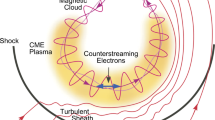
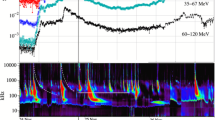
Abstract
We analyze the statistics, solar sources, and properties of interplanetary coronal mass ejections (ICMEs) in the solar wind. The total number of coronal mass ejections (CMEs) registered in the Coordinated Data Analysis Workshops catalog (CDAW) during the first eight years of Cycle 24 was 61% larger than in the same period of Cycle 23, but the number of X-ray flares registered by the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES) was 20 % smaller because the solar activity was lower. The total number of ICMEs in the given period of Cycle 24 in the Richardson and Cane list was 29% smaller than in Cycle 23, which may be explained by a noticeable number of non-classified ICME-like events in the beginning of Cycle 24. For the period January 2010 – August 2011, we identify solar sources of the ICMEs that are included in the Richardson and Cane list. The solar sources of ICME were determined from coronagraph observations of the Earth-directed CMEs, supplemented by modeling of their propagation in the heliosphere using kinematic models (a ballistic and drag-based model). A detailed analysis of the ICME solar sources in the period under study showed that in 11 cases out of 23 (48%), the observed ICME could be associated with two or more sources. For multiple-source events, the resulting solar wind disturbances can be described as complex (merged) structures that are caused by stream interactions, with properties depending on the type of the participating streams. As a reliable marker to identify interacting streams and their sources, we used the plasma ion composition because it freezes in the low corona and remains unchanged in the heliosphere. According to the ion composition signatures, we classify these cases into three types: complex ejecta originating from weak and strong CME–CME interactions, as well as merged interaction regions (MIRs) originating from the CME high-speed stream (HSS) interactions. We describe temporal profiles of the ion composition for the single-source and multi-source solar wind structures and compared them with the ICME signatures determined from the kinematic and magnetic field parameters of the solar wind. In single-source events, the ion charge state, as a rule, has a one-peak enhancement with an average duration of \(\text{about one}\) day, which is similar to the mean ICME duration of 1.12 days derived from the Richardson and Cane list. In the multi-source events, the total profile of the ion charge state consists of a sequence of enhancements that is associated with the interaction between the participating streams. On average, the total duration of the complex structures that appear as a result of the CME–CME and CME–HSS interactions as determined from their ion composition is 2.4 days, which is more than twice longer than that of the single-source events.






Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
References
Andrews, M.-D.: 2003, A search for CMEs associated with big flares. Solar Phys.218, 261. DOI .
Behannon, K.W., Burlaga, L.F., Hewish, A.: 1991, Structure and evolution of compound streams at not greater than 1 AU. J. Geophys. Res.96, 21. DOI .
Brueckner, G.E., Howard, R.A., Koomen, M.J., Korendyke, C.M., Michels, D.J., Moses, J.D., Socker, D.G., Dere, K.P., Lamy, P.L., Llebaria, A., Bout, M.V., Schwenn, R., Simnett, G.M., Bedford, D.K., Eyles, C.J.: 1995, The Large Angle Spectroscopic Coronagraph (LASCO). Solar Phys.162, 357. DOI .
Burlaga, L.F., Behannon, K.W., Klein, L.W.: 1987, Compound streams, magnetic clouds, and major geomagnetic storms. J. Geophys. Res.92, 5725. DOI .
Burlaga, L.F., Plunkett, S.P., St. Cyr, O.C.: 2002, Successive CMEs and complex ejecta. J. Geophys. Res.107, 1266. DOI .
Burlaga, L., Sittler, E., Mariani, F., Schwenn, R.: 1981, Magnetic loop behind an interplanetary shock – Voyager, Helios, and IMP 8 observations. J. Geophys. Res.86, 6673. DOI .
Burlaga, L., Berdichevsky, D., Gopalswamy, N., Lepping, R., Zurbuchen, T.: 2003, Merged interaction regions at 1 AU. J. Geophys. Res.108, 1425. DOI .
Compagnino, A., Romano, P., Zuccarello, F.: 2017, A statistical study of CME properties and of the correlation between flares and CMEs over the Solar Cycles 23 and 24. Solar Phys.292, 5. DOI .
Delaboudinière, J.-P., Artzner, G.E., Brunaud, J., Gabriel, A.H., Hochedez, J.F., Millier, F., Song, X.Y., Au, B., Dere, K.P., Howard, R.A., Kreplin, R., Michels, D.J., Moses, J.D., Defise, J.M., Jamar, C., Rochus, P., Chauvineau, J.P., Marioge, J.P., Catura, R.C., Lemen, J.R., Shing, L., Stern, R.A., Gurman, J.B., Neupert, W.M., Maucherat, A., Clette, F., Cugnon, P., van Dessel, E.L.: 1995, EIT: Extreme-ultraviolet Imaging Telescope for the SOHO mission. Solar Phys.162, 291. DOI .
Echer, E., Alves, M.V., Gonzalez, W.D.: 2005, A statistical study of magnetic cloud parameters and geoeffectiveness. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys.67, 839. DOI .
Emslie, A.G., Dennis, B.R., Shih, A.Y., Chamberlin, P.C., Mewaldt, R.A., Moore, C.S., Share, G.H., Vourlidas, A., Welsch, B.T.: 2012, Global energetics of thirty-eight large solar eruptive events. Astrophys. J.759, 71. DOI .
Farrugia, C.J., Burlaga, L.F., Lepping, R.P.: 1997, Magnetic clouds and the quiet-storm effect at Earth. In: Tzurutani, B.T., Gonzalez, W.D., Kamide, Y., Arballo, J.K. (eds.) Magnetic Storms, Geophys. Mon. Ser.98, Am. Geophys. Union, Washington, 91.
Feldman, U.: 1992, Elemental abundances in the upper solar atmosphere. Phys. Scr. T46, 202.
Feldman, U., Landi, E., Schwadron, N.-A.: 2005, On the sources of fast and slow solar wind. J. Geophys. Res.110, A07109. DOI .
Galvin, A.B.: 2013, Solar wind ion observations: comparison from the depths of solar minimum to the rising of the cycle. AIP Conf. Proc.1539, 15. DOI .
Gloeckler, G., Cain, J., Ipavich, F.M., Tums, E.O., Bedini, P., Fisk, L.A., Zurbuchen, T.H., Bochsler, P., Fischer, J., Wimmer-Schweingruber, R.F., Geiss, J., Kallenbach, R.: 1998, Investigation of the composition of solar and interstellar matter using solar wind and pickup ion measurements with SWICS and SWIMS on the ACE spacecraft. Space Sci. Rev.86, 497. DOI .
Gopalswamy, N., Mäkelä, P., Akiyama, S., Xie, H., Yashiro, S., Reinard, A.A.: 2013, The solar connection of enhanced heavy ion charge states in the interplanetary medium: implications for the flux-rope structure of CMEs. Solar Phys.284, 17. DOI .
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Xie, H., Akiyama, S., Mäkelä, P.: 2015, Properties and geoeffectiveness of magnetic clouds during Solar Cycles 23 and 24. J. Geophys. Res.120, 9221. DOI .
Gosling, J.T., Bame, S.J., McComas, D.J., Phillips, J.L.: 1990, Coronal mass ejections and large geomagnetic storms. Geophys. Res. Lett.17, 901. DOI .
Gosling, J.-T., McComas, D.-J., Phillips, J.-L., Bame, S.-J.: 1991, Geomagnetic activity associated with Earth passage of interplanetary shock disturbances and coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res.96, 7831. DOI .
Harrison, R.A., Davies, J.A., Möstl, C., Liu, Y., Temmer, M., Bisi, M.M., Eastwood, J.P., de Koning, C.A., Nitta, N., Rollett, T., Farrugia, C.J., Forsyth, R.J., Jackson, B.V., Jensen, E.A., Kilpua, E.K.J., Odstrcil, D., Webb, D.F.: 2012, An analysis of the origin and propagation of the multiple coronal mass ejections of 2010 August 1. Astrophys. J.750, 45. DOI .
Heidrich-Meisner, V., Peleikis, T., Kruse, M., Berger, L., Wimmer-Schweingruber, R.: 2016, Observations of high and low Fe charge states in individual solar wind streams with coronal-hole origin. Astron. Astrophys.593, A70. DOI .
Hess, P., Zhang, J.: 2017, A study of the Earth-affecting CMEs of Solar Cycle 24. Solar Phys.292, 80. DOI .
Howard, R.A., Moses, J.D., Vourlidas, A., Newmark, J.S., Socker, D.G., Plunkett, S.P., et al.: 2008, Sun Earth Connection Coronal and Heliospheric Investigation (SECCHI). Space Sci. Rev.136, 67. DOI .
Hudson, H.S., Cliver, E.W.: 2001, Observing coronal mass ejections without coronagraphs. J. Geophys. Res.106, 25199. DOI .
Hundhausen, A.-J., Gilbert, H.-E., Bame, S.-J.: 1968, Ionization state of the interplanetary plasma. J. Geophys. Res.73, 5485. DOI .
Kataoka, R., Shiota, D., Kilpua, E., Keika, K.: 2015, Pileup accident hypothesis of magnetic storm on 17 March 2015. Geophys. Res. Lett.42, 5155. DOI .
Kilpua, E.K.J., Jian, L.K., Li, Y., Luhmann, J.G., Russell, C.T.: 2012, Observations of ICMEs and ICME-like solar wind structures from 2007 – 2010 using near-Earth and STEREO observations. Solar Phys.281, 391. DOI .
Kilpua, E.K.J., Mierla, M., Zhukov, A.N., Rodriguez, L., Vourlidas, A., Wood, B.: 2014, Solar sources of interplanetary coronal mass ejections during the Solar Cycle 23/24 minimum. Solar Phys.289, 3773. DOI .
Kocher, M., Lepri, S.T., Landi, E., Zhao, L., Manchester, W.B. IV: 2017, Anatomy of depleted interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J.834, 147. DOI .
Laming, J.M.: 2015, The FIP and inverse FIP effects in solar and stellar coronae. Living Rev. Solar Phys.12, 2. DOI .
Lawrance, M.B., Shanmugaraju, A., Moon, Y.-J., Ibrahim, M.S., Umapathy, S.: 2016, Relationships between interplanetary coronal mass ejection characteristics and geoeffectiveness in the rising phase of Solar Cycles 23 and 24. Solar Phys.291, 1547. DOI .
Lemen, J.R., Title, A.M., Akin, D.J., Boerner, P.F., Chou, C., Drake, J.F., et al.: 2012, The Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) on the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Solar Phys.275, 17. DOI .
Lepri, S.T., Zurbuchen, T.H., Fisk, L.A., Richardson, I.G., Cane, H.V., Gloeckler, G.: 2001, Iron charge distribution as an identifier of interplanetary coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res.106, 29231. DOI .
Liu, Y.D., Yang, Z., Wang, R., Luhmann, J.G., Richardson, J.D., Lugaz, N.: 2014a, Sun-to-Earth characteristics of two coronal mass ejections interacting near 1 AU: formation of a complex ejecta and generation of a two-step geomagnetic storm. Astrophys. J. Lett.793, L41. DOI .
Liu, Y.D., Yang, Z., Wang, R., Luhmann, J.G., Richardson, J.D., Lugaz, N.: 2014b, Sun-to-Earth characteristics of two coronal mass ejections interacting near 1 AU: formation of a complex ejecta and generation of a two-step geomagnetic storm. Astrophys. J. Lett.793, L41. DOI .
Liu, Y.D., Hu, H., Wang, R., Yang, Z., Zhu, B., Liu, Y.A., Luhmann, J.G., Richardson, J.D.: 2015, Plasma and magnetic field characteristics of solar coronal mass ejections in relation to geomagnetic storm intensity and variability. Astrophys. J. Lett.809, L34. DOI .
Liu, Y., Luhmann, J.G., Bale, S.D., Lin, R.P.: 2011, Solar source and heliospheric consequences of the 2010 April 3 coronal mass ejection: a comprehensive view. Astrophys. J.734, 84. DOI .
Lugaz, N., Farrugia, C.J., Davies, J.A., Möstl, C., Davis, C.J., Roussev, I.I., Temmer, M.: 2012, The deflection of the two interacting coronal mass ejections of 2010 May 23 – 24 as revealed by combined in situ measurements and heliospheric imaging. Astrophys. J.759, 68. DOI .
Lugaz, N., Temmer, M., Wang, Y., Farrugia, C.J.: 2017, The interaction of successive coronal mass ejections: a review. Solar Phys.292, 64. DOI .
McComas, D.J., Bame, S.J., Barker, P., Feldman, W.C., Phillips, J.L., Riley, P., Griffee, J.W.: 1998, Solar Wind Electron Proton Alpha Monitor (SWEPAM) for the advanced composition explorer. Space Sci. Rev.86, 563. DOI .
Moon, Y.-J., Choe, G.S., Wang, H., Park, Y.D.: 2003, Sympathetic coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J.588, 1176. DOI .
Möstl, C., Temmer, M., Rollett, T., Farrugia, C.J., Liu, Y., Veronig, A.M., Leitner, M., Galvin, A.B., Biernat, H.K.: 2010, STEREO and wind observations of a fast ICME flank triggering a prolonged geomagnetic storm on 5 – 7 April 2010. Geophys. Res. Lett.37, L24103. DOI .
Möstl, C., Farrugia, C.J., Kilpua, E.K.J., Jian, L.K., Liu, Y., Eastwood, J.P., Harrison, R.A., Webb, D.F., Temmer, M., Odstrcil, D., Davies, J.A., Rollett, T., Luhmann, J.G., Nitta, N., Mulligan, T., Jensen, E.A., Forsyth, R., Lavraud, B., de Koning, C.A., Veronig, A.M., Galvin, A.B., Zhang, T.L., Anderson, B.J.: 2012, Multi-point shock and flux rope analysis of multiple interplanetary coronal mass ejections around 2010 August 1 in the inner heliosphere. Astrophys. J.758, 10. DOI .
Mrozek, T., Gburek, S., Siarkowski, M., Sylwester, B., Sylwester, J., Kȩpa, A., Gryciuk, M.: 2013, Solar flares observed simultaneously with SphinX, GOES and RHESSI. In: Kosovichev, A.G., de Gouveia Dal Pino, E., Yan, Y. (eds.) Solar and Astrophysical Dynamos and Magnetic Activity, IAU Symposium294, 571. DOI .
Nolte, J.T., Roelof, E.C.: 1973, Large-scale structure of the interplanetary medium, I: high coronal source longitude of the quiet-time solar wind. Solar Phys.33, 241. DOI .
Ogilvie, K.W., Chornay, D.J., Fritzenreiter, R.J., Hunsaker, F., Keller, J., Lobell, J., Miller, G., Scudder, J.D., Sittler, E.C. Jr., Torbert, R.B., Bodet, D., Needell, G., Lazarus, A.J., Steinberg, J.T., Tappan, J.H., Mavretic, A., Gergin, E.: 1995, SWE, a comprehensive plasma instrument for the wind spacecraft. Space Sci. Rev.71, 55. DOI .
Richardson, I.G., Cane, H.V.: 2004, Identification of interplanetary coronal mass ejections at 1 AU using multiple solar wind plasma composition anomalies. J. Geophys. Res.109, A09104. DOI .
Richardson, I.G., Cane, H.V.: 2010, Near-Earth interplanetary coronal mass ejections during Solar Cycle 23 (1996 – 2009): catalog and summary of properties. Solar Phys.264, 189. DOI .
Robbrecht, E., Patsourakos, S., Vourlidas, A.: 2009, No trace left behind: STEREO observation of a coronal mass ejection without low coronal signatures. Astrophys. J.701, 283. DOI .
Rodkin, D.G., Shugay, Y.S., Slemzin, V.A., Veselovskii, I.S.: 2016, Interaction of high-speed and transient fluxes of solar wind at the maximum of Solar Cycle 24. Bull. Lebedev Phys. Inst.43, 287. DOI .
Rod’kin, D.G., Shugay, Y.S., Slemzin, V.A., Veselovskii, I.S.: 2016, The effect of solar activity on the evolution of solar wind parameters during the rise of the 24th cycle. Solar Syst. Res.50, 44. DOI .
Rodkin, D., Goryaev, F., Pagano, P., Gibb, G., Slemzin, V., Shugay, Y., Veselovsky, I., Mackay, D.H.: 2017, Origin and ion charge state evolution of solar wind transients during 4 – 7 August 2011. Solar Phys.292, 90. DOI .
Rouillard, A.P., Lavraud, B., Sheeley, N.R., Davies, J.A., Burlaga, L.F., Savani, N.P., Jacquey, C., Forsyth, R.J.: 2010, White light and in situ comparison of a forming merged interaction region. Astrophys. J.719, 1385. DOI .
Schwenn, R., Raymond, J.C., Alexander, D., Ciaravella, A., Gopalswamy, N., Howard, R., Hudson, H., Kaufmann, P., Klassen, A., Maia, D., Munoz-Martinez, G., Pick, M., Reiner, M., Srivastava, N., Tripathi, D., Vourlidas, A., Wang, Y.-M., Zhang, J.: 2006, Coronal observations of CMEs. Report of working group A. Space Sci. Rev.123, 127. DOI .
Shen, F., Wang, Y., Shen, C., Feng, X.: 2017, On the collision nature of two coronal mass ejections: a review. Solar Phys.292, 104. DOI .
Shi, T., Wang, Y., Wan, L., Cheng, X., Ding, M., Zhang, J.: 2015, Predicting the arrival time of coronal mass ejections with the graduated cylindrical shell and drag force model. Astrophys. J.806, 271. DOI .
Shugay, Y.S., Veselovsky, I.S., Seaton, D.B., Berghmans, D.: 2011, Hierarchical approach to forecasting recurrent solar wind streams. Solar Syst. Res.45, 546. DOI .
Shugay, Y.S., Veselovsky, I.S., Slemzin, V.A., Yermolaev, Y.I., Rodkin, D.G.: 2017, Possible causes of the discrepancy between the predicted and observed parameters of high-speed solar wind streams. Cosm. Res.55, 20. DOI .
Smith, C.W., L’Heureux, J., Ness, N.F., Acuña, M.H., Burlaga, L.F., Scheifele, J.: 1998, The ACE magnetic fields experiment. Space Sci. Rev.86, 613. DOI .
Somov, B.V. (ed.): 2013, Plasma Astrophysics, Part II, Astrophysics and Space Science Library392. DOI .
Stone, E.C., Frandsen, A.M., Mewaldt, R.A., Christian, E.R., Margolies, D., Ormes, J.F., Snow, F.: 1998, The advanced composition explorer. Space Sci. Rev.86, 1. DOI .
Temmer, M., Rollett, T., Möstl, C., Veronig, A.M., Vršnak, B., Odstrčil, D.: 2011, Influence of the ambient solar wind flow on the propagation behavior of interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J.743, 101. DOI .
Temmer, M., Vršnak, B., Rollett, T., Bein, B., de Koning, C.A., Liu, Y., Bosman, E., Davies, J.A., Möstl, C., Žic, T., Veronig, A.M., Bothmer, V., Harrison, R., Nitta, N., Bisi, M., Flor, O., Eastwood, J., Odstrcil, D., Forsyth, R.: 2012, Characteristics of kinematics of a coronal mass ejection during the 2010 August 1 CME–CME interaction event. Astrophys. J.749, 57. DOI .
Temmer, M., Reiss, M.A., Nikolic, L., Hofmeister, S.J., Veronig, A.M.: 2017, Preconditioning of interplanetary space due to transient CME disturbances. Astrophys. J.835, 141. DOI .
Žic, T., Vršnak, B., Temmer, M.: 2015, Heliospheric propagation of coronal mass ejections: drag-based model fitting. Astrophys. J. Suppl.218, 32. DOI .
Verbanac, G., Živković, S., Vršnak, B., Bandić, M., Hojsak, T.: 2013, Comparison of geoeffectiveness of coronal mass ejections and corotating interaction regions. Astron. Astrophys.558, A85. DOI .
von Steiger, R., Christon, S.P., Gloeckler, G., Ipavich, F.M.: 1992, Variable carbon and oxygen abundances in the solar wind as observed in Earth’s magnetosheath by AMPTE/CCE. Astrophys. J.389, 791. DOI .
Webb, D.F., Howard, T.A.: 2012, Coronal mass ejections: observations. Living Rev. Solar Phys.9. DOI .
Wu, C.-C., Liou, K., Lepping, R.P., Hutting, L., Plunkett, S., Howard, R.A., Socker, D.: 2016, The first super geomagnetic storm of Solar Cycle 24: “The St. Patrick’s day event (17 March 2015)”. Earth Planets Space68, 151. DOI .
Yashiro, S., Gopalswamy, N.: 2009, Statistical relationship between solar flares and coronal mass ejections. In: Gopalswamy, N., Webb, D.-F. (eds.) Universal Heliophysical Processes, IAU Symposium257, 233. DOI .
Yermolaev, Y.I., Yermolaev, M.Y., Lodkina, I.G., Nikolaeva, N.S.: 2007, Statistical investigation of heliospheric conditions resulting in magnetic storms. Cosm. Res.45, 1. DOI .
Yermolaev, Y.-I., Nikolaeva, N.-S., Lodkina, I.-G., Yermolaev, M.-Y.: 2012, Geoeffectiveness and efficiency of CIR, sheath, and ICME in generation of magnetic storms. J. Geophys. Res.117, A00L07. DOI .
Zhang, G., Burlaga, L.F.: 1988, Magnetic clouds, geomagnetic disturbances, and cosmic ray decreases. J. Geophys. Res.93, 2511. DOI .
Zhang, J., Wang, J.: 2002, Are homologous flare-coronal mass ejection events triggered by moving magnetic features? Astrophys. J. Lett.566, L117. DOI .
Zhang, J., Liemohn, M.W., Kozyra, J.U., Lynch, B.J., Zurbuchen, T.H.: 2004, A statistical study of the geoeffectiveness of magnetic clouds during high solar activity years. J. Geophys. Res.109, A09101. DOI .
Zhang, J., Richardson, I.G., Webb, D.F., Gopalswamy, N., Huttunen, E., Kasper, J.C., Nitta, N.V., Poomvises, W., Thompson, B.J., Wu, C.-C., Yashiro, S., Zhukov, A.N.: 2007, Solar and interplanetary sources of major geomagnetic storms (\(\mathrm{Dst}< = -100~\mbox{nT}\)) during 1996 – 2005. J. Geophys. Res.112, A10102. DOI .
Zhao, L., Landi, E., Kocher, M., Lepri, S.T., Fisk, L.A.: 2016, Anomalously low C6+/C5+ ratio in solar wind: ACE/SWICS observation. In: AIP Publishing LLC, AIP Conference Proceedings1720, 020006. DOI .
Zhukov, A.N.: 2007, Using CME observations for geomagnetic storm forecasting. In: Lilensten, J. (ed.) Space Weather : Research Towards Applications in Europe 2nd European Space Weather Week (ESWW2), Astrophysics and Space Science Library344, 5. DOI .
Zurbuchen, T.H., Richardson, I.G.: 2006, In-situ solar wind and magnetic field signatures of interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Space Sci. Rev.123, 31. DOI .
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Ian Richardson and Hilary Cane for their list of Near-Earth Interplanetary Coronal Mass Ejections,Footnote 10 which we used in our investigations. This paper also uses data from the CACTus CME catalog,Footnote 11 generated and maintained by the SIDC at the Royal Observatory of Belgium, and the SEEDS CME catalog.Footnote 12 The SEEDS project has been supported by NASA Living With a Star Program and NASA Applied Information Systems Research Program. We have used the CME catalog that is generated and maintained at the CDAW Data CenterFootnote 13 by NASA and The Catholic University of America in cooperation with the Naval Research Laboratory. SOHO is a project of international cooperation between ESA and NASA. The authors thank the STEREO, GOES, SDO/AIA, and ACE research teams for their open data policy. We are grateful for the opportunity to use the results of the simulation obtained by the WSA-Enlil Cone and DBM models.Footnote 14 This work was supported by the Russian Scientific Foundation project 17-12-01567. A.N. Zhukov acknowledges support from the Belgian Federal Science Policy Office through the ESA-PRODEX programme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodkin, D., Slemzin, V., Zhukov, A.N. et al. Single ICMEs and Complex Transient Structures in the Solar Wind in 2010 – 2011. Sol Phys 293, 78 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-018-1295-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-018-1295-4