Abstract
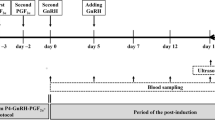
Environmental heat stress has a deleterious impact on farm animal reproductive performance. The purpose of this study was to see how the addition of melatonin affected the efficacy of the superovulation regimen in goats in hot climatic conditions. Sixteen Shiba goats were synchronized and divided into two equal groups (n = 8, each): the melatonin group, which received a single S/C dose of melatonin, and a control group, treated with one ml of corn oil only. Ultrasonographic assessment of ovarian structures (Graafian follicles; GFs and corpus lutea; CLs) morphometry and hemodynamics were performed during the estrous phase of the superovulation (D0) and at day7 after ovulation (D7) of the superovulation regimen. The peripheral reproductive hormones were measured, and microRNAs were characterized. The mean diameter and the total-colored area of GFs during the D0 were significantly (P˂0.05) higher in the melatonin group (5.42 ± 0.11 mm and 1592.20 ± 45.26 pixels, respectively) compared to the control group (4.62 ± 0.12 mm and 1052.55 ± 29.47 pixels, respectively). Concentrations of LH and E2 increased significantly (P˂0.05) in the melatonin group (1.06 ± 0.06 ng/ml and 46.34 ± 2.77 pg/ml, respectively) compared to the control group (0.75 ± 0.12 ng/ml and 29.33 ± 1.89 pg/ml, respectively). At D7, the melatonin-received goats attained greater values in the mean count (6.75 ± 0.33, P˂0.005), diameters (6.08 ± 0.12 mm, P˂0.01), and total-colored area (17137.30 ± 128.53 pixels, P˂0.01) of detected CLs and progesterone concentrations (4.08 ± 0.24 ng/ml) compared to control goats (4.00 ± 0.28, 4.50 ± 0.19 mm, 11156.87 ± 117.90 pixels, and 2.90 ± 0.18 ng/ml respectively). MiRNA expression analysis was identified during both stages denoting several up and downregulated miRNA candidates among the studied groups. In conclusion, incorporating melatonin enhanced the efficiency of the superovulation regimen in goats under hot climatic conditions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acosta TJ, Miyamoto A (2004) Vascular control of ovarian function: ovulation, corpus luteum formation and regression. Anim Reprod Sci 82–83:127–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anireprosci.2004.04.022
Acosta TJ, Hayashi KG, Ohtani M, Miyamoto A (2003) Local changes in blood flow within the preovulatory follicle wall and early corpus luteum in cows. Reproduction 125(5):759–767 PMID: 12713439
Agarwal A, Gupta S, Sharma RK (2005) Role of oxidative stress in female reproduction. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 3:28. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-7827-3-28
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW, Bartel DP (2015) Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. Elife 4:e05005. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.05005
Al-Zubaidi U, Adhikari D, Cinar O, Zhang QH, Yuen WS, Murphy MP, Rombauts L, Robker RL, Carroll J (2021) Mitochondria-targeted therapeutics, MitoQ and BGP-15, reverse aging-associated meiotic spindle defects in mouse and human oocytes. Hum Reprod 36(3):771–784. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/deaa300
Antolín I, Rodríguez C, Saínz RM, Mayo JC, Uría H, Kotler ML, Rodríguez-Colunga MJ, Tolivia D, Menéndez-Peláez A (1996) Neurohormone melatonin prevents cell damage: effect on gene expression for antioxidant enzymes. FASEB J 10(8):882–890. https://doi.org/10.1096/fasebj.10.8.8666165
Arai K, Watanabe G, Fujimoto M, Nagata S, Takemura Y, Taya K, Sasamoto S (1995) A sensitive radioimmunoassay for cortisol using 125I-labeled radioligand. J Reprod Dev 41:j15–j20. https://doi.org/10.1262/jrd.95-415j15
Araki K, Arai KY, Watanabe G, Taya K (2000) Involvement of inhibin in the regulation of follicle-stimulating hormone secretion in the young adult male Shiba goat. J Androl 21(4):558–565
Arashiro EKN, Ungerfeld R, Clariget RP, Pinto PHN, Balaro MFA, Bragança GM, Ribeiro LS, Fonseca JFD, Brandão FZ (2018) Early pregnancy diagnosis in ewes by subjective assessment of luteal vascularisation using colour Doppler Ultrasonography. Theriogenology 106:247–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2017.10.029
Badinga L, Thatcher WW, Diaz T, Drost M, Wolfenson D (1993) Effect of environmental heat stress on follicular development and steroidogenesis in lactating Holstein cows. Theriogenology 39(4):797–810. https://doi.org/10.1016/0093-691x(93)90419-6
Balaro MFA, Santos AS, Moura LFGM, Fonseca JF, Brandão FZ (2017) Luteal dynamic and functionality assessment in dairy goats by luteal blood flow, luteal biometry, and hormonal assay. Theriogenology 95:118–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2017.02.021
Barritt JA, Brenner CA, Cohen J, Matt DW (1999) Mitochondrial DNA rearrangements in human oocytes and embryos. Mol Hum Reprod 5(10):927–933. https://doi.org/10.1093/molehr/5.10.927
Berlinguer F, Leoni GG, Succu S, Spezzigu A, Madeddu M, Satta V, Bebbere D, Contreras-Solis I, Gonzalez-Bulnes A, Naitana S (2009) Exogenous melatonin positively influences follicular dynamics, oocyte developmental competence and blastocyst output in a goat model. J Pineal Res 46(4):383–391. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2009.00674.x
Bollwein H, Heppelmann M, Lüttgenau J (2016) Ultrasonographic Doppler Use for Female Reproduction Management. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract 32(1):149–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cvfa.2015.09.005
Brockus KE, Hart CG, Gilfeather CL, Fleming BO, Lemley CO (2016) Dietary melatonin alters uterine artery hemodynamics in pregnant Holstein heifers. Domest Anim Endocrinol 55:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.domaniend.2015.10.006
Cao Y, Li R, Li W, Liu H, Cai Y (2021) Melatonin attenuates Peroxynitrite-Induced Meiosis Dysfunction in Porcine oocytes. Reprod Sci 28(5):1281–1289. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43032-020-00331-2
Cesana BM, Antonelli P (2016) Sample size calculations in clinical research should also be based on ethical principles. Trials 17(1):149. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-016-1277-5
Chen X, Ba Y, Ma L, Cai X, Yin Y, Wang K, Guo J, Zhang Y, Chen J, Guo X, Li Q, Li X, Wang W, Zhang Y, Wang J, Jiang X, Xiang Y, Xu C, Zheng P, Zhang J, Li R, Zhang H, Shang X, Gong T, Ning G, Wang J, Zen K, Zhang J, Zhang CY (2008) Characterization of microRNAs in serum: a novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other Diseases. Cell Res 18(10):997–1006. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2008.282
Chow S, Shao J, Wang H (2008) Sample size calculations in Clinical Research, 2nd edn. Chapman & Hall/CRC Biostatistics Series, p 58
Cognié Y, Baril G, Poulin N, Mermillod P (2003) Current status of embryo technologies in sheep and goat. Theriogenology 59(1):171–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0093-691x(02)01270-0
Cook JS, Sauder CL, Ray CA (2011) Melatonin differentially affects vascular blood flow in humans. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 300(2):H670–H674. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00710.2010
Cosentino IO, Balaro MFA, Leal FSC, Carvalho ABDS, Cortat de Souza PR, Arashiro EKN, Brandão FZ (2018) Accuracy of assessment of luteal morphology and luteal blood flow for prediction of early pregnancy in goats. Theriogenology 121:104–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2018.08.007
Deguettes Q, Fattal E, Moreau M, Lego E, Bochot A (2020) Controlled delivery of follicle-stimulating hormone in cattle. Int J Pharm 590:119904. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.119904
Dickey RP (1997) Doppler ultrasound investigation of uterine and ovarian blood flow in infertility and early pregnancy. Hum Reprod Update 3(5):467–503. https://doi.org/10.1093/humupd/3.5.467
Donadeu FX, Sontakke SD, Ioannidis J (2016) MicroRNA indicators of follicular steroidogenesis. Reprod Fertil Dev. https://doi.org/10.1071/RD15282
El-Tarabany MS, El-Tarabany AA, Atta MA (2017) Physiological and lactation responses of Egyptian dairy Baladi goats to natural thermal stress under subtropical environmental conditions. Int J Biometeorol 61(1):61–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-016-1191-2
Esposito L, Salzano A, Russo M, de Nicola D, Prandi A, Gasparrini B, Campanile G, Neglia G (2020) Corpus Luteum Color Doppler Ultrasound and pregnancy outcome in Buffalo during the Transitional Period. Anim (Basel) 10(7):1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10071181
Galano A, Tan DX, Reiter RJ (2011) Melatonin as a natural ally against oxidative stress: a physicochemical examination. J Pineal Res 51(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2011.00916.x
Gonźalez-Bulnes A, Baird DT, Campbell BK, Cocero MJ, García-García RM, Inskeep EK, López-Sebastián A, McNeilly AS, Santiago-Moreno J, Souza CJ, Veiga-López A (2004) Multiple factors affecting the efficiency of multiple ovulation and embryo transfer in sheep and goats. Reprod Fertil Dev 16(4):421–435. https://doi.org/10.10371/RD04033
Guimarães CR, Oliveira ME, Rossi JR, Fernandes CA, Viana JH, Palhao MP (2015) Corpus luteum blood flow evaluation on Day 21 to improve the management of embryo recipient herds. Theriogenology 84(2):237–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2015.03.005
Hamada T, Watanabe G, Kokuho T, Taya K, Sasamoto S, Hasegawa Y, Miyamoto K, Igarashi M (1989) Radioimmunoassay of inhibin in various mammals. J Endocrinol 122(3):697–704. https://doi.org/10.1677/joe.0.1220697
Hanke M, Hoefig K, Merz H, Feller AC, Kausch I, Jocham D, Warnecke JM, Sczakiel G (2010) A robust methodology to study urine microRNA as Tumor marker: microRNA-126 and microRNA-182 are related to urinary Bladder cancer. Urol Oncol 28(6):655–661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2009.01.027
Hansen PJ (2009) Effects of heat stress on mammalian reproduction. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 364(1534):3341–33450. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2009.0131
Hansen PJ, Drost M, Rivera RM, Paula-Lopes FF, al-Katanani YM, Krininger CE 3rd, Chase CC Jr (2001) Adverse impact of heat stress on embryo production: causes and strategies for mitigation. Theriogenology 55(1):91–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0093-691x(00)00448-9
Holtz W (2005) Recent developments in assisted reproduction in goats. Small Rumin Res 60:95–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2005.06.032
Hossain MM, Salilew-Wondim D, Schellander K, Tesfaye D (2012) The role of microRNAs in mammalian oocytes and embryos. Anim Reprod Sci 134(1–2):36–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anireprosci.2012.08.009
Hsieh RH, Au HK, Yeh TS, Chang SJ, Cheng YF, Tzeng CR (2004) Decreased expression of mitochondrial genes in human unfertilized oocytes and arrested embryos. Fertil Steril 81(Suppl 1):912–918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2003.11.013
Ishizuka B, Kuribayashi Y, Murai K, Amemiya A, Itoh MT (2000) The effect of melatonin on in vitro fertilization and embryo development in mice. J Pineal Res 28(1):48–51. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-079x.2000.280107.x
Khan S, Jamal MA, Khan IM, Ullah I, Jabbar A, Khan NM, Liu Y (2023) Factors affecting superovulation induction in goats (Capra hericus): an analysis of various approaches. Front Vet Sci 10:1152103. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2023.1152103
Kimura K (2016) Superovulation with a single administration of FSH in aluminum hydroxide gel: a novel superovulation method for cattle. J Reprod Dev 62(5):423–429. https://doi.org/10.1262/jrd.2016-066
Kimura K, Hirako M, Iwata H, Aoki M, Kawaguchi M, Seki M (2007) Successful superovulation of cattle by a single administration of FSH in aluminum hydroxide gel. Theriogenology 68(4):633–639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2007.02.016
Kosaka N, Izumi H, Sekine K, Ochiya T (2010) microRNA as a new immune-regulatory agent in breast milk. Silence 1(1):7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1758-907X-1-7
Kowaltowski AJ, Vercesi AE (1999) Mitochondrial damage induced by conditions of oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 26(3–4):463–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0891-5849(98)00216-0
Kozomara A, Birgaoanu M, Griffiths-Jones S (2019) miRBase: from microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res 47(D1). https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky1141. D155-D162
Lasheen ME, Badr HM, Kandiel MMM, Abo El-Maaty AM, Samir H, Farouk M, Eldawy MH (2018) Predicting early pregnancy in Egyptian buffalo cows via measuring uterine and luteal blood flows, and serum and saliva progesterone. Trop Anim Health Prod 50(1):137–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-017-1413-6
Lemley CO, Meyer AM, Camacho LE, Neville TL, Newman DJ, Caton JS, Vonnahme KA (2012) Melatonin supplementation alters uteroplacental hemodynamics and fetal development in an ovine model of intrauterine growth restriction. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 302(4):R454–R467. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00407.2011
Lew R, Komesaroff P, Williams M, Dawood T, Sudhir K (2003) Endogenous estrogens influence endothelial function in young men. Circ Res 93(11):1127–1133. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.RES.0000103633.57225.BC
Li Y, Han B, Salmeron AG, Bai J, Chen DB (2021) Estrogen-Induced Uterine Vasodilation in pregnancy and Preeclampsia. Matern Fetal Med 4(1):52–60. https://doi.org/10.1097/FM9.0000000000000132
Liang J, Wang S, Wang Z (2017) Role of microRNAs in embryo implantation. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 15(1):90. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12958-017-0309-7
Liu CG, Calin GA, Meloon B, Gamliel N, Sevignani C, Ferracin M, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Zupo S, Dono M, Alder H, Bullrich F, Negrini M, Croce CM (2004) An oligonucleotide microchip for genome-wide microRNA profiling in human and mouse tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(26):9740–9744. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0403293101
Lord-Fontaine S, Averill-Bates DA (2002) Heat shock inactivates cellular antioxidant defenses against hydrogen peroxide: protection by glucose. Free Radic Biol Med 32(8):752–765. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0891-5849(02)00769-4
Mason HD, Willis DS, Beard RW, Winston RM, Margara R, Franks S (1994) Estradiol production by granulosa cells of normal and polycystic ovaries: relationship to menstrual cycle history and concentrations of gonadotropins and sex steroids in follicular fluid. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 79(5):1355–1360. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.79.5.7962330
Mayo JC, Sainz RM, Antoli I, Herrera F, Martin V, Rodriguez C (2002) Melatonin regulation of antioxidant enzyme gene expression. Cell Mol Life Sci 59(10):1706–1713. https://doi.org/10.1007/pl00012498
Miller VM, Mulvagh SL (2007) Sex steroids and endothelial function: translating basic science to clinical practice. Trends Pharmacol Sci 28(6):263–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2007.04.004
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR, Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Peterson A, Noteboom J, O’Briant KC, Allen A, Lin DW, Urban N, Drescher CW, Knudsen BS, Stirewalt DL, Gentleman R, Vessella RL, Nelson PS, Martin DB, Tewari M (2008) Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(30):10513–10518. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0804549105
Momen-Heravi F, Trachtenberg AJ, Kuo WP, Cheng YS (2014) Genomewide Study of salivary MicroRNAs for detection of Oral Cancer. J Dent Res 93(7 Suppl):86S–93S. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034514531018
Mori Y, Kano Y (1984) Changes in plasma concentrations of LH, progesterone and oestradiol in relation to the occurrence of luteolysis, oestrus and time of ovulation in the Shiba goat (Capra hircus). J Reprod Fertil 72(1):223–230. https://doi.org/10.1530/jrf.0.0720223
Nett TM, Turzillo AM, Baratta M, Rispoli LA (2002) Pituitary effects of steroid hormones on secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone. Domest Anim Endocrinol 23(1–2):33–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0739-7240(02)00143-1
Noda Y, Matsumoto H, Umaoka Y, Tatsumi K, Kishi J, Mori T (1991) Involvement of superoxide radicals in the mouse two-cell block. Mol Reprod Dev. 1991;28(4):356 – 60. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrd.1080280408
Nowshari MA, Backers JF, Holtz W (1995) Superovulation of goats with purified pFSH supplemented with defined amounts of pLH. Theriogenology 43(4):797–802. https://doi.org/10.1016/0093-691x(95)00022-z
Oliveira M, Ribeiro IF, Rodriguez M, Maciel GS, Fonseca JF, Brandão FZ, Bartlewski PM (2018) Assessing the usefulness of B-mode and colour Doppler Sonography, and measurements of circulating progesterone concentrations for determining ovarian responses in superovulated ewes. Reprod Domest Anim 53(3):742–750. https://doi.org/10.1111/rda.13165
Papis K, Poleszczuk O, Wenta-Muchalska E, Modlinski JA (2007) Melatonin effect on bovine embryo development in vitro in relation to oxygen concentration. J Pineal Res 43(4):321–326. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2007.00479.x
Paradies G, Petrosillo G, Paradies V, Reiter RJ, Ruggiero FM (2010) Melatonin, cardiolipin and mitochondrial bioenergetics in health and Disease. J Pineal Res 48(4):297–310. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2010.00759.x
Piccioni F, Zappavigna V, Verrotti AC (2005) Translational regulation during oogenesis and early development: the cap-poly(A) tail relationship. C R Biol 328(10–11):863–881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crvi.2005.05.006
Pierson RA, Ginther OJ (1998) Ultrasonic imaging of the ovaries and uterus in cattle. Theriogenology 29:21–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/0093-691X(88)90029-5
Pohler KG, Green JA, Moley LA, Gunewardena S, Hung WT, Payton RR, Hong X, Christenson LK, Geary TW, Smith MF (2017) Circulating microRNA as candidates for early embryonic viability in cattle. Mol Reprod Dev 84(8):731–743. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrd.22856
Rajamahendran R, Robinson J, Desbottes S, Walton JS (1989) Temporal relationships among estrus, body temperature, milk yield, progesterone and luteinizing hormone levels, and ovulation in dairy cows. Theriogenology 31(6):1173–1182. https://doi.org/10.1016/0093-691x(89)90086-1
Raza SHA, Abdelnour SA, Dhshan AIM, Hassanin AA, Noreldin AE, Albadrani GM, Abdel-Daim MM, Cheng G, Zan L (2021) Potential role of specific microRNAs in the regulation of thermal stress response in livestock. J Therm Biol 96:102859. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtherbio.2021.102859
Reiter RJ, Melchiorri D, Sewerynek E, Poeggeler B, Barlow-Walden L, Chuang J, Ortiz GG, Acuña-Castroviejo D (1995) A review of the evidence supporting melatonin’s role as an antioxidant. J Pineal Res 18(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079x.1995.tb00133.x
Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Manchester LC, Lopez-Burillo S, Sainz RM, Mayo JC (2003) Melatonin: detoxification of oxygen and nitrogen-based toxic reactants. Adv Exp Med Biol 527:539–548. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-0135-0_62
Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Manchester LC, Paredes SD, Mayo JC, Sainz RM (2009) Melatonin and reproduction revisited. Biol Reprod 81(3):445–456. https://doi.org/10.1095/biolreprod.108.075655
Rosenfeld CR, Roy T, Cox BE (2002) Mechanisms modulating estrogen-induced uterine vasodilation. Vascul Pharmacol 38(2):115–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0306-3623(02)00135-0
Roth Z (2015) Physiology and endocrinology symposium: Cellular and molecular mechanisms of heat stress related to bovine ovarian function. J Ani Sci 93(5):2034–2044. https://doi.org/10.2527/jas.2014-8625
Samir H, Kandiel MMM (2019) Accuracy of subjective evaluation of luteal blood flow by color Doppler ultrasonography for early diagnosis of pregnancy in Egyptian buffalo. Anim Reprod Sci 208:106129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anireprosci.2019.106129
Samir H, Karen A, Ashmawy T, Abo-Ahmed M, El-Sayed M, Watanabe G (2016) Monitoring of embryonic and fetal losses in different breeds of goats using real-time B-mode ultrasonography. Theriogenology 85(2):207–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2015.09.039
Samir H, Nyametease P, Nagaoka K, Watanabe G (2018a) Effect of seasonality on testicular blood flow as determined by color Doppler ultrasonography and hormonal profiles in Shiba goats. Anim Reprod Sci 197:185–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anireprosci.2018.08.027
Samir H, Nagaoka K, Watanabe G (2018b) The stimulatory effect of subluteal progesterone environment on the superovulatory response of passive immunization against inhibin in goats. Theriogenology 121:188–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2018.07.031
Samir H, Kandiel MMM, El-Maaty AMA, Sediqyar M, Sasaki K, Watanabe G (2019) Ovarian follicular changes and hemodynamics in Egyptian buffaloes under CIDR-PGF2α and Ovsynch-CIDR estrus synchronization treatments. J Reprod Dev 65(5):451–457. https://doi.org/10.1262/jrd.2019-035
Samir H, Nyametease P, Elbadawy M, Nagaoka K, Sasaki K, Watanabe G (2020) Administration of melatonin improves testicular blood flow, circulating hormones, and semen quality in Shiba goats. Theriogenology 146:111–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2020.01.053
Samir H, Swelum AA, Kandiel MMM (2022) Editorial: exploring roles of diagnostic ultrasonography in veterinary medicine. Front Vet Sci 9:1084676. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2022.1084676
Samir H, ElSayed MI, Radwan F, Hedia M, Hendawy H, Hendawy AO, Elbadawy M, Watanabe G (2023a) An updated insight on testicular hemodynamics: Environmental, physiological, and technical perspectives in farm and companion animals. Vet Res Commun 47(2):323–345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-022-10022-9
Samir H, El-Shalofy AS, El-Sherbiny HR (2023b) Effects of a single dose of long-acting FSH on testicular blood flow, testicular echotexture, and circulating testosterone, estradiol, and nitric oxide in rams during the non-breeding season. Domest Anim Endocrinol 82:106765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.domaniend.2022.106765
Samir H, Mandour AS, Radwan F, Ahmed AE, Momenah MA, Aldawood NA, Yoshida T, Watanabe G, El-Sherbiny HR (2023c) Effect of acute melatonin injection on metabolomic and testicular artery hemodynamic changes and circulating hormones in Shiba goats under sub-tropical environmental conditions. Animals 13:1794. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13111794
Samir H, El-Sherbiny HR, Ahmed AE, Ahmad Sindi R, Al Syaad KM, Abdelnaby EA (2023d) Administration of estradiol benzoate enhances ovarian and uterine hemodynamics in postpartum dairy buffaloes. Anim (Basel) 13(14):2340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13142340
Santos PH, Satrapa RA, Fontes PK, Franchi FF, Razza EM, Mani F, Nogueira MFG, Barros CM, Castilho ACS (2018) Effect of superstimulation on the expression of microRNAs and genes involved in steroidogenesis and ovulation in Nelore cows. Theriogenology 110:192–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2017.12.045
Schoenemann HM, Humphrey WD, Crowder ME, Nett TM, Reeves JJ (1985) Pituitary luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone receptors in ovariectomized cows after challenge with ovarian steroids. Biol Reprod 32(3):574–583. https://doi.org/10.1095/biolreprod32.3.574
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B, Ideker T (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13(11):2498–2504. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.1239303
Singh J, Domínguez M, Jaiswal R, Adams GP (2004) A simple ultrasound test to predict the superstimulatory response in cattle. Theriogenology 62(1–2):227–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2003.09.020
Siqueira LG, Areas VS, Ghetti AM, Fonseca JF, Palhao MP, Fernandes CA, Viana JH (2013) Color Doppler flow imaging for the early detection of nonpregnant cattle at 20 days after timed artificial insemination. J Dairy Sci 96(10):6461–6472. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2013-6814
Sohel MMH, Akyuz B, Konca Y, Arslan K, Sariozkan S, Cinar MU (2019) Oxidative stress modulates the expression of apoptosis-associated microRNAs in bovine granulosa cells in vitro. Cell Tissue Res 376(2):295–308. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-019-02990-3
Sontakke SD, Mohammed BT, McNeilly AS, Donadeu FX (2014) Characterization of microRNAs differentially expressed during bovine follicle development. Reproduction 148(3):271–283. https://doi.org/10.1530/REP-14-0140
Sticht C, De La Torre C, Parveen A, Gretz N (2018) miRWalk: an online resource for prediction of microRNA binding sites. PLoS ONE 13(10):e0206239. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0206239
Tamura H, Nakamura Y, Korkmaz A, Manchester LC, Tan DX, Sugino N, Reiter RJ (2009) Melatonin and the ovary: physiological and pathophysiological implications. Fertil Steril 92(1):328–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2008.05.016
Tamura H, Jozaki M, Tanabe M, Shirafuta Y, Mihara Y, Shinagawa M, Tamura I, Maekawa R, Sato S, Taketani T, Takasaki A, Reiter RJ, Sugino N (2020) Importance of melatonin in assisted Reproductive Technology and ovarian aging. Int J Mol Sci 21(3):1135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031135
Tan DX, Manchester LC, Terron MP, Flores LJ, Reiter RJ (2007) One molecule, many derivatives: a never-ending interaction of melatonin with reactive oxygen and nitrogen species? J Pineal Res 42(1):28–42. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2006.00407.x
Taya K, Watanabe G, Sasamoto S (1985) Radioimmunoassay for progesterone, testosterone and estradiol 17 b using 125I- iodohistamine radioligands. Jpn J Anim Reprod 31:186–197
Thakor AS, Herrera EA, Serón-Ferré M, Giussani DA (2010) Melatonin and vitamin C increase umbilical blood flow via nitric oxide-dependent mechanisms. J Pineal Res 49(4):399–406. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2010.00813.x
Tian XZ, Wen Q, Shi JM, Liang-Wang, Zeng SM, Tian JH, Zhou GB, Zhu SE, Liu GS (2010) Effects of melatonin on in vitro development of mouse two-cell embryos cultured in HTF medium. Endocr Res 35(1):17–23. https://doi.org/10.3109/07435800903539607
Tokar T, Pastrello C, Rossos AEM, Abovsky M, Hauschild AC, Tsay M, Lu R, Jurisica I (2018) mirDIP 4.1-integrative database of human microRNA target predictions. Nucleic Acids Res 46(D1):D360–D370. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx1144
Tseng JK, Chen CH, Chou PC, Yeh SP, Ju JC (2004) Influences of follicular size on parthenogenetic activation and in vitro heat shock on the cytoskeleton in cattle oocytes. Reprod Domest Anim 39(3):146–153. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0531.2004.00493.x
Vlachos IS, Zagganas K, Paraskevopoulou MD, Georgakilas G, Karagkouni D, Vergoulis T, Dalamagas T, Hatzigeorgiou AG (2015) DIANA-miRPath v3.0: deciphering microRNA function with experimental support. Nucleic Acids Res 43(W1):W460–W466. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv403
Wang L, Zhuo ZY, Shi WQ, Tan DX, Gao C, Tian XZ, Zhang L, Zhou GB, Zhu SE, Yun P, Liu GS (2014) Melatonin promotes superovulation in sika deer (Cervus nippon). Int J Mol Sci 15(7):12107–12118. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150712107
Yamada O, Abe M, Takehana K, Iwasa K, Hiraga T, Hiratsuka T (1994) Microvasculature of mature bovine follicles and its changes with ovulation. J Reprod Dev 40:307–315. https://doi.org/10.1262/jrd.40.307
Yang L, Chen Y, Liu Y, Xing Y, Miao C, Zhao Y, Chang X, Zhang Q (2021) The role of oxidative stress and natural antioxidants in ovarian aging. Front Pharmacol 11:617843. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.617843
Yong W, Ma H, Na M, Gao T, Zhang Y, Hao L, Yu H, Yang H, Deng X (2021) Roles of melatonin in the field of reproductive medicine. Biomed Pharmacother 144:112001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112001
Zuelke KA, Jones DP, Perreault SD (1997) Glutathione oxidation is associated with altered microtubule function and disrupted fertilization in mature hamster oocytes. Biol Reprod 57(6):1413–1419. https://doi.org/10.1095/biolreprod57.6.1413
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. A.F. Parlow (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, Beltsville, MD) for supplementing the first antibodies for measurement of FSH and LH by RIA, and Dr. G.D. Niswender (Animal Reproduction and Biotechnology Laboratory, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO) for providing antisera against estradiol-17β (GDN 244). The authors would like to extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University for supporting this study under the large group project number (R.G.P 2/161/44). Also, the authors acknowledge Dr. Natsumi Endo and Dr. Kentaro Nagaoka for their technical support.
Funding
JSPS postdoctoral fellowship for research in Japan (FY19-ID No. P19101) partially supported this research through the first and last authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.S: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Visualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Validation, Writing - original draft, Writing- review & editing. M.S: Methodology, Analysis, Validation, and Editing of the manuscript. F.R: Software, Writing-review & editing. A. S. M., H.R. El-S., and A.E.A.: Validation, Analysis, and Writing- review & editing. K.M. Al-S. and F.A. Al-S.: Writing- review & editing. G. W.: Supervision, Visualization, Validation, Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing - review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All methods in this investigation were performed following the Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology, Japan, rules for the research use of animals (Ethical No. R02-73).
Consent to participate
All authors participate in the final version of the manuscript.
Consent to Publish
The manuscript is not under consideration in other journals.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors stated no conflict of interest in this study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Samir, H., Samir, M., Radwan, F. et al. Effect of pre-treatment of melatonin on superovulation response, circulatory hormones, and miRNAs in goats during environmental heat stress conditions. Vet Res Commun 48, 459–474 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-023-10239-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-023-10239-2