Abstract
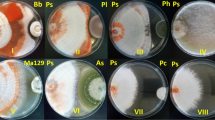
This work presents a preliminary report of a series of studies on the ability of several indigenous wood-rotting fungi from Chile to produce hydrolytic and ligninolytic enzymes and the evaluation of these native microorganism to future research on potential applications in bioremediation programs. Wood-rotting Basidiomycete fungi were collected from indigenous hardwood forest in the South of Chile. Twenty-eight strains were identified and qualitative enzymatic tests for peroxidases, laccase, tyrosinase, xylanase and cellulase production were performed in solid medium. Eleven selected strains were evaluated in liquid medium to quantify their ligninolytic enzyme production and their capacity to grow in solid medium supplemented with 2,4-dichlorophenol (2,4-DCF), 2,4,6-trichlorophenol (2,4,6-TCF) and pentachlorophenol (PCP). PCP degradation and ligninolytic enzymes production were also evaluated in liquid medium. Results showed that laccase was present in 28 of the selected strains (≈73%). Peroxidase was present in 40% and cellulase in 37% of the strains. Xilanase and tyrosinase were obtained in a smaller percentage in the strains (28% and 7%, respectively). The 11 selected strains showed high concentrations of lignin peroxidase (Lip) and manganese peroxidase (MnP). Anthracophyllum discolor (Sp4), produced LiP and MnP at 90.3 and MnP 125.5 U L−1 respectively, compared to the control fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium CECT-2798 that produced 58.1 and 118.4 U L−1 of LiP and MnP. Tolerance test showed that native Chilean fungi did not present high tolerance to 2,4,6-TCF and PCP but were quite tolerant to 25 and 50 mg L−1 of 2,4-DCF. However, pre-acclimatization in 2,4-DCP notably improved the growth in medium with 2,4,6-TCP and PCP. PCP in liquid medium was efficiently degraded by the fungi Anthracophyllum discolor, Lenzites betulina (Ru-30) and Galerina patagónica (Sp3), and the major MnP activity was produced by A. discolor (Sp4) (67 U L−1).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agosín E, Daudin J, Odier E (1985) Screening of white-rot fungi on (14C) lignin-labelled and (14C) whole-labelled wheat straw. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 22:132–138. doi:10.1007/BF00250033
Alleman BC, Logan BE, Gilbertson RL (1992) Toxicity of pentachlorophenol to six species of white rot fungi as a function of chemical dose. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:4048–4050
Alleman BC, Logan BE, Gilbertson RL (1993) A rapid method to screen fungi for resistance to toxic chemicals. Biodegradation 4:125–129. doi:10.1007/BF00702329
Ander P, Eriksson KE (1977) Selective degradation of wood components by white rot fungi. Plant Physiol 41:239–248. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1977.tb04877.x
Atik C, Imamoglu S, Bermek H (2006) Impact of xylanase pre-treatment on peroxide bleaching stage of biokraft pulp. Int Biodet Biodeg 18:22–26. doi:10.1016/j.ibiod.2006.04.003
Barr DP, Aust SD (1994) Enzyme degradation of lignin. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 138:49–72
Breitenbach J, Kränzlin F (1986) Fungi of Switzerland. Non gilled fungi, vol. 2. Verlag Mykologia, Switzerland, 411 p
Buckley KF, Dobson ADW (1998) Extracellular ligninolytic enzyme production and polymeric dye decolorization in immobilized cultures of Chrysosporium lignorum CL1. Biotech Lett 20:301–306
Cea M, Rubilar O, Tortella G, Diez MC (2007) Utilization of straw as substrate to enhance the ligninolytic and degradative activity of Anthracopyllum discolor and indigenous microorganisms in a Chilean soil contaminated with PCP. In: Proceeding of third international conference, enzymes in the environment. Viterbo, Italia, July 15–19
deJong E, Field JA, Debont JAM (1994) Aryl alcohols in the physiology of ligninolytic fungi. FEBS Microbiol Rev 13:153–188
de Koker TH, Zhao J, Cullen D, Janse BJH (1998) Biochemical and molecular characterization of South African strains of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Mycol Res 102:88–92. doi:10.1017/S095375629700453X
de Koker T, Zhao J, Allsop S, Janse B (2000) Isolation and enzymic characterization of South African white-rot fungi. Mycol Res 104:820–824. doi:10.1017/S0953756299002373
Dhouib A, Hamza M, Zouari H, Mechichi T, Hmidi R, Labat M, Martinez MJ, Sayadi S (2005) Screening for ligninolytic enzyme production by diverse fungi from Tunisia. World J Microbiol Technol 21:1514–1523
Donoso C, Becerra J, Martínez M, Garrido N, Silva M (2008) Degradative ability of 2,4,6-tribromophenol by saprophytic fungi Trametes versicolor and Agaricus augustus isolated from Chilean forestry. World J Microbiol Technol 24:961–968
D’Souza TM, Merritt CS, Reddy CA (1999) Lignin-modifying enzymes of the white rot basidiomycete Ganoderma lucidum. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:5307–5313
Durán N, Esposito E (2000) Potential applications of oxidative enzymes and phenoloxidase-like compounds in wastewater and soil treatment: a review. Appl Catal B Environ 28:83–99
Elissetche JP, Ferraz A, Parra C, Freer J, Baeza J, Rodríguez J (2001) Biodegradation of Chilean native wood species Drimys winteri and Nothofagus dombeyi, by Ganoderma australe. World J Microbiol Technol 17:577–581
Field JA, de Jong E, Costa GF, de Bont JA (1992) Biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by new isolates of white- rot fungi. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:2219–2226
Ford CI, Walter M, Northcott GL, Di HJ, Cameron KC, Trower T (2007a) Fungal inoculum properties: extracellular enzyme expression and pentachlorophenol removal in highly contaminated field soils. J Environ Qual 36:1599–1608
Ford CI, Walter M, Northcott GL, Di HJ, Cameron KC, Trower T (2007b) Fungal inoculum properties: extracellular enzyme expression and pentachlorophenol removal by New Zealand Trametes species in contaminated field soils. J Environ Qual 36:1749–1759
Galeno G, Agosin E (1990) Screening of white-rot fungi for efficient decolourization of bleach pulp effluents. Biotechnol Lett 12:869–872
Galliano H, Gas G, Seris JL, Boudet AM (1991) Lignin degradation by Rigidoporus lignosus involves synergistic action of two oxidizing enzymes: Mn peroxidase and laccase. Enzyme Microb Technol 13:478–482
Gianfreda L, Rao M (2004) Potencial of extra cellular enzymes in remediation of polluted soils: a review. Enzyme Microb Technol 35:339–354
Gianfreda L, Xu F, Bollag JM (1999) Laccases: a useful group of oxidoreductive enzymes. Bioremediat J 3:1–25
Guimarães L, Peixoto-Nogueira S, Michelin M, Rizzatti A, Sandrim V, Zanoelo F, Aquino A, Barbosa B Jr, Polizeli ML (2006) Screening of filamentous fungi for production of enzymes of biotechnological interest. Braz J Microbiol 37:474–480
Hernandez-Luna CE, Gutierrez-Soto G, Salcedo-Martinez SM (2008) Screening for decolorizing basidiomycetes in Mexico. World J Microbiol Technol 24:465–473
Husain Q (2006) Potential applications of the oxidoreductive enzymes in the decolorization and detoxification of textile and other synthetic dyes from polluted water: a review. Crit Rev Biotechnol 60:201–221
Kachlishvili E, Penninckx MJ, Tsiklauri N, Elisashvili V (2006) Effect of nitrogen source on lignocellulolytic enzyme production by white-rot basidiomycetes under solid-state cultivation. World J Microbiol Technol 22:391–397
Kersten P, Cullen D (2007) Extracellular oxidative systems of the lignin-degrading basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Fungal Genet Biol 44:77–87
Lamar RT, Larsen MT, Kirk TK (1990) Sensitivity to and degradation of pentachlorophenol by Phanerochaete spp. Appl Environ Microbiol 56(11):3519–3526
Lazo W (2001) Hongos de Chile. Atlas Micológico. Facultad de Ciencias de la Universidad de Chile, Salesianos S.A, Chile, 231 p
Leontievsky A, Myasoedova N, Golovleva L, Sedaraty M, Evans C (2002) Adaptation of the white rot basidiomycete Panus tigrinus for transformation of high concentrations of chlorophenols. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 59:599–604
Leung P, Pointing S (2002) Effect of different carbon and nitrogen regimes on Poly-R decolorization by white rot fungi. Mycol Res 106:86–92
Levin L, Forchiassin F, Ramos AM (2002) Copper induction of lignin modifying enzymes in the white rot fungus Trametes trogii. Mycologia 94:377–383
Levin L, Papinutti L, Forchiassin F (2004) Evaluation of Argentinean white rots fungi for their ability to produce lignin-modifying enzymes and decolorize industrial dyes. Biores Technol 2:169–176
Machado K, Matheus D, Bononi V (2005) Ligninolytic enzymes production and Remazol brilliant blue R decolorization by tropical Brazilian Basidiomycetes fungi. Braz J Microbiol 36:246–252
Marr CD, Grund DW, Harrison KA (1986) The taxonomic potential of laccase and tyrosinase spot tests. Mycologia 78:169–184
Martinez M, Baeza J, Freer J, Rodriguez J (2000) Chlorophenol tolerant and degradative bacteria isolated from a river receiving pulp mill discharger. Toxicol Environ Chem 77:159–170
Mendoza-Cantú A, Albores A, Fernández-Linares L, Rodríguez-Vázquez R (2000) Pentachlorophenol biodegradation and detoxification by the white rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Environ Toxicol 15:107–113
Mileski GJ, Bumpus JA, Jurek MA, Aust SD (1988) Biodegradation of penthachorophenol by the white rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:2885–2889
Montiel AM, Fernández FJ, Marcial J, Soriano J, Barrios-González J, Tomasini A (2004) A fungal phenoloxidase (tyrosinase) involved in pentachlorophenol degradation. Biotechnol Lett 26(17):1353–1357
Moreno G, Manjon J, Zugaza A (1986) La guía de INCAFO de los hongos de la Península Ibérica, volumen 1. Incafo, Madrid, 650 p
Novotny C, Svobodova K, Erbanova P, Cajthaml T, Kasinath A, Lang E, Sasek V (2004) Ligninolytic fungi in bioremediation: extracellular enzyme production and degradation rate. Soil Biol Biochem 36:1545–1551
Peláes F, Martínez MJ, Martínez AT (1995) Screening of 68 species of basidiomycetes for enzymes evolved in lignin degradation. Mycol Res 99:37–42
Pointing S (1999) Qualitative methods for the determination of lignocellulolytic enzyme production by tropical fungi. Fungal Divers 2:17–33
Pointing SB, Vrijmoed LLP, Jones EBG (1999) Laccase is produced as the sole lignin modifying enzyme in submerged liquid culture by the white-rot fungus Pycnoporus sanguineus. L. Mycologia 91:345–349
Reddy GB, Gold M (2000) Degradation of pentachlorophenol by Phanerochaete chrysosporium: intermediates and reactions involved. Microbiology 146:405–413
Rho D, Desrochers M, Jurasek L, Driguez H, Defaye J (1982) Induction of cellulase in Schizophyllum commune: thiocellobioseas a new inducer. J Bacteriol 149:47–53
Rigas F, Marchant R, Dritsa V, Kapsanaki-Gotsi E, Avramides L (2003) Screening of wood rotting fungi potentially useful for the degradation of organic pollutants. WASP Focus 3:201–210
Rubilar O, Feijoo G, Diez MC, Lu-Chau TA, Moreira MT, Lema JM (2007) Biodegradation of pentachlorophenol in soil slurry cultures by Bjerkandera adusta and Anthracophyllum discolor. Ind Eng Chem Res 46:744–6751
Sedarati MR, Keshavarz T, Leontievsky AA, Evans CS (2003) Transformation of high concentrations of chlorophenols by the white-rot basidiomycete Trametes versicolor immobilized on nylon mesh. Electron J Biotechnol 6:104–114
Steiner W, Lafferty RM, Gomes I, Esterbauer H (2004) Studies on a wild strain of Schizophyllum commune: cellulase and xylanase production and formation of the extracellular polysaccharide Schizophyllan. Biotechnol Bioeng 30:169–178
Tekere M, Ncube I, Read JS, Zvauya R (2001) Biodegradation of the organochlorine pesticide, lindane by a subtropical white rot fungus in batch and packed bed bioreactor system. Environ Technol 23:199–206
Tien M, Kirk TK (1983) Lignin-degrading enzyme from the hymenomycete Phanerochaete chrysosprium Burd. Science 221:661–663
Tien M, Kirk TK (1984) Lignin-degrading enzyme from Phanerochaete chrysosporium: purification, characterization, and catalytic properties of a unique H2O2-requiring oxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:2280–2284
Tortella G, Diez MC, Durán N (2005) Fungal diversity and use in decomposition of environmental pollutants. Crit Rev Microbiol 31:197–212
Tortella G, Rubilar O, Donoso C, Acevedo F, Diez MC (2006a) Utilización de Anthracophyllum discolor inmovilizado sobre sustrato orgánico para la descontaminación de residuos líquidos. In: Proceeding of AIDIS congress, Punta del Este, Uruguay, 26–11 de November 2006
Tortella G, Rubilar O, Mora ML, Diez MC (2006b) Selection of Chilean native wood-rot fungi for bioremediation of allophanic soil contaminated with chlorophenols. In: Proceeding of 18th world congress of soil science, Pensylvania USA, 9 al 15 de July 2006
Walter M, Guthrie J, Sivakumaran S, Parker E, Slade A, McNaughton D, Boyd-Wilson K (2003) Screening of New Zealand native white-rot isolates for PCP degradation. Bioremediat J 7:119–128
Walter M, Boul L, Chong R, Ford C (2004) Growth substrate selection and biodegradation of PCP by New Zealand white-rot fungi. J Environ Manage 71:361–369
Willick GE, Morosoli R, Seligy VL, Yaguchi M, Desrochers M (1984) Extracellular proteins secreted by the basidiomycete Schizophyllum commune in response to carbon source. J Bacteriol 159:294–299
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by FONDECYT 1050614 project—DIUFRO 160606 y DIUFRO GAP-2007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tortella, G.R., Rubilar, O., Gianfreda, L. et al. Enzymatic characterization of Chilean native wood-rotting fungi for potential use in the bioremediation of polluted environments with chlorophenols. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24, 2805–2818 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-008-9810-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-008-9810-7