microorganisms and novel biocatalysts. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 96:219–262
Brenchley JE (1996) Psychrophilic microorganisms and their cold-active enzymes. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 17:432–437. doi:10.1007/BF01574774
Feller G, Gerday C (2003) Psychrophilic enzymes: hot topics in cold adaptation. Nat Rev Microbiol 1:200–208. doi:10.1038/nrmicro773
Fogliano V, Andreoli C, Martello A, Caiazzo M, Lobosco O, Formisano F, Carlino PA, Meca G, Graziani G, Di Martino Rigano V, Vona V, Carfagna S, Rigano C (2010) Functional ingredients produced by culture of Koliella antarctica. Aquaculture 299:115–120. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2009.11.008
Gonzales JA, Gallardo CS, Combar A, Rego P, Rodríguez LA (2004) Determination of enzymatic activity in ecotypic Saccharomyces and non-Saccharomyces. Electron J Environ Agric Food Chem 3(5):743–750
Gratia E, Weekers F, Margesin R, D’Amico S, Thonart P, Feller G (2009) Selection of a cold-adapted bacterium for bioremediation of wastewater at low temperatures. Extremophiles 13:763–768. doi:10.1007/s00792-009-0264-0
Higgins D, Thompson J, Gibson T, Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucl Acids Res 22:4673–4680. doi:10.1093/nar/22.22.4673
León J, Liza L, Soto I, Cuadra DL, Patiño L, Zerpa R (2007) Bioactive Actinomycetes of marine sediment from the central coast of Peru. Rev Peruana Biol 14(2):259–270
Li J, Chi Z, Wang X, Peng Y, Chi Z (2009) The selection of alkaline protease-producing yeasts from marine environments and evaluation of their bioactive peptide production. Chin J Oceanol Limnol 27(4):753–761. doi:10.1007/s00343-009-9198-8
Lo Giudice A, Casella P, Caruso C, Mangano S, Bruni V, De Domenico M, Michaud L (2010) Occurrence and characterization of psychrotolerant hydrocarbon-oxidizing bacteria from surface seawater along the Victoria Land coast (Antarctica). Polar Biol 33:929–943. doi:10.1007/s00300-010-0770-7
Lupo S, Bettucci L, Pérez A, Martínez S, Césari C, Escoriaza G, Gatica M (2006) Characterization and identification of the basidiomycetous fungus associated with “hoja de malvón” grapevine disease in Argentina. Phytopatholog Mediterr 45:S110–S116
Margesin R, Miteva V (2011) Diversity and ecology of psychrophilic microorganisms. Res Microbiol 162:346–361. doi:10.1016/j.resmic.2010.12.004
Margesin R, Feller G, Gerday C, Russell NJ (2002) Cold-adapted microorganisms: adaptation strategies and biotechnological potential. In: Bitton G (ed) Encyclopedia of environmental microbiology, vol 2. Wiley, New York, pp 871–885
Margesin R, Fauster V, Fonteyne PA (2005) Characterization of cold-active pectate lyases from psychrophilic Mrakia frigida. Lett Appl Microbiol 40:453–459. doi:10.1111/j.1472765X.2005.01704.x
Mikán Venegas JF, Castellanos Suárez DE (2004) Screening for isolation and characterization of microorganisms and enzymes with useful potential for degradation of cellulose and hemicellulose. Rev Colomb Biotecnol VI(1):58–71
Mtui G, Nakamura Y (2004) Lignin-degrading enzymes from mycelial cultures of Basiodiomycete fungi isolated in Tanzania. J Chem Eng Jpn 37(1):113–118. doi:10.1252/jcej.37.113
Nigam P, Singh D (1995) Enzyme and microbial systems involved in starch processing. Enzym Microb Tech 17:770–778. doi:10.1016/0141-0229(94)00003-A
Pandey A, Nigam P, Soccol C, Soccol V, Singh D, Mohan R (2000) Advances in microbial amylases. Biotechnol Appl Bioc 31:135–152. doi:10.1042/BA19990073
Paterson RRM, Bridge PD (1994) Biochemical techniques for filamentous fungi. IMI technical handbook 1, CAB Int
Pathan AAK, Bhadra B, Begum Z, Shivaji S (2010) Diversity of yeasts from Puddles in the vicinity of Midre Love′nbreen Glacier, Arctic and Bioprospecting for enzymes and fatty Acids. Curr Microbiol 60:307–314. doi:10.1007/s00284-009-9543-3
Rivas R, García-Fraile P, Mateos PF, Martínez-Molina E, Velázquez E (2007) Characterization of xylanolytic bacteria present in the bract phyllosphere of the date palm Phoenix dactylifera. Lett Appl Microbiol 44:181–187. doi:10.1111/j.1472-765X.2006.02050.x
Rodríguez K, Echer Ferreira MK, Salamoni Pinto S, Cofre Barragana V, Van Der Sand S (2007) Perfil da atividade enzimática de actinomicetos isolados de proceso de compostagem. Sinaferm XVI, BAM 0626
Ruisi S, Barreca D, Selbmann L, Zucconi L, Onofri S (2007) Fungi in Antarctica. Rev Environ Sci Biot 6:127–141. doi:10.1007/s11157-006-9107-y
Seeley HW Jr, Vandemark PJ, Lee JJ (1991) Microbes in action, 4th edn. Freeman WH and Company, New York
Selbmann L, Zucconi L, Ruisi S, Grube M, Cardinale M, Onofri S (2010) Culturable bacteria associated with Antarctic lichens: affiliation and psychrotolerance. Polar Biol 33:71–83. doi:10.1007/s00300-009-0686-2
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599. doi:10.1093/molbev/msm092
Tosi S, Kostadinova N, Krumova E, Pashova S, Dishliiska V, Spassova B, Vassilev S, Angelova M (2010) Antioxidant enzyme activity of filamentous fungi isolated from Livingston Island, Maritime Antarctica. Polar Biol 33:1227–1237. doi:10.1007/s00300-010-0812-1
Vihinen M, Mäntsälä P (1989) Microbial amylolytic enzymes. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 24:329–418. doi:10.3109/10409238909082556
Villalba LS, Mikan JF, Sánchez J (2004) Actividades hidrolíticas y caracterización enzimática de poblaciones microbianas aisladas del patrimonio documental del Archivo General de Colombia. Nova 2(2):49–58
Wang HY, Liu DM, Liu Y, Cheng CF, Ma QY, Huang Q, Zhang YZ (2007) Screening and mutagenesis of a novel Bacillus pumilus strain producing alkaline protease for dehairing. Lett Appl Microbiol 44:1–6. doi:10.1111/j.1472-765X.2006.02039.x
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ (eds) PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 315–322
Wickström MB (1983) Detection of microbial proteolytic activity by a cultivation plate assay in which different proteins adsorbed to a hydrophobic surface are used as substrates. Appl Environ Microb 45(2):393–400
Zhang J, Zeng R (2011) Molecular cloning and expression of an extracellular a-amylase gene from an Antarctic deep sea psychrotolerant Pseudomonas stutzeri strain 7193. World J Microb Biot 27:841–850. doi:10.1007/s11274-010-0526-0
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. Paul R. Gill for English corrections and valuable comments. This study was supported by a grant from the Comisión Sectorial de Investigación Científica—Universidad de la República and by Instituto Antártico Uruguayo.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Loperena, L., Soria, V., Varela, H. et al. Extracellular enzymes produced by microorganisms isolated from maritime Antarctica. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28, 2249–2256 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-012-1032-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-012-1032-3