Abstract
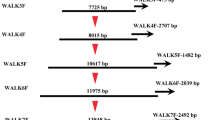
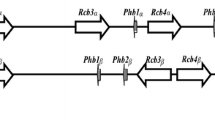
The edible fungus Lentinula edodes is a heterothallic homobasidiomycete whose mating is controlled by a bifactorial incompatibility mating system determined by two unlinked factors (the A and B mating-type factors). Although this mechanism is well accepted, there is a lack of understanding about its molecular basis, as the incompatibility factors have not been cloned and sequenced. In this study, by means of degenerate PCR we obtained one 773 bp DNA fragment cosegregating with B 2 mating-type factor in L. edodes stock HL01. Sequencing analysis revealed that it belonged to a pheromone receptor, suggesting that the genetic basis for B factor in L. edodes is the same as in the two model mushroom species, Schizophyllum commune and Coprinus cinereus, the structure and function of whose B incompatibility factors have been studied in detail. So far as we know, this is the first report about the cloning of B mating factor in L. edodes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Casselton LA, Olesnicky NS (1998) Molecular genetics of mating recognition in basidiomycete fungi. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:55–70
Darmono TW, Burdsall HH (1992) Morphological characteristics of incompatibility reactions and evidence for nuclear migration in Armillaria mellea. Mycologia 84:367–375
Giasson L, Specht CA, Milgrim C, Novotny CP, Ullrich RC (1989) Cloning and comparison of Aα mating-type alleles of the basidiomycete Schizophyllum commune. Mol Gen Genet 218:72–77
Gieser PT, May G (1994) Comparison of two b1 alleles from within the A mating-type of the basidiomycete Coprinus cinereus. Gene 146:167–176
Halsall JR, Milner MJ, Casselton LA (2000) Three subfamilies of pheromone and receptor genes generate multiple B mating specificities in the mushroom Coprinus cinereus. Genetics 154:1115–1123
James TY, Liou SR, Vilgalys R (2004) The genetic structure and diversity of the A and B mating type genes from the tropical oyster mushroom, Pleurotus djamor. Fungal Genet Biol 41:813–825
Kothe E (2001) Mating-type genes for basidiomycete strain improvement in mushroom farming. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56:602–612
Kronstad JV, Staben C (1997) Mating type in filamentous fungi. Annl Rev Genet 31:245–276
Kües U, Wendy VJ, Tymon AM, Mutasa ES, Gottgens B, Gaubatz S, Gregoriades A, Casselton LA (1992) The combination of dissimilar alleles of the Aα and Aβ gene complexes, whose proteins contain homeo domain motifs, determines sexual development in the mushroom Coprinus cinereus. Genes Develop 6:568–577
Kües U, Rachel NAO, Mutasa ES, Pardo EH, O’Shea SF, Gottgens B, Casselton LA (1994a) Two classes of homedomain proteins specify the multiple A mating types of mushroom Coprinus cinereus. Plant Cell 6:1467–1475
Kües U, Tymon AM, Richardson WV, May G, Gieser PT, Casselton LA (1994b) A mating-type factors of Coprinus cinereus have variable numbers of specificity genes encoding two classes of homeodomain proteins. Mol Gen Genet 245:45–52
Larraya L, Penas MM, Perez G, Santos C, Ritter E, Pisabarro AG, Ramirez L (1999) Identification of incompatibility alleles and characterization of molecular marker genetically linked to the A incompatibility locus in the white rot fungus Pleurotus ostreatus. Curr Genet 34:486–493
Larraya LM, Perez G, Iribarren I, Blanco JA, Alfonso M, Pisabarro AG, Ramirez L (2001) Relationship between monokaryotic growth rate and mating type in the edible basidiomycete Pleurotus ostreatus. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:3385–3390
Lin FC, Wang ZW, Yang XM (2000a) Cultivation of the black oak mushroom Lentinula edodes in China, p.955–958. In: Van Griesven LJLD (ed) Science and cultivation of Edible Fungi. Balkema Publishers, Rotterdam. ISBN 9058091449
Lin FC, Wang ZW, Dai JH (2000b) Application of OWE-SOJ technique to the determination of mating interactions in Lentinula edodes. Acta Edulis Fungi 7:8–10
Lin FC, Wang ZW, Sun Y, Cai YJ (2003) Analysis of the mating type factors in natural population of lentinula edodes in China. Mycosystema 22:235–240 (In Chinese)
May G, Chevanton LL, Pukkila PJ (1991) Molecular analysis of the Coprinus cinereus mating type A factor demonstrates an unexpectedly complex structure. Genetics 128:529–538
May G, Matzke E (1995) Recombination and variation at the A mating-type of Coprinus cinereus. Mol Biol Evol 12:794–802
Murakami S, Takemaru T (1975) “Puff” mutation induced by UV irradiation in Lentinus edodes (Berk.) Sing. Rep Tottori Mycol Inst 12:47–51
O’Shea SF, Chaure PT, Halsall JR, Olesnicky NS, Leibbrandt A, Connerton IF, Casselton LA (1998) A large pheromone and receptor gene complex determines multiple B mating type specificities in Coprinus cinereus. Genetics 148:1081–1090
Specht CA (1995) Isolation of the Bα and Bβ mating-type loci of Schizophyllum commune. Curr Genet 28:374–379
Specht CA, Stankis MM, Giasson L, Novotny CP, Ullrich RC (1992) Functional analysis of the homeodomain-related proteins of the Aα locus of Schizophyllum commune. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:7174–7178
Specht CA, Stankis MM, Novotny CP, Ullrich RC (1994) Mapping the heterogeneous DNA region hat determines the nine Aα mating-type specificities of Schizophyllum commune. Genetics 137:709–714
Stankis MM, Specht CA, Yang H, Giasson L, Ullrich RC, Novotny CP (1992) The Aα mating locus of Schizophyllum commune encodes two dissimilar multiallelic homeodomain proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:7169–7173
Tanaka A, Miyazaki K, Murakami H, Shiraishi S (2004) Sequence characterized amplified region markers tightly linked to the mating factors of Lentinula edodes. Genome 47:156–162
Tokimoto K, Komatsu M, Takemaru T (1973) Incompatibility factors in the natural population of Lentinula edodes in Japan. Rep. Tottori Mycol Inst 10:371–376 (In Japanese)
Vaillancourt LJ, Raudaskoski M, Specht CA, Raper GA (1997) Multiple genes encoding pheromones and a pheromone receptor define the Bβ1 mating-type specificity in Schizophyllum commune. Genetics 146:541–551
Wendland J, Vaillancourt LJ, Hegner J, Lengeler KB, Laddison KJ, Specht CA, Raper CA, Kothe E (1995) The mating-type locus B alpha 1 of Schizophyllum commune contains a pheromone receptor gene and putative pheromone genes. EMBO J 14:5271–5278
Zhang YF, Molina FI (1995) Strain typing of Lentinula edodes by random amplified polymorphic DNA assay. FEMS Microbiol Letts 131:17–20
Zhao J, Chang ST (1993) Monokaryotization by protoplasting heterothallic species of edible mushrooms. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 9:538–543
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge support for this work from National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 30170024), the Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (Grant No. 2002050421) and the Research Fund of Huazhong Agricultural University of China (Grant No. 2006073).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, AZ., Xu, XF., Lin, FX. et al. Cloning and identification of partial DNA fragment for the B mating-type factor in Lentinula edodes using degenerate PCR. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 23, 411–415 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-006-9239-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-006-9239-9