Abstract
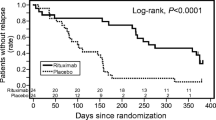
Patients with steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome (SRNS) who develop resistance to immunosuppressive agents, defined as refractory SRNS, have poor renal outcomes. Although the chimeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody rituximab has shown efficacy for frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome and steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome, its efficacy for refractory SRNS remains uncertain due to limited data. According to previous case reports, 50.4% of patients with refractory SRNS showed clinical improvements after rituximab treatment. Remission rates in patients with initial steroid resistance and late steroid resistance were 43.9 and 57.7%, respectively, and 41.5 and 63.6% in patients with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis and minor glomerular abnormalities, respectively. However, various factors (race, disease severity, number of rituximab doses, concomitant treatments, and observation period) differed among these observational studies and their consensus may also have been affected by potential publication bias. Rituximab monotherapy may have some degree of efficacy and lead to satisfactory outcomes in a subset of patients with refractory SRNS. However, administration of concomitant treatments during rituximab-mediated B cell depletion, such as methylprednisolone pulse therapy, daily oral prednisolone therapy, and immunosuppressive agents, may lead to better outcomes in these patients. Large-scale, multi-center prospective studies are needed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of such regimens.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kikunaga K, Ishikura K, Terano C, Sato M, Komaki F, Hamasaki Y, Sasaki S, Iijima K, Yoshikawa N, Nakanishi K, Nakazato H, Matsuyama T, Ando T, Ito S, Honda M, Japanese Pediatric Survey Holding Information of Nephrotic syndrome (JP-SHINE) study of the Japanese Study Group of Renal Disease in Children (2017) High incidence of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in East Asian children: a nationwide survey in Japan (JP-SHINE study). Clin Exp Nephrol 21:651–657
Mekahli D, Liutkus A, Ranchin B, Yu A, Bessenay L, Girardin E, Van Damme-Lombaerts R, Palcoux JB, Cachat F, Lavocat MP, Bourdat-Michel G, Nobili F, Cochat P (2009) Long-term outcome of idiopathic steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome: a multicenter study. Pediatr Nephrol 24:1525–1532
Trautmann A, Schnaidt S, Lipska-Ziętkiewicz BS, Bodria M, Ozaltin F, Emma F, Anarat A, Melk A, Azocar M, Oh J, Saeed B, Gheisari A, Caliskan S, Gellermann J, Higuita LMS, Jankauskiene A, Drozdz D, Mir S, Balat A, Szczepanska M, Paripovic D, Zurowska A, Bogdanovic R, Yilmaz A, Ranchin B, Baskin E, Erdogan O, Remuzzi G, Firszt-Adamczyk A, Kuzma-Mroczkowska E, Litwin M, Murer L, Tkaczyk M, Jardim H, Wasilewska A, Printza N, Fidan K, Simkova E, Borzecka H, Staude H, Hees K, Schaefer F, PodoNet Consortium (2017) Long-term outcome of steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome in children. J Am Soc Nephrol 28:3055–3065
Hamasaki Y, Yoshikawa N, Hattori S, Sasaki S, Iijima K, Nakanishi K, Matsuyama T, Ishikura K, Yata N, Kaneko T, Honda M, Japanese Study Group of Renal Disease (2009) Cyclosporine and steroid therapy in children with steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 24:2177–2185
Yorgin PD, Krasher J, Al-Uzri AY (2001) Pulse methylprednisolone treatment of idiopathic steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 16:245–250
Shenoy M, Plant ND, Lewis MA, Bradbury MG, Lennon R, Webb NJ (2010) Intravenous methylprednisolone in idiopathic childhood nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 25:899–903
Mori K, Honda M, Ikeda M (2004) Efficacy of methylprednisolone pulse therapy in steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 19:1232–1236
Bagga A, Mudigoudar BD, Hari P, Vasudev V (2004) Enalapril dosage in steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 19:45–50
Yi Z, Li Z, Wu XC, He QN, Dang XQ, He XJ (2006) Effect of fosinopril in children with steroid-resistant idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 21:967–972
Feld SM, Figueroa P, Savin V, Nast CC, Sharma R, Sharma M, Hirschberg R, Adler SG (1998) Plasmapheresis in the treatment of steroid-resistant focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in native kidneys. Am J Kidney Dis 32:230–237
Franke D, Zimmering M, Wolfish N, Ehrich JH, Filler G (2000) Treatment of FSGS with plasma exchange and immunadsorption. Pediatr Nephrol 14:965–969
Hattori M, Chikamoto H, Akioka Y, Nakakura H, Ogino D, Matsunaga A, Fukazawa A, Miyakawa S, Khono M, Kawaguchi H, Ito K (2003) A combined low-density lipoprotein apheresis and prednisone therapy for steroid-resistant primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in children. Am J Kidney Dis 42:1121–1130
Kidney Disease: Improving global outcomes (KDIGO) (2012) Steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome in children. Kidney Int Suppl 2:172–176
Ishikura K, Matsumoto S, Sako M, Tsuruga K, Nakanishi K, Kamei K, Saito H, Fujinaga S, Hamasaki Y, Chikamoto H, Ohtsuka Y, Komatsu Y, Ohta T, Nagai T, Kaito H, Kondo S, Ikezumi Y, Tanaka S, Kaku Y, Iijima K, Japanese Society for Pediatric Nephrology; Japanese Society for Pediatric Nephrology (2015) Clinical practice guideline for pediatric idiopathic nephrotic syndrome 2013: medical therapy. Clin Exp Nephrol 19:6–33
Iijima K, Sako M, Nozu K, Mori R, Tuchida N, Kamei K, Miura K, Aya K, Nakanishi K, Ohtomo Y, Takahashi S, Tanaka R, Kaito H, Nakamura H, Ishikura K, Ito S, Ohashi Y, Rituximab for Childhood-onset Refractory Nephrotic Syndrome (RCRNS) Study Group (2014) Rituximab for childhood-onset, complicated, frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome or steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome: a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 384:1273–1281
Iijima K, Sako M, Kamei K, Nozu K (2018) Rituximab in steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome: lessons from clinical trials. Pediatr Nephrol 33:1449–1455
Nakayama M, Kamei K, Nozu K, Matsuoka K, Nakagawa A, Sako M, Iijima K (2008) Rituximab for refractory focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Pediatr Nephrol 23:481–485
Peters HP, van de Kar NC, Wetzels JF (2008) Rituximab in minimal change nephropathy and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: report of four cases and review of the literature. Neth J Med 66:408–415
Suri M, Tran K, Sharma AP, Filler G, Grimmer J (2008) Remission of steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome due to focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis using rituximab. Int Urol Nephrol 40:807–810
Sharma AP, Filler G (2009) Role of mycophenolate mofetil in remission maintenance after a successful response to rituximab. Pediatr Nephrol 24:423–424
Fernandez-Fresnedo G, Segarra A, González E, Alexandru S, Delgado R, Ramos N, Egido J, Praga M, Trabajo de Enfermedades Glomerulares de la Sociedad Española de Nefrología (GLOSEN) (2009) Rituximab treatment of adult patients with steroid-resistant focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4:1317–1323
Chaumais MC, Garnier A, Chalard F, Peuchmaur M, Dauger S, Jacqz-Agrain E, Deschênes G (2009) Fatal pulmonary fibrosis after rituximab administration. Pediatr Nephrol 24:1753–1755
Kaito H, Kamei K, Kikuchi E, Ogura M, Matsuoka K, Nagata M, Iijima K, Ito S (2010) Successful treatment of collapsing focal segmental glomerulosclerosis with a combination of rituximab, steroids and ciclosporin. Pediatr Nephrol 25:957–959
Hirano D, Fujinaga S, Nishizaki N (2012) The uncertainty of rituximab and steroid dosing in refractory steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. Clin Nephrol 77:510–512
Janardan J, Ooi K, Menahem S (2014) Sustained complete remission of steroid- and cyclophosphamide-resistant minimal-change disease with a single course of rituximab therapy. Clin Kidney J 7:293–295
Fujinaga S, Hara T (2014) Re-treatment with high-dose prednisolone after rituximab infusion for childhood-onset steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 29:1291–1292
Counsilman CE, Jol-van der Zijde CM, Stevens J, Cransberg K, Bredius RG, Sukhai RN (2015) Pharmacokinetics of rituximab in a pediatric patient with therapy-resistant nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 30:1367–1370
Nakagawa T, Shiratori A, Kawaba Y, Kanda K, Tanaka R (2016) Efficacy of rituximab therapy against intractable steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Int 58:1003–1008
Fujinaga S, Sakuraya K (2017) Repeated administrations of rituximab along with steroids and immunosuppressive agents in refractory steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. Indian Pediatr 54:49–50
Bagga A, Sinha A, Moudgil A (2007) Rituximab in patients with the steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. N Engl J Med 356:2751–2752
Gulati A, Sinha A, Jordan SC, Hari P, Dinda AK, Sharma S, Srivastava RN, Moudgil A, Bagga A (2010) Efficacy and safety of treatment with rituximab for difficult steroid-resistant and -dependent nephrotic syndrome: multicentric report. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 5:2207–2212
Prytuła A, Iijima K, Kamei K, Geary D, Gottlich E, Majeed A, Taylor M, Marks SD, Tuchman S, Camilla R, Ognjanovic M, Filler G, Smith G, Tullus K (2010) Rituximab in refractory nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 25:461–468
Kari JA, El-Morshedy SM, El-Desoky S, Alshaya HO, Rahim KA, Edrees BM (2011) Rituximab for refractory cases of childhood nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 26:733–737
Ito S, Kamei K, Ogura M, Udagawa T, Fujinaga S, Saito M, Sako M, Iijima K (2013) Survey of rituximab treatment for childhood-onset refractory nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 28:257–264
Kamei K, Okada M, Sato M, Fujimaru T, Ogura M, Nakayama M, Kaito H, Iijima K, Ito S (2014) Rituximab treatment combined with methylprednisolone pulse therapy and immunosuppressants for childhood steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 29:1181–1187
Sinha A, Bhatia D, Gulati A, Rawat M, Dinda AK, Hari P, Bagga A (2015) Efficacy and safety of rituximab in children with difficult-to-treat nephrotic syndrome. Nephrol Dial Transplant 30:96–106
Basu B, Mahapatra TK, Mondal N (2015) Mycophenolate mofetil following rituximab in children with steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. Pediatrics 136:e132–e139
Hoseini R, Sabzian K, Otukesh H, Zafaranloo N, Panahi P, Rahimzadeh N, Nakhaie S, Akhavan Sepehi M (2018) Efficacy and safety of rituximab in children with steroid- and cyclosporine-resistant and steroid- and cyclosporine-dependent nephrotic syndrome. Iran J Kidney Dis 12:27–32
Magnasco A, Ravani P, Edefonti A, Murer L, Ghio L, Belingheri M, Benetti E, Murtas C, Messina G, Massella L, Porcellini MG, Montagna M, Regazzi M, Scolari F, Ghiggeri GM (2012) Rituximab in children with resistant idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 23:1117–1124
Pelletier JH, Kumar KR, Engen R, Bensimhon A, Varner JD, Rheault MN, Srivastava T, Straatmann C, Silva C, Davis TK, Wenderfer SE, Gibson K, Selewski D, Barcia J, Weng P, Licht C, Jawa N, Kallash M, Foreman JW, Wigfall DR, Chua AN, Chambers E, Hornik CP, Brewer ED, Nagaraj SK, Greenbaum LA, Gbadegesin RA (2018) Recurrence of nephrotic syndrome following kidney transplantation is associated with initial native kidney biopsy findings. Pediatr Nephrol 33:1773–1780
Francis A, Trnka P, McTaggart SJ (2016) Long-term outcome of kidney transplantation in recipients with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 11:2041–2046
Ding WY, Koziell A, McCarthy HJ, Bierzynska A, Bhagavatula MK, Dudley JA, Inward CD, Coward RJ, Tizard J, Reid C, Antignac C, Boyer O, Saleem MA (2014) Initial steroid sensitivity in children with steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome predicts post-transplant recurrence. J Am Soc Nephrol 25:1342–1348
Bierzynska A, Saleem MA (2018) Deriving and understanding the risk of post-transplant recurrence of nephrotic syndrome in the light of current molecular and genetic advances. Pediatr Nephrol 33:2027–2035
Nozu K, Iijima K, Fujisawa M, Nakagawa A, Yoshikawa N, Matsuo M (2005) Rituximab treatment for posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD) induces complete remission of recurrent nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 20:1660–1663
Araya CE, Dharnidharka VR (2011) The factors that may predict response to rituximab therapy in recurrent focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: a systematic review. J Transp Secur 2011:374213
Kumar J, Shatat IF, Skversky AL, Woroniecki RP, Del Rio M, Perelstein EM, Johnson VL, Mahesh S (2013) Rituximab in post-transplant pediatric recurrent focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Pediatr Nephrol 28:333–338
Kamei K, Ogura M, Sato M, Ito S, Ishikura K (2018) Infusion reactions associated with rituximab treatment for childhood-onset complicated nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 33:1013–1018
Kamei K, Takahashi M, Fuyama M, Saida K, Machida H, Sato M, Ogura M, Ito S (2015) Rituximab-associated agranulocytosis in children with refractory idiopathic nephrotic syndrome: case series and review of literature. Nephrol Dial Transplant 30:91–96
Kamei K, Ito S, Iijima K (2010) Severe respiratory adverse events associated with rituximab infusion. Pediatr Nephrol 25:1193
Sato M, Ito S, Ogura M, Kamei K, Miyairi I, Miyata I, Higuchi M, Matsuoka K (2013) Atypical Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia with multiple nodular granulomas after rituximab for refractory nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 28:145–149
Ardelean DS, Gonska T, Wires S, Cutz E, Griffiths A, Harvey E, Tse SM, Benseler SM (2010) Severe ulcerative colitis after rituximab therapy. Pediatrics 126:e243–e246
Sellier-Leclerc AL, Belli E, Guérin V, Dorfmüller P, Deschênes G (2013) Fulminant viral myocarditis after rituximab therapy in pediatric nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 28:1875–1879
Delbe-Bertin L, Aoun B, Tudorache E, Lapillone H, Ulinski T (2013) Does rituximab induce hypogammaglobulinemia in patients with pediatric idiopathic nephrotic syndrome? Pediatr Nephrol 28:447–451
Boren EJ, Cheema GS, Naguwa SM, Ansari AA, Gershwin ME (2008) The emergence of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) in rheumatic diseases. J Autoimmun 30:90–98
Tsutsumi Y, Kanamori H, Mori A, Tanaka J, Asaka M, Imamura M, Masauzi N (2005) Reactivation of hepatitis B virus with rituximab. Expert Opin Drug Saf 4:599–608
Trautmann A, Bodria M, Ozaltin F, Gheisari A, Melk A, Azocar M, Anarat A, Caliskan S, Emma F, Gellermann J, Oh J, Baskin E, Ksiazek J, Remuzzi G, Erdogan O, Akman S, Dusek J, Davitaia T, Özkaya O, Papachristou F, Firszt-Adamczyk A, Urasinski T, Testa S, Krmar RT, Hyla-Klekot L, Pasini A, Özcakar ZB, Sallay P, Cakar N, Galanti M, Terzic J, Aoun B, Caldas Afonso A, Szymanik-Grzelak H, Lipska BS, Schnaidt S, Schaefer F, PodoNet Consortium (2015) Spectrum of steroid-resistant and congenital nephrotic syndrome in children: the PodoNet registry cohort. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 10:592–600
Sadowski CE, Lovric S, Ashraf S, Pabst WL, Gee HY, Kohl S, Engelmann S, Vega-Warner V, Fang H, Halbritter J, Somers MJ, Tan W, Shril S, Fessi I, Lifton RP, Bockenhauer D, El-Desoky S, Kari JA, Zenker M, Kemper MJ, Mueller D, Fathy HM, Soliman NA, SRNS Study Group, Hildebrandt F (2015) A single-gene cause in 29.5% of cases of steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 26:1279–1289
Büscher AK, Beck BB, Melk A, Hoefele J, Kranz B, Bamborschke D, Baig S, Lange-Sperandio B, Jungraithmayr T, Weber LT, Kemper MJ, Tönshoff B, Hoyer PF, Konrad M, Weber S, German Pediatric Nephrology Association (GPN) (2016) Rapid response to cyclosporin a and favorable renal outcome in nongenetic versus genetic steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 11:245–253
Ashraf S, Kudo H, Rao J, Kikuchi A, Widmeier E, Lawson JA, Tan W, Hermle T, Warejko JK, Shril S, Airik M, Jobst-Schwan T, Lovric S, Braun DA, Gee HY, Schapiro D, Majmundar AJ, Sadowski CE, Pabst WL, Daga A, van der Ven AT, Schmidt JM, Low BC, Gupta AB, Tripathi BK, Wong J, Campbell K, Metcalfe K, Schanze D, Niihori T, Kaito H, Nozu K, Tsukaguchi H, Tanaka R, Hamahira K, Kobayashi Y, Takizawa T, Funayama R, Nakayama K, Aoki Y, Kumagai N, Iijima K, Fehrenbach H, Kari JA, El Desoky S, Jalalah S, Bogdanovic R, Stajić N, Zappel H, Rakhmetova A, Wassmer SR, Jungraithmayr T, Strehlau J, Kumar AS, Bagga A, Soliman NA, Mane SM, Kaufman L, Lowy DR, Jairajpuri MA, Lifton RP, Pei Y, Zenker M, Kure S, Hildebrandt F (2018) Mutations in six nephrosis genes delineate a pathogenic pathway amenable to treatment. Nat Commun 9:1960
Gee HY, Ashraf S, Wan X, Vega-Warner V, Esteve-Rudd J, Lovric S, Fang H, Hurd TW, Sadowski CE, Allen SJ, Otto EA, Korkmaz E, Washburn J, Levy S, Williams DS, Bakkaloglu SA, Zolotnitskaya A, Ozaltin F, Zhou W, Hildebrandt F (2014) Mutations in EMP2 cause childhood-onset nephrotic syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 94:884–890
Gee HY, Zhang F, Ashraf S, Kohl S, Sadowski CE, Vega-Warner V, Zhou W, Lovric S, Fang H, Nettleton M, Zhu JY, Hoefele J, Weber LT, Podracka L, Boor A, Fehrenbach H, Innis JW, Washburn J, Levy S, Lifton RP, Otto EA, Han Z, Hildebrandt F (2015) KANK deficiency leads to podocyte dysfunction and nephrotic syndrome. J Clin Invest 125:2375–2384
Bierzynska A, Soderquest K, Dean P, Colby E, Rollason R, Jones C, Inward CD, McCarthy HJ, Simpson MA, Lord GM, Williams M, Welsh GI, Koziell AB, Saleem MA, Nephro S, UK study of nephrotic syndrome (2017) MAGI2 mutations cause congenital nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 28:1614–1621
Hinkes B, Wiggins RC, Gbadegesin R, Vlangos CN, Seelow D, Nürnberg G, Garg P, Verma R, Chaib H, Hoskins BE, Ashraf S, Becker C, Hennies HC, Goyal M, Wharram BL, Schachter AD, Mudumana S, Drummond I, Kerjaschki D, Waldherr R, Dietrich A, Ozaltin F, Bakkaloglu A, Cleper R, Basel-Vanagaite L, Pohl M, Griebel M, Tsygin AN, Soylu A, Müller D, Sorli CS, Bunney TD, Katan M, Liu J, Attanasio M, O'toole JF, Hasselbacher K, Mucha B, Otto EA, Airik R, Kispert A, Kelley GG, Smrcka AV, Gudermann T, Holzman LB, Nürnberg P, Hildebrandt F (2006) Positional cloning uncovers mutations in PLCE1 responsible for a nephrotic syndrome variant that may be reversible. Nat Genet 38:1397–1405
Acknowledgements
We thank Edanz Group (www.edanzediting.com/ac) for editing a draft of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
KK has received lecture fees from Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. and AbbVie GK. KIs has received lecture fees from Asahi Kasei Pharma, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Zenyaku Kogyo Co., Ltd., and Novartis Pharma K.K. and grants from Asahi Kasei Pharma, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and NovartisPharma K.K. MS has received a consulting fee from Zenyaku Kogyo Co. Ltd. SI has received grants from AbbVie GK., Asahi kasei Pharma Corporation, Astellas Pharma Inc., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., CSL Behring, Eisai Co. Ltd., Maruho Co. Ltd., Japan Blood Product Organization, Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co., Ltd., Phizer Co. Ltd. and Teijin Pharma Ltd. SI has received lecture fees and/or consultant fees from AbbVie LLC, Astellas Pharma Inc., Alexion Pharma LLC, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Eisai Co. Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo, Co., Ltd., Novartis Pharma K.K., Japan Blood Product Organization, JCR Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Teijin Pharma Ltd., Sanofi Genzyme Co. Ltd., Tanabe Mitsubishi Pharma, Novo Nordisk Pharma Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. and Zenyaku Kogyo Co. Ltd.. KN has received lecture fees from Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Novartis Pharma K.K. and Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. KIi has received grants from Novartis Pharma K.K., Japan Blood Product Organization, AbbVie LLC, JCR Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo, Co., Ltd., Teijin Pharma Ltd., CSL Behring, Novo Nordisk Pharma Ltd., Air Water Medical Inc., Astellas Pharma Inc., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Taisho Toyama Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Eisai Co. Ltd.,Biofermin Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Zenyaku Kogyo Co. Ltd., and lecture fees and/or consulting fees from Zenyaku Kogyo Co., Ltd., Novartis Pharma K.K., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Astellas Pharma Inc., Springer Japan K.K., Meiji Seika Pharma Co., Ltd., Asahi kasei Pharma Corporation, Medical Review Co.,Ltd., Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ltd., Baxter Limited, Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Sanwa Kagaku Kenkyusho Co.,Ltd., Sanofi K.K., Alexion Pharma LLC., and Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co., Ltd.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PPTX 69 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamei, K., Ishikura, K., Sako, M. et al. Rituximab therapy for refractory steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome in children. Pediatr Nephrol 35, 17–24 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-018-4166-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-018-4166-1