Abstract
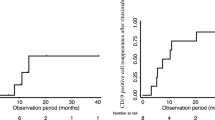
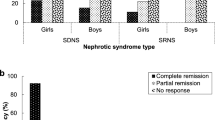
We conducted a multicenter prospective trial to evaluate the efficacy, safety and pharmacokinetics of a single dose of rituximab (375 mg/m2 body surface area) for the treatment of children with refractory steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome (SDNS). All patients (n = 12) were able to discontinue steroids at a median of 74 days after treatment. The frequency of relapses per 6 months was significantly reduced and the steroid-free period per 6 months was significantly increased after treatment compared with those before treatment. The condition in nine of the patients (75%) relapsed at a median of 129 days after treatment, and seven patients were given additional rituximab due to steroid dependency. Most of the relapses developed simultaneously with recovery of B-cells. However, three patients (25%) did not have a relapse with B-cell recovery and the disease was kept in remission for more than 1 year. None of the patients developed life-threatening adverse events. This is the first report of a prospective study of a single dose of rituximab for refractory SDNS. Treatment with a single dose of rituximab may be effective for refractory SDNS, but its efficacy to prevent relapses was transient in most of the patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iijima K, Hamahira K, Tanaka R, Kobayashi A, Nozu K, Nakamura H, Yoshikawa N (2002) Risk factors for cyclosporine-induced tubulointerstitial lesions in children with minimal change nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int 61:1801–1805
Kranz B, Vester U, Büscher R, Wingen AM, Hoyer PF (2008) Cyclosporine-A-induced nephrotoxicity in children with minimal-change nephrotic syndrome: long-term treatment up to 10 years. Pediatr Nephrol 23:581–586
Benz K, Dötsch J, Rascher W, Stachel D (2004) Change of the course of steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome after rituximab therapy. Pediatr Nephrol 19:794–797
Gilbert RD, Hulse E, Rigden S (2006) Rituximab therapy for steroid-dependent minimal change nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 21:1698–1700
François H, Daugas E, Bensman A, Ronco P (2007) Unexpected efficacy of rituximab in multirelapsing minimal change nephrotic syndrome in the adult: first case report and pathophysiological considerations. Am J Kidney Dis 49:158–161
Smith GC (2007) Is there a role for rituximab in the treatment of idiopathic childhood nephrotic syndrome? Pediatr Nephrol 22:893–898
Kemper MJ, Möller K, Ludwig K, Rink N, Muller-Wiefel DE (2006) Rituximab in the treatment of refractory steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome (abstract). Pediatr Nephrol 21:1528
Dallachio IA, Trimoreau F, Feuillard J, Guigoinis V (2006) A case of steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome treated with rituximab (abstract). Pediatr Nephrol 21:1615
Hofstra JM, Deegens JK, Wetzels JF (2007) Rituximab: effective treatment for severe steroid-dependent minimal change nephrotic syndrome? Nephrol Dial Transplant 22:2100–2102
Guigonis V, Dallocchio A, Baudouin V, Dehennault M, Hachon-Le Camus C, Afanetti M, Groothoff J, Llanas B, Niaudet P, Nivet H, Raynaud N, Taque S, Ronco P, Bouissou F (2008) Rituximab treatment for severe steroid- or cyclosporine-dependent nephrotic syndrome: a multicentric series of 22 cases. Pediatr Nephrol 23:269–279
Bagga A, Sinha A, Moudgil A (2007) Rituximab in patients with the steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. N Engl J Med 356:2751–2752
Nakayama M, Kamei K, Nozu K, Matsuoka K, Nakagawa A, Sako M, Iijima K (2008) Rituximab for refractory focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Pediatr Nephrol 23:481–485
Yang T, Nast CC, Vo A, Jordan SC (2008) Rapid remission of steroid and mycophenolate mofetil (MMF)-resistant minimal change nephrotic syndrome after rituximab therapy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23:377–380
Suri M, Tran K, Sharma AP, Filler G, Grimmer J (2008) Remission of steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome due to focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis using rituximab. Int Urol Nephrol 40:807–810
Tabata K, Yamaoka K, Kaibara A, Suzuki S, Terakawa M, Hata T (1999) Moment analysis program available on Microsoft Excel. Xenobiot Metab Dispos 14:286–293
Vieira CA, Agarwal A, Book BK, Sidner RA, Bearden CM, Gebel HM, Roggero AL, Fineberg NS, Taber T, Kraus MA, Pescovitz MD (2004) Rituximab for reduction of anti-HLA antibodies in patients awaiting renal transplantation: 1. Safety, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics. Transplantation 77:542–548
Berinstein NL, Grillo-López AJ, White CA, Bence-Bruckler I, Maloney D, Czuczman M, Green D, Rosenberg J, McLaughlin P, Shen D (1998) Association of serum rituximab (IDEC-C2B8) concentration and anti-tumor response in the treatment of recurrent low-grade or follicular non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Ann Oncol 9:995–1001
Davis TA, Maloney DG, Grillo-López AJ, White CA, Williams ME, Weiner GJ, Dowden S, Levy R (2000) Combination immunotherapy of relapsed or refractory low-grade or follicular non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma with rituximab and interferon-alpha-2a. Clin Cancer Res 6:2644–2652
Tobinai K, Kobayashi Y, Narabayashi M, Ogura M, Kagami Y, Morishima Y, Ohtsu T, Igarashi T, Sasaki Y, Kinoshita T, Murate T (1998) Feasibility and pharmacokinetic study of a chimeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (IDEC-C2B8, rituximab) in relapsed B-cell lymphoma. The IDEC-C2B8 Study Group. Ann Oncol 9:527–534
Iacona I, Lazzarino M, Avanzini MA, Rupolo M, Arcaini L, Astori C, Lunghi F, Orlandi E, Morra E, Zagonel V, Regazzi MB (2000) Rituximab (IDEC-C2B8): validation of a sensitive enzyme-linked immunoassay applied to a clinical pharmacokinetic study. Ther Drug Monit 22:295–301
Regazzi MB, Iacona I, Avanzini MA, Rupolo M, Arcaini L, Astori C, Lunghi F, Orlandi E, Morra E, Zagonel V, Regazzi MB (2005) Pharmacokinetic behavior of rituximab: a study of different schedules of administration for heterogeneous clinical settings. Ther Drug Monit 27:785–792
Breedveld F, Agarwal S, Yin M, Ren S, Li NF, Shaw TM, Davies BE (2007) Rituximab pharmacokinetics in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: B-cell levels do not correlate with clinical response. J Clin Pharmacol 47:1119–1128
Kemper MJ, Meyer-Jark T, Lilova M, Müller-Wiefel DE (2003) Combined B- and T-cell activation in childhood steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome. Clin Nephrol 60:242–247
Cho BS, Yoon SR, Jang JY, Pyun KH, Lee CE (1999) Up-regulation of interleukin-4 and CD23/FcepsilonRII in minimal change nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 13:199–204
Kimata H, Fujimoto M, Furusho K (1995) Involvement of interleukin (IL)-13, but not IL-4, in spontaneous IgE and IgG4 production in nephrotic syndrome. Eur J Immunol 25:1497–1450
Martin F, Chan AC (2004) Pathogenic roles of B cells in human autoimmunity; insights from the clinic. Immunity 20:517–527
Tokunaga M, Saito K, Kawabata D, Imura Y, Fujii T, Nakayamada S, Tsujimura S, Nawata M, Iwata S, Azuma T, Mimori T, Tanaka Y (2007) Efficacy of rituximab (anti-CD20) for refractory systemic lupus erythematosus involving the central nervous system. Ann Rheum Dis 66:470–475
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Health and Labor Sciences Research Grant for the Large Scale Clinical Trial Network Project (to K.I.). The authors are grateful to Professor Shuki Mizutani, Department of Pediatrics and Developmental Biology, Tokyo Medical and Dental University, and the Zenyaku Corporation, for their helpful advice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamei, K., Ito, S., Nozu, K. et al. Single dose of rituximab for refractory steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome in children. Pediatr Nephrol 24, 1321–1328 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-009-1191-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-009-1191-0