Abstract
Objective
The evidence from epidemiological research on whether the efficacy of rituximab in treatment of refractory nephrotic syndrome (NS) is better than other agents is inconsistent. This meta-analysis aimed to assess the efficacy of rituximab in the treatment of NS compared with other immunosuppressive agents.
Methods
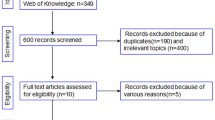
Relevant literatures were identified and evaluated for quality before October 2019 through multiple search strategies on PubMed and EMBASE. Statistical evidence of the symmetry of the funnel plot obtained from Begg’s test was indicated by Egger’s linear regression and a sensitivity analysis identified heterogeneity. A fixed- or a random-effects model was applied to calculate the pooled SMDs and RRs.
Results
A total of 12 studies, involving 383 patients and 354 controls, were included. Compared with other agents, rituximab significantly improved complete remission both in children and adults [Overall: RR = 1.313, 95% CI = 1.170–1.475, P < 0.001; Adult: RR = 1.359, 95% CI = 1.053–1.753, P = 0.019 Children: RR = 1.354, 95% CI = 1.072–1.709, P < 0.001], and dramatically decreased the relapse rate in children [Overall: RR = 0.349, 95% CI = 0.166–0.732, P < 0.001; Children: RR = 0.286, 95% CI = 0.176–0.463, P < 0.001].
Conclusions
Rituximab might be a promising treatment for refractory NS. Compared with other agents, rituximab significantly improves the complete remission and decreased the relapse rate. However, to confirm the efficacy of rituximab in the treatment of refractory NS, more high-quality, large sample, and multicenter randomized controlled trials are needed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Crew RJ, Radhakrishnan J, Appel G (2004) Complications of the nephrotic syndrome and their treatment. Clin Nephrol 62(4):245–259
Basu B, Mahapatra TK, Mondal N (2015) Mycophenolate mofetil following rituximab in children with steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. Pediatrics 136(1):e132–e139. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2015-0486
Lombel RM, Gipson DS, Hodson EM (2013) Treatment of steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome: new guidelines from KDIGO. Pediatr Nephrol 28(3):415–426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-012-2310-x
Sinha A, Bagga A (2013) Rituximab therapy in nephrotic syndrome: implications for patients’ management. Nat Rev Nephrol 9(3):154–169. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneph.2012.289
Larkins N, Kim S, Craig J, Hodson E (2016) Steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome: an evidence-based update of immunosuppressive treatment in children. Arch Dis Child 101(4):404–408. https://doi.org/10.1136/archdischild-2015-308924
Colucci M, Carsetti R, Cascioli S, Casiraghi F, Perna A, Rava L et al (2016) B cell reconstitution after rituximab treatment in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 27(6):1811–1822. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2015050523
Sellier-Leclerc AL, Baudouin V, Kwon T, Macher MA, Guerin V, Lapillonne H et al (2012) Rituximab in steroid-dependent idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in childhood—follow-up after CD19 recovery. Nephrol Dial Transplant 27(3):1083–1089. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfr405
Jayne D (2010) Role of rituximab therapy in glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 21(1):14–17. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2008070786
Benz K, Dotsch J, Rascher W, Stachel D (2004) Change of the course of steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome after rituximab therapy. Pediatr Nephrol 19(7):794–797. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-004-1434-z
Ravani P, Bonanni A, Rossi R, Caridi G, Ghiggeri GM (2016) Anti-CD20 antibodies for idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in children. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 11(4):710–720. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.08500815
Cravedi P, Sghirlanzoni MC, Marasa M, Salerno A, Remuzzi G, Ruggenenti P (2011) Efficacy and safety of rituximab second-line therapy for membranous nephropathy: a prospective, matched-cohort study. Am J Nephrol 33(5):461–468. https://doi.org/10.1159/000327611
Webb H, Jaureguiberry G, Dufek S, Tullus K, Bockenhauer D (2016) Cyclophosphamide and rituximab in frequently relapsing/steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 31(4):589–594. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-015-3245-9
Zhao Z, Liao G, Li Y, Zhou S, Zou H (2015) The efficacy and safety of rituximab in treating childhood refractory nephrotic syndrome: a meta-analysis. Sci Rep 5:8219. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep08219
Solomon N, Lalayiannis AD (2019) Rituximab is more effective than tacrolimus in steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome. Arch Dis Child Educ Pract Ed 104(5):279–280. https://doi.org/10.1136/archdischild-2018-316537
Magnasco A, Ravani P, Edefonti A, Murer L, Ghio L, Belingheri M et al (2012) Rituximab in children with resistant idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 23(6):1117–1124. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2011080775
Ravani P, Magnasco A, Edefonti A, Murer L, Rossi R, Ghio L et al (2011) Short-term effects of rituximab in children with steroid- and calcineurin-dependent nephrotic syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 6(6):1308–1315. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.09421010
Ravani P, Rossi R, Bonanni A, Quinn RR, Sica F, Bodria M et al (2015) Rituximab in children with steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome: a multicenter, open-label, noninferiority, randomized controlled tTrial. J Am Soc Nephrol 26(9):2259–2266. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2014080799
DaSilva I, Huerta A, Quintana L, Redondo B, Iglesias E, Draibe J et al (2017) Rituximab for steroid-dependent or frequently relapsing idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in adults: a retrospective multicenter study in Spain. BioDrugs 31(3):239–249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40259-017-0221-x
Iijima K, Sako M, Nozu K, Mori R, Tuchida N, Kamei K et al (2014) Rituximab for childhood-onset, complicated, frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome or steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome: a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 384(9950):1273–1281. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60541-9
Dahan K, Debiec H, Plaisier E, Cachanado M, Rousseau A, Wakselman L et al (2017) Rituximab for severe membranous nephropathy: a 6-month trial with extended follow-up. J Am Soc Nephrol 28(1):348–358. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2016040449
van den Brand J, Ruggenenti P, Chianca A, Hofstra JM, Perna A, Ruggiero B et al (2017) Safety of rituximab compared with steroids and cyclophosphamide for idiopathic membranous nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 28(9):2729–2737. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2016091022
Sinha A, Bagga A, Gulati A, Hari P (2012) Short-term efficacy of rituximab versus tacrolimus in steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 27(2):235–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-011-1997-4
Iorember F, Aviles D, Kallash M, Bamgbola O (2018) Cost analysis on the use of rituximab and calcineurin inhibitors in children and adolescents with steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 33(2):261–267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-017-3789-y
Basu B, Sander A, Roy B, Preussler S, Barua S, Mahapatra TKS et al (2018) Efficacy of rituximab vs tacrolimus in pediatric corticosteroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Pediatr 172(8):757–764. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2018.1323
Ahn YH, Kim SH, Han KH, Cho HY, Shin JI, Cho MH, Park YS, Kim SY, Lee SJ, Cheong HI, Ha I-S (2014) Selected abstracts from the 34th Annual Spring Meeting of the Korean Society of Nephrology 2014. Kidney Res Clin Pract 33:A1–A2
Nielsen C, Laustrup H, Voss A, Junker P, Husby S, Lillevang ST (2004) A putative regulatory polymorphism in PD-1 is associated with nephropathy in a population-based cohort of systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Lupus 13(7):510–516
Zeng X, Zhang Y, Kwong JS, Zhang C, Li S, Sun F et al (2015) The methodological quality assessment tools for preclinical and clinical studies, systematic review and meta-analysis, and clinical practice guideline: a systematic review. J Evid Based Med 8(1):2–10. https://doi.org/10.1111/jebm.12141
Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gotzsche PC, Juni P, Moher D, Oxman AD et al (2011) The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 343:d5928. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.d5928
Higgins JP, Thompson SG (2002) Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 21(11):1539–1558. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.1186
Gulati A, Sinha A, Jordan SC, Hari P, Dinda AK, Sharma S et al (2010) Efficacy and safety of treatment with rituximab for difficult steroid-resistant and -dependent nephrotic syndrome: multicentric report. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 5(12):2207–2212. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.03470410
Tellier S, Brochard K, Garnier A, Bandin F, Llanas B, Guigonis V et al (2013) Long-term outcome of children treated with rituximab for idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 28(6):911–918. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-012-2406-3
Kamei K, Ito S, Nozu K, Fujinaga S, Nakayama M, Sako M et al (2009) Single dose of rituximab for refractory steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome in children. Pediatr Nephrol 24(7):1321–1328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-009-1191-0
Fujinaga S, Hirano D, Nishizaki N, Kamei K, Ito S, Ohtomo Y et al (2010) Single infusion of rituximab for persistent steroid-dependent minimal-change nephrotic syndrome after long-term cyclosporine. Pediatr Nephrol 25(3):539–544. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-009-1377-5
Cravedi P, Ruggenenti P, Sghirlanzoni MC, Remuzzi G (2007) Titrating rituximab to circulating B cells to optimize lymphocytolytic therapy in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2(5):932–937. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.01180307
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Science Foundation of Anhui Medical University (2018xkj028). Refinement and implementation of the study were supported by The Second Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, JP., Wang, J., Yuan, L. et al. The efficacy of rituximab in the treatment of refractory nephrotic syndrome: a meta-analysis. Int Urol Nephrol 52, 1093–1101 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-020-02460-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-020-02460-8