Abstract
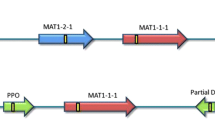
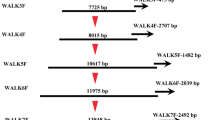
We have identified the seven genes that constitute the A43 mating-type factor of Coprinus cinereus and compare the organisation of A43 with the previously characterised A42 factor. In both, the genes that trigger clamp cell development, the so-called specificity genes, are separated into α and β loci by 7 kb of noncoding sequence and are flanked by homologous genes α-fg and β-fg. The specificity genes are known to encode two classes of dissimilar homeodomain (HD1 and HD2) proteins and have different allelic forms which show little or no cross-hybridisation. By partial sequencing we identified a divergently transcribed HD1 (a1-2) and HD2 (a2-2) gene in the A43 α locus. a2-2 failed to elicit clamp cell development in three different hosts, suggesting that it is non-functional. a1-2 elicited clamp cells in an A42 host that has only an HD2 gene (a2-1) in its α locus, thus demonstrating that the compatible Aα mating interaction is between an HD1 and an HD2 protein. The A43 β locus contains three specificity genes, the divergently transcribed HD1 and HD2 genes b1-2 and b2-2 and a third HD1 gene (d1-1) that was shown by hybridisation and transformation analyses to be functionally equivalent to d1-1 in A42. An untranscribed footprint of a third A42 HD1 gene, c1-1, was detected between the A43 b2-2 and d1-1 genes by Southern hybridisation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakkeren G, Kronstad J. (1993) Conservation of the b mating-type gene complex among bipolar and tetrapolar smut fungi. Plant Cell 5:123–136
Binninger DM, Skrzynia C, Pukkila PJ, Casselton LA (1987) DNA-mediated transformation of the basidiomycete Coprinus cinereus. EMBO J 6:835–840
Casselton LA (1978) Dikaryon formation in higher basidiomycetes. In: Smith JE, Berry DR (eds) The filamentous fungi, vol 3. Edward Arnold, London, pp 275–295
Casselton LA, de la Fuente Herce A (1989) Heterologous gene expression in the basidiomycete fungus Coprinus cinereus. Curr Genet 16:35–40
Casselton LA, Kües U (1994) The multiallelic mating-type genes of homobasidiomycetes. In: Esser K, Lemke P (eds) The Mycota, vol 1. Wessels JGH, Meinhardt F (eds) Growth, Differentiation and Sexuality. Springer-Verlag Berlin (in press)
Day PR (1960) The structure of the A mating type locus in Coprinus lagopus. Genetics 45:641–650
Gieser PT, May G (1994) Comparison of two b1 alleles from within the A mating type of the basidiomycete Coprinus cinereus. Gene (in press)
Gillissen B, Bergemann J, Sandmann C, Schroer B, Bölker M, Kahmann R (1992) A two-component system for self/non-self recognition in Ustilago maydis. Cell 68:647–657
Kronstad JW, Leong SA (1990) The b mating type locus of Ustilago maydis contains variable and constant regions. Genes Dev 4:1384–1395
Kües U, Casselton LA (1992) Homeodomains and regulation of sexual development in basidiomycetes. Trends Genet 8:154–155
Kües U, Casselton LA (1993) The origin of multiple mating types in mushrooms. J Cell Sci 104:227–230
Kües U, Richardson WVJ, Tymon AM, Mutasa ES, Göttgens B, Gaubatz S, Gregoriades A, Casselton LA (1992) The combination of dissimilar alleles of the Aα and Aβ gene complexes, whose proteins contain homeo domain motifs, determines sexual development in the mushroom Coprinus cinereus. Genes Dev. 6:568–577
May G, Le Chevanton L, Pukkila PJ (1991) Molecular analysis of the Coprinus cinereus mating-type A factor demonstrates an unexpectedly complex structure. Genetics 128:529–538
Mellon FM, Little PFR, Casselton LA (1987) Gene cloning and transformation in the basidiomycete fungus Coprinus cinereus: isolation and expression of the isocitrate lyase gene (acu-7). Mol Gen Genet 210:352–357
Mutasa ES, Tymon AM, Göttgens B, Mellon FM, Little PFR, Casselton LA (1990) Molecular organisation of an A mating type factor of the basidiomycete fungus Coprinus cinereus. Curr Genet 18:223–229
Phillips CL, Vershon AK, Johnson AD, Dahlquist FW (1991) Secondary structure of the homeodomain of yeast α2 repressor determined by NMR spectroscopy. Genes Dev 5:764–772
Raper JR (1966) Genetics of Sexuality in Higher Fungi. The Ronald Press Company, New York
Rao PS, Niederpruem DJ (1969) Carbohydrate metabolism during morphogenesis of Coprinus cinereus (sensu Buller). J Bact 100:1222–1228
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbour Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Schulz B, Banuett F, Dahl M, Schlesinger R, Schäfer W, Martin T, Herskowitz I, Kahmann R (1990) The b alleles of U. maydis, whose combinations program pathogenic development, code for polypeptides containing a homeodomain-related motif. Cell 60:295–306
Specht CA, Stankis MM, Giasson L, Novotny CP, Ullrich RC (1992) Functional analysis of the A homeodomain-related proteins of the Aα locus of Schizophyllum commune. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:7174–7178.
Stankis MM, Specht CA, Yang H, Giasson L, Ullrich RC, Novotny CP (1992) The Aα mating type locus of Schizophyllum commune encodes two dissimilar, multiallelic, homeodomain proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:7169–7173
Tymon AM, Kües U, Richardson WVJ, Casselton LA (1992) A fungal mating type protein that regulates sexual and asexual development contains a POU-related domain. EMBO J 11:1805–1813
Wolberger C, Vershon AK, Liu B, Johnson AD, Pabo CO (1991) Crystal structure of a MATT homeodomain-operator complex suggests a general model for homeodomain-DNA interactions. Cell 67:517–528
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by C. A. M. J. J. van den Hondel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kües, U., Tymon, A.M., Richardson, W.V.J. et al. A mating-type factors of Coprinus cinereus have variable numbers of specificity genes encoding two classes of homeodomain proteins. Molec. Gen. Genet. 245, 45–52 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00279749
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00279749