Abstract
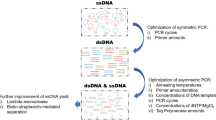
The generation of DNA aptamer by Systematic Evolution of Ligands by Exponential Enrichment requires a good method of ssDNA generation. There are various methods developed to generate ssDNA such as streptavidin-biotin based separation techniques, asymmetric PCR and strand separation of the PCR product containing primer with a terminator and an extension of 20 nucleotides on denaturing urea-polyacrylamide gel. In the present investigation, we have shown the possible improvements for the regular lambda nuclease digestion under optimized conditions. Optimization of the PCR cycles, time course studies on lambda nuclease digestion and purification of the ssDNA from the lambda exonuclease digestion mixture was found to be able to recover ssDNA amounting up to 39.19 ± 2.48 % of the starting amount of dsDNA. These strategies can be applied to the techniques involving essential usage of ssDNA.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adali AM, Paul A, Wilhem N, Ziemer G, Wendel HP (2001) Upgrading SELEX technology by using lambda exonuclease digestion for single-stranded dna generation. Molecules 15:1–11
Breaker RR (1997) DNA aptamers and DNA enzymes. Curr Opin Chem Biol 1:26–31
Brockstedt U, Uzarowska A, Montpetit A, Pfau W, Labuda D (2004) In vitro evolution of RNA aptamers recognizing carcinogenic aromatic amines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 313:1004–1008
Dapprich J (1999) Single-molecule DNA digestion by lambda-exonuclease. Cytometry 36:163–168
Ellington AD, Szostak JW (1990) In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 346:818–822
Gilbert W (1986) The RNA world. Nature 319:618
Gopinath SCB (2007) Methods developed for SELEX. Anal Bioanal Chem 1:171–182
Gopinath SCB, Kawasaki K, Kumar PK (2005) Selection of RNA-aptamer against human influenza B virus. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser (Oxf) 49:85–86
Gopinath SCB, Balasundaresan D, Akitomi J, Mizuno H (2006a) An RNA aptamer that discriminates bovine factor IX from human factor IX. J Biochem 140:667–676
Gopinath SCB, Misono TS, Kawasaki K, Mizuno T, Imai M, Odagiri T, Kumar PK (2006b) An RNA aptamer that distinguishes between closely related human influenza viruses and inhibits haemagglutinin-mediated membrane fusion. J Gen Virol 87:479–487
Gopinath SCB, Yuriko S, Kazunori K, Kumar PKR (2006c) An efficient RNA aptamer against human influenza B virus hemagglutinin. J Biochem 139:837–846
Gyllensten UB, Erlich HA (1988) Generation of single-stranded DNA by the polymerase chain reaction and its application to direct sequencing of the HLA-DQA locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:7652–7656
Hermann T, Patel DJ (2000) Adaptive recognition by nucleic acid aptamers. Science 287:820–825
Hultman T, Stahl S, Hornes E, Uhlen M (1989) Direct solid phase sequencing of genomic and plasmid DNA using magnetic beads as solid support. Nucleic Acids Res 17:4937–4946
Kujau MJ, Wolfl S (1997) Efficient preparation of single-stranded DNA for in vitro selection. Mol Biotechnol 7:333–335
Lato SM, Boles AR, Ellington AD (1995) In-vitro selection of RNA Lectins using combinatorial chemistry to interpret ribozyme evolution. Chem Biol 2:291–303
Little JW (1967) An exonuclease induced by bacteriophage lambda. II. Nature of the enzymatic reaction. J Biol Chem 242:679–686
Majerfeld I, Puthenvedu D, Yarus M (2005) RNA affinity for molecular Lhistidine; genetic code origins. J Mol Evol 61:226–235
Mendonsa SD, Bowser MT (2004) In vitro selection of high-affinity DNA ligands for human IgE using capillary electrophoresis. Anal Chem 76:5387–5392
Null AP, Hannis JC, Muddiman DC (2000) Preparation of single-stranded PCR products for electrospray ionization mass spectrometry using the DNA repair enzyme lambda exonuclease. Analyst 125:619–626
Paul A, Avci-Adali M, Ziemer G, Wendel HP (2009) Streptavidin-coated magnetic beads for DNA strand separation implicate a multitude of problems during cell-SELEX. Oligonucleotides 19:243–254
Saran D, Frank J, Burke DH (2003) The tyranny of adenosine recognition among RNA aptamers to coenzyme A. BMC Evol Biol 3:26
Sassanfar M, Szostak JW (1993) An RNA motif that binds ATP. Nature 364:550–553
Schou C, Heegaard NH (2006) Recent applications of affinity interactions in capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 27:44–59
Skrypina NA, Savochkina LP, Beabealashvilli RS (2004) In vitro selection of single-stranded DNA aptamers that bind human pro-urokinase. Nucleos Nucleot Nucl 23:891–893
Stojanovic MN, de Prada P, Landry DW (2000) Fluorescent sensors based on aptamer self-assembly. J Am Chem Soc 122:11547–11548
Tang J, Xie J, Shao N, Yan Y (2006) The DNA aptamers that specifically recognize ricin toxin are selected by two in vitro selection methods. Electrophoresis 27:1303–1311
Thomas KR, Olivera BM (1978) Processivity of DNA exonucleases. J Biol Chem 253:424–429
Wiegand TW, Williams PB, Dreskin SC, Jouvin MH, Kinet JP, Tasset D (1996) High-affinity oligonucleotide ligands to human IgE inhibit binding to Fc epsilon receptor I. J Immunol 157:221–230
Williams KP, Bartel DP (1995) PCR product with strands of unequal length. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4220–4221
Wooddell CI, Burgess RR (2010) Use of asymmetric PCR to generate long primers and single-stranded DNA for incorporating cross-linking analogs into specific sites in a DNA probe. Genome Res 6:886–892
Zha W, Zhu T, Zhao H (2003) Family shuffling with single-stranded DNA. Methods Mol Biol 231:91–97
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Universiti Sains Malaysia for awarding postgraduate fellowship to Citartan for this work and the support rendered by the Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation (MOSTI), under Brain Gain Malaysia, for the travelling and subsistence of Dr. Subash C.B. Gopinath to Malaysia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11274_2010_563_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Supplementary Fig. 1. Schematic flow for complete optimization processes carried out. (PDF 13 kb)
11274_2010_563_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
Supplementary Table 1. Statistical analysis of percentage of recovery of ssDNA after lambda exonuclease digestion (PDF 13 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Citartan, M., Tang, TH., Tan, SC. et al. Conditions optimized for the preparation of single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) employing lambda exonuclease digestion in generating DNA aptamer. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27, 1167–1173 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-010-0563-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-010-0563-8