Abstract
Background
Rituximab (RTX) has recently showed promising results in the treatment of steroid-dependent idiopathic nephrotic syndrome (SDNS).
Methods
This was a retrospective multicenter study of 18 children treated with RTX for SDNS, with a mean follow-up of 3.2 years. RTX was introduced because of side effects or relapses during therapy with immunosuppressive agents. The children received one to four infusions of RTX during the first course of treatment, and subsequent infusions were given due to CD19-cell recovery (CD19 >1 %; 54 % of children) or relapse (41 %), as well as systematically (5 %).
Results
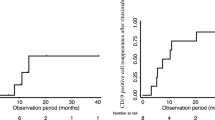
Treatment with RTX maintained sustained remission without relapse in 22 % of patients and increased the duration of remission in all other patients. The time between two successive relapses was 9 months in the absence of re-treatment and 24.5 months when infusions were performed at the time of CD19-cell recovery. At the last follow-up, 44.5 % of patients were free of oral drug therapy. Of those still receiving oral drugs, all doses had been decreased. No serious adverse events occurred.
Conclusion
The results of this retrospective study confirm the efficacy and very good safety of RTX in the treatment of SDNS. The optimal therapeutic protocol seems to be a repeated single infusion at the time of CD19-cell recovery.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haffner D, Fischer DC (2009) Nephrotic syndrome and rituximab: facts and perspectives. Pediatr Nephrol 24:1433–1438
Hodson EM, Alexander SI (2008) Evaluation and management of steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome. Curr Opin Pediatr 20:145–150
Guigonis V, Dallocchio A, Baudouin V, Dehennault M, Hachon-Le Camus C, Afanetti M, Groothoff J, Llanas B, Niaudet P, Nivet H, Raynaud N, Taque S, Ronco P, Bouissou F (2008) Rituximab treatment for severe steroid- or cyclosporine-dependent nephrotic syndrome: a multicentric series of 22 cases. Pediatr Nephrol 23:1269–1279
Sellier-Leclerc AL, Macher MA, Loirat C, Guerin V, Watier H, Peuchmaur M, Baudouin V, Deschenes G (2010) Rituximab efficiency in children with steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 25:1109–1115
Dantal J, Bigot E, Bogers W, Testa A, Kriaa F, Jacques Y, Hurault de Ligny B, Niaudet P, Charpentier B, Soulillou JP (1994) Effect of plasma protein adsorption on protein excretion in kidney-transplant recipients with recurrent nephrotic syndrome. New Eng J Med 330:7–14
Yap HK, Cheung W, Murugasu B, Sim SK, Seah CC, Jordan SC (1999) Th1 and Th2 cytokine mRNA profiles in childhood nephrotic syndrome: evidence for increased IL-13 mRNA expression in relapse. J Am Soc Nephrol 10:529–537
Iharada A, Kaneko K, Tsuji S, Hasui M, Kanda S, Nishiyama T (2009) Increased nitric oxide production by T- and B-cells in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 24:1033–1038
Habib R, Girardin E, Gagnadoux MF, Hinglais N, Levy M, Broyer M (1988) Immunopathological findings in idiopathic nephrosis: clinical significance of glomerular "immune deposits". Pediatr Nephrol 2:402–408
Dantal J, Godfrin Y, Koll R, Perretto S, Naulet J, Bouhours JF, Soulillou JP (1998) Antihuman immunoglobulin affinity immunoadsorption strongly decreases proteinuria in patients with relapsing nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 9:1709–1715
Hultin LE, Hausner MA, Hultin PM, Giorgi JV (1993) CD20 (pan-B cell) antigen is expressed at a low level on a subpopulation of human T lymphocytes. Cytometry 14:196–204
Benz K, Dotsch J, Rascher W, Stachel D (2004) Change of the course of steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome after rituximab therapy. Pediatr Nephrol 19:794–797
Smith GC (2007) Is there a role for rituximab in the treatment of idiopathic childhood nephrotic syndrome? Pediatr Nephrol 22:893–898
Gilbert RD, Hulse E, Rigden S (2006) Rituximab therapy for steroid-dependent minimal change nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 21:1698–1700
Hofstra JM, Deegens JK, Wetzels JF (2007) Rituximab: effective treatment for severe steroid-dependent minimal change nephrotic syndrome? Nephrol Dial Transpl 22:2100–2102
Bagga A, Sinha A, Moudgil A (2007) Rituximab in patients with the steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. New Eng J Med 356:2751–2752
Nakayama M, Kamei K, Nozu K, Matsuoka K, Nakagawa A, Sako M, Iijima K (2008) Rituximab for refractory focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Pediatr Nephrol 23:481–485
Gulati A, Sinha A, Jordan SC, Hari P, Dinda AK, Sharma S, Srivastava RN, Moudgil A, Bagga A (2010) Efficacy and safety of treatment with rituximab for difficult steroid-resistant and -dependent nephrotic syndrome: multicentric report. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 5:2207–2212
Prytula A, Iijima K, Kamei K, Geary D, Gottlich E, Majeed A, Taylor M, Marks SD, Tuchman S, Camilla R, Ognjanovic M, Filler G, Smith G, Tullus K (2010) Rituximab in refractory nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 25:461–468
Pescovitz MD, Book BK, Sidner RA (2006) Resolution of recurrent focal segmental glomerulosclerosis proteinuria after rituximab treatment. New Eng J Med 354:1961–1963
Nozu K, Iijima K, Fujisawa M, Nakagawa A, Yoshikawa N, Matsuo M (2005) Rituximab treatment for posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD) induces complete remission of recurrent nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 20:1660–1663
Kemper MJ, Gellermann J, Habbig S, Krmar RT, Dittrich K, Jungraithmayr T, Pape L, Patzer L, Billing H, Weber L, Pohl M, Rosenthal K, Rosahl A, Mueller-Wiefel DE, Dotsch J (2011) Long-term follow-up after rituximab for steroid-dependent idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Nephrol Dial Transplant 27:1910–1915
Sellier-Leclerc AL, Baudouin V, Kwon T, Macher MA, Guerin V, Lapillonne H, Deschenes G, Ulinski T (2012) Rituximab in steroid-dependent idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in childhood–follow-up after CD19 recovery. Nephrol Dial Transplant 27:1083–1089
Ito S, Kamei K, Ogura M, Sato M, Fujimaru T, Ishikawa T, Udagawa T, Iijima K (2011) Maintenance therapy with mycophenolate mofetil after rituximab in pediatric patients with steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 26:1823–1828
Filler G, Huang SH, Sharma AP (2011) Should we consider MMF therapy after rituximab for nephrotic syndrome? Pediatr Nephrol 26:1759–1762
Mansour H, Cheval L, Elalouf JM, Aude JC, Alyanakian MA, Mougenot B, Doucet A, Deschenes G (2005) T-cell transcriptome analysis points up a thymic disorder in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int 67:2168–2177
Valanciute A, le Gouvello S, Solhonne B, Pawlak A, Grimbert P, Lyonnet L, Hue S, Lang P, Remy P, Salomon R, Bensman A, Guellaen G, Sahali D (2004) NF-kappa B p65 antagonizes IL-4 induction by c-maf in minimal change nephrotic syndrome. J Immunol 172:688–698
Sahali D, Pawlak A, Le Gouvello S, Lang P, Valanciute A, Remy P, Loirat C, Niaudet P, Bensman A, Guellaen G (2001) Transcriptional and post-transcriptional alterations of IkappaBalpha in active minimal-change nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:1648–1658
Dejardin E (2006) The alternative NF-kappaB pathway from biochemistry to biology: pitfalls and promises for future drug development. Biochem Pharmacol 72:1161–1179
Voll RE, Jimi E, Phillips RJ, Barber DF, Rincon M, Hayday AC, Flavell RA, Ghosh S (2000) NF-kappa B activation by the pre-T cell receptor serves as a selective survival signal in T lymphocyte development. Immunity 13:677–689
Coppo R, Camilla R, Porcellini MG, Peruzzi L, Gianoglio B, Amore A, Dapra V, Loiacono E, Fonsato V, Dal Canton A, Esposito C, Esposito P, Tovo PA (2012) Saquinavir in steroid-dependent and -resistant nephrotic syndrome: a pilot study. Nephrol Dial Transplant 27:1902–1910
Bosch X, Saiz A, Ramos-Casals M (2011) Monoclonal antibody therapy-associated neurological disorders. Nat Rev Neurol 7:165–172
Ricciardiello L, Laghi L, Ramamirtham P, Chang CL, Chang DK, Randolph AE, Boland CR (2000) JC virus DNA sequences are frequently present in the human upper and lower gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterology 119:1228–1235
Shackelton LA, Rambaut A, Pybus OG, Holmes EC (2006) JC virus evolution and its association with human populations. J Virol 80:9928–9933
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tellier, S., Brochard, K., Garnier, A. et al. Long-term outcome of children treated with rituximab for idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 28, 911–918 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-012-2406-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-012-2406-3