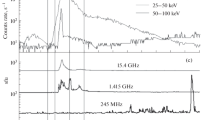
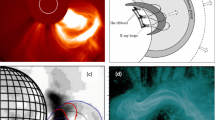
Abstract
We investigated a set of 54 interplanetary coronal mass ejection (ICME) events whose solar sources are very close to the disk center (within ± 15∘ from the central meridian). The ICMEs consisted of 23 magnetic-cloud (MC) events and 31 non-MC events. Our analyses suggest that the MC and non-MC ICMEs have more or less the same eruption characteristics at the Sun in terms of soft X-ray flares and CMEs. Both types have significant enhancements in ion charge states, although the non-MC structures have slightly lower levels of enhancement. The overall duration of charge-state enhancement is also considerably smaller than that in MCs as derived from solar wind plasma and magnetic signatures. We find very good correlation between the Fe and O charge-state measurements and the flare properties such as soft X-ray flare intensity and flare temperature for both MCs and non-MCs. These observations suggest that both MC and non-MC ICMEs are likely to have a flux-rope structure and the unfavorable observational geometry may be responsible for the appearance of non-MC structures at 1 AU. We do not find any evidence for an active region expansion resulting in ICMEs lacking a flux-rope structure because the mechanism of producing high charge states and the flux-rope structure at the Sun is the same for MC and non-MC events.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar-Rodriguez, E., Blanco-Cano, X., Gopalswamy, N.: 2006, Composition and magnetic structure of interplanetary coronal mass ejections at 1 AU. Adv. Space Res. 38, 522.
Antiochos, S.K., DeVore, C.R., Klimchuk, J.A.: 1999, A model for solar coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 510, 485.
Bame, S.J., Asbridge, J.R., Feldman, W.C., Fenimore, E.E., Gosling, J.T.: 1979, Solar wind heavy ions from flare-heated coronal plasma. Solar Phys. 62, 179.
Burlaga, L., Sittler, E., Mariani, F., Schwenn, R.: 1981, Magnetic loop behind an interplanetary shock – Voyager, Helios, and IMP 8 observations. J. Geophys. Res. 86, 6673.
Burlaga, L., Fitzenreiter, R., Lepping, R., Ogilvie, K., Szabo, A., Lazarus, A., et al.: 1998, A magnetic cloud containing prominence material – January 1997. J. Geophys. Res. 10, 277.
Cho, K.-S., Park, S.-H., Marubashi, K., Gopalswamy, N., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S., Kim, R.-S.: 2013, Comparison of helicity signs in interplanetary CMEs and their solar source regions. Solar Phys., in this issue.
Garcia, H.: 1994, Temperature and emission measure from GOES soft X-ray measurements. Solar Phys. 154, 275.
Gilbert, J.A., Lepri, S.T., Landi, E., Zurbuchen, T.H.: 2012, First measurements of the complete heavy-ion charge state distributions of C, O, and Fe associated with interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 751, 20.
Gopalswamy, N.: 2006a, Properties of interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Space Sci. Rev. 124, 145.
Gopalswamy, N.: 2006b, Coronal mass ejections and type II radio bursts. In: Gopalswamy, N., Mewaldt, R., Torsti, J. (eds.) Solar Eruptions and Energetic Particles, Geophys. Monogr. Ser. 165, AGU, Washington, 207.
Gopalswamy, N.: 2006c, Consequences of coronal mass ejections in the heliosphere. Sun Geosph. 1, 5.
Gopalswamy, N.: 2010, Coronal mass ejections: a summary of recent results. In: Proceedings of the 20th National Solar Physics Meeting, held 31 May – 4 June, 2010, Papradno, Slovakia, 108 – 130.
Gopalswamy, N., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S.: 2009, Major solar flares without coronal mass ejections. In: Gopalswamy, N., Webb, D.F. (eds.) Proceedings of IAU Symposium 257, Universal Heliophysical Processes, 283.
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Akiyama, S.: 2007, Geoeffectiveness of halo coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 112, A06112. doi: 10.1029/2006JA012149 .
Gopalswamy, N., Raulin, J.-P., Kundu, M.R., Nitta, N., Lemen, J.R., Herrmann, R., Zarro, D., Kosugi, T.: 1995, VLA and YOHKOH observations of an M1.5 flare. Astrophys. J. 455, 715.
Gopalswamy, N., Hanaoka, Y., Kosugi, T., Lepping, R.P., Steinberg, J.T., Plunkett, S., et al.: 1998, On the relationship between coronal mass ejections and magnetic clouds. Geophys. Res. Lett. 25, 2485.
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Krucker, S., Stenborg, G., Howard, R.A.: 2004, Intensity variation of large solar energetic particle events associated with coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 109, A12105. doi: 10.1029/2004JA010602 .
Gopalswamy, N., Aguilar-Rodriguez, E., Yashiro, S., Nunes, S., Kaiser, M.L., Howard, R.A.: 2005, Type II radio bursts and energetic solar eruptions. J. Geophys. Res. 110, A12S07. doi: 10.1029/2005JA011158 .
Gopalswamy, N., Mäkelä, P., Xie, H., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S.: 2009a, CME interactions with coronal holes and their interplanetary consequences. J. Geophys. Res. 114, A00A22. doi: 10.1029/2008JA013686 .
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Michalek, G., Stenborg, G., Vourlidas, A., Freeland, S., Howard, R.: 2009b, The SOHO/LASCO CME catalog. Earth Moon Planets 104, 295.
Gopalswamy, N., Dal Lago, A., Yashiro, S., Akiyama, S.: 2009c, The expansion and radial speeds of coronal mass ejections. Cent. Eur. Astrophys. Bull. 33, 115.
Gopalswamy, N., Xie, H., Mäkelä, P., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S., Kaiser, M.L., Howard, R.A., Bougeret, J.-L.: 2010a, Interplanetary shocks lacking type II radio bursts. Astrophys. J. 710, 1111.
Gopalswamy, N., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S., Mäkelä, P.: 2010b, Coronal mass ejections from sunspot and non-sunspot regions. In: Hasan, S.S., Rutten, R.J. (eds.) Magnetic Coupling Between the Interior and Atmosphere of the Sun, Astrophysics and Space Science Proceedings, Springer, Berlin, 289.
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Michalek, G., Xie, H., Mäkelä, P., Vourlidas, A., Howard, R.A.: 2010c, A catalog of halo coronal mass ejections from SOHO. Sun Geosph. 5, 7.
Gopalswamy, N., Nitta, N., Akiyama, S., Mäkelä, P., Yashiro, S.: 2012, Coronal magnetic field measurement from EUV images made by the solar dynamics observatory. Astrophys. J. 744, 72.
Gosling, J.T.: 1990, Coronal Mass Ejections and Magnetic Flux Ropes in Interplanetary Space in Physics of Magnetic Flux Ropes, Geophys. Monogr. Ser. 58, 343.
Hanaoka, Y., Kurokawa, H., Enome, S., Nakajima, H., Shibasaki, K., Nishio, M., et al.: 1994, Simultaneous observations of a prominence eruption followed by a coronal arcade formation in radio, soft X-rays, and H(alpha). Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan 46, 205.
Henke, T., Woch, J., Mall, U., Livi, S., Wilken, B., Schwenn, R., et al.: 1998, Differences in the O7+/O6+ ratio of magnetic cloud and non-cloud coronal mass ejections. Geophys. Res. Lett. 25, 3465.
Henke, T., Woch, J., Schwenn, R., Mall, U., Gloeckler, G., von Steiger, R., et al.: 2001, Ionization state and magnetic topology of coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 10613.
Hundhausen, A.J., Gilbert, H.E., Bame, S.J.: 1968, Ionization state of the interplanetary plasma. J. Geophys. Res. 73, 5485.
Kim, R.-S., Gopalswamy, N., Cho, K.-S., Moon, Y.-J., Yashiro, S.: 2013, Propagation characteristics of CMEs associated magnetic clouds and ejecta. Solar Phys., in this issue.
Lepri, S.T., Zurbuchen, T.H.: 2004, Iron charge state distributions as an indicator of hot ICMEs: possible sources and temporal and spatial variations during solar maximum. J. Geophys. Res. 109, A01112. doi: 10.1029/2003JA009954 .
Lepri, S.T., Zurbuchen, T.H.: 2010, Direct observational evidence of filament material within interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. Lett. 723, L22.
Lepri, S.T., Zurbuchen, T.H., Fisk, L.A., Richardson, I.G., Cane, H.V., Gloeckler, G.: 2001, Iron charge state distributions as an identifier of interplanetary coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 29231.
Lin, J., Raymond, J.C., van Ballegooijen, A.A.: 2004, The role of magnetic reconnection in the observable features of solar eruptions. Astrophys. J. 602, 422.
Lynch, B.J., Reinard, A.A., Mulligan, T., Reeves, K.K., Rakowski, C.E., Allred, J.C., et al.: 2011, Ionic composition structure of coronal mass ejections in axisymmetric magnetohydrodynamic models. Astrophys. J. 740, 112.
Marubashi, K.: 1997, Interplanetary magnetic flux ropes and solar filaments. In: Crooker, N., Joselyn, J.A., Feynman, J. (eds.) Coronal Mass Ejections, Geophys. Monogr. Ser. 99, AGU, Washington, 147.
Owens, M.J., Cargill, P.J., Pagel, C., Siscoe, G.L., Crooker, N.U.: 2005, Characteristic magnetic field and speed properties of interplanetary coronal mass ejections and their sheath regions. J. Geophys. Res. 110, A01105. doi: 10.1029/2004JA010814 .
Qiu, J., Hu, Q., Howard, T.A., Yurchyshyn, V.B.: 2007, On the magnetic flux budget in low-corona magnetic reconnection and interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 659, 758.
Rakowski, C.E., Laming, M.J., Lepri, S.T.: 2007, Ion charge states in halo coronal mass ejections: what can we learn about the explosion? Astrophys. J. 667, 602.
Reinard, A.: 2005, Comparison of interplanetary CME charge state composition with CME-associated flare magnitude. Astrophys. J. 620, 501.
Reinard, A.A.: 2008, Analysis of interplanetary coronal mass ejection parameters as a function of energetics, source location, and magnetic structure. Astrophys. J. 682, 1289.
Reinard, A.A., Zurbuchen, T.H., Fisk, L.A., Lepri, S.T., Skoug, R.M., Gloeckler, G.: 2001, Comparison between average charge states and abundances of ions in CMEs and the slow solar wind. AIP Conf. Proc. 598(1), 139.
Riley, P., Schatzman, C., Cane, H.V., Richardson, I.G., Gopalswamy, N.: 2006, On the rates of coronal mass ejections: remote solar and in situ observations. Astrophys. J. 647, 648.
Schmahl, E.J., Schmelz, J.T., Saba, J.L.R., Strong, K.T., Kundu, M.R.: 1990, Microwave and X-ray observations of a major confined solar flare. Astrophys. J. 358, 654.
Uchida, Y., McAllister, A., Strong, K.T., Ogawara, Y., Shimizu, T., Matsumoto, R., Hudson, H.S.: 1992, Continual expansion of the active region corona observed by the Yohkoh soft X-ray telescope. Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan 44, L155.
Xie, H., Gopalswamy, N., St. Cyr, O.C.: 2013, Near-Sun flux rope structure of CMEs. Solar Phys. in this issue. doi: 10.1007/s11207-012-0209-0 .
Yashiro, S., Gopalswamy, N.: 2009, Statistical relationship between solar flares and coronal mass ejections. In: Gopalswamy, N., Webb, D.F. (eds.) IAU Symposium 257, Universal Heliophysical Processes, Cambridge Univ. Press, London, 233.
Yashiro, S., Gopalswamy, N., Michalek, G., St. Cyr, O.C., Plunkett, S.P., Rich, N.B., Howard, R.A.: 2004, A catalog of white light coronal mass ejections observed by the SOHO spacecraft. J. Geophys. Res. 109, A07105. doi: 10.1029/2003JA010282 .
Zhao, L., Zurbuchen, T.H., Fisk, L.A.: 2009, Global distribution of the solar wind during solar cycle 23: ACE observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 36, L14104. doi: 10.1029/2009GL039181 .
Acknowledgements
We thank the ACE, Wind, and SOHO teams for providing the data on line. SOHO is a project of international collaboration between ESA and NASA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Flux-Rope Structure of Coronal Mass Ejections
Guest Editors: N. Gopalswamy, T. Nieves-Chinchilla, M. Hidalgo, J. Zhang, and P. Riley
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gopalswamy, N., Mäkelä, P., Akiyama, S. et al. The Solar Connection of Enhanced Heavy Ion Charge States in the Interplanetary Medium: Implications for the Flux-Rope Structure of CMEs. Sol Phys 284, 17–46 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-012-0215-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-012-0215-2