Abstract
Over 20 years ago, Hanahan and Weinberg published a seminal review that addressed the biological processes that underly malignant transformation. This classical review, along with two revisions published in 2011 and 2022, has remain a classic of the oncology literature. Since many of the addressed biological processes may apply to non-malignant tumorigenesis, we evaluated to what extent these hallmarks pertain to the development of pituitary adenomas.
Some of the biological processes analyzed in this review include genome instability generated by somatic USP8 and GNAS mutations in Cushing’s diseases and acromegaly respectively; non-mutational epigenetic reprograming through changes in methylation; induction of angiogenesis through alterations of VEGF gene expression; promotion of proliferative signals mediated by EGFR; evasion of growth suppression by disrupting cyclin dependent kinase inhibitors; avoidance of immune destruction; and the promotion of inflammation mediated by alteration of gene expression of immune check points. We also elaborate further on the existence of oncogene induced senescence in pituitary tumors. We conclude that a better understanding of these processes can help us dilucidated why pituitary tumors are so resistant to malignant transformation and can potentially contribute to the development of novel anticancer treatments.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PA:
-
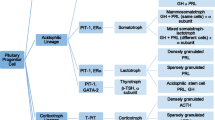
Pituitary Adenoma
- CNFPA:
-
Clinically Non-Functioning Pituitary Adenoma
- GH:
-
Growth Hormone
- PRL:
-
Prolactin
- TSH:
-
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone
- ACTH:
-
Adrenocorticotrophic Hormone
- POU1F1 / Pit-1:
-
Pituitary-specific Positive Transcription factor-1
- TBX19 / T-Pit:
-
T-Box Transcription Factor 19
- LH:
-
Luteinizing Hormone
- FSH:
-
Follicle-Stimulating Hormone
- NR5A1 / SF-1:
-
Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 5 Group A Member 1 / Steroidogenic Factor-1
- MEN:
-
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia
- CDKN:
-
Cyclin Dependent Kinase
- PRKAR1A:
-
Regulatory Alpha-subunit of Protein Kinase A
- SDNH:
-
Succinate-Dehydrogenase
- RNAse:
-
Ribonuclease
- FIPA:
-
Familial Isolated Pituitary Adenoma
- AIP:
-
Aryl-hydrocarbon receptor Interacting Protein
- X-LAG:
-
X-Linked Acrogigantism
- GPR101:
-
G Protein-coupled Receptor 101
- USP8:
-
Ubiquitin Specific peptidase 8
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor
- POMC:
-
Proopiomelanocortin
- GNAS:
-
Guanine Nucleotide binding protein Alpha Subunit
- GHRH:
-
Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone
- CREB:
-
CAMP Response Element Binding protein
- CNV:
-
Copy number variation
- CACNA2D4:
-
Calcium Voltage-Gated Channel Auxiliary Subunit Alpha2delta 4
- GRIA2 / GRIA4:
-
Glutamate Ionotropic Receptor AMPA Type Subunit 2 / Subunit 4
- AVPR1B:
-
Arginine Vasopressin Receptor 1B
- EPHA4:
-
EPH Receptor A4
- GRIN2B:
-
Glutamate Receptor subiunit epsilon 2
- TMEM233:
-
Transmembrane Protein 233
- miRNA:
-
MicroRNA (miR)
- UTR:
-
Untranslated Regions
- mRNA:
-
Messenger RNA
- lncRNA:
-
Long non-coding RNAs
- LINC00473:
-
Long Intergenic Non-Protein Coding RNA 473
- KMT5A:
-
Lysine Methyltransferase 5A
- RPSAP52:
-
Ribosomal protein SA pseudogene 52
- HMGA1 / 2:
-
High Mobility Group AT-Hook 1 / 2
- XIST:
-
X-Inactive Specific Transcript
- VEGF:
-
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor
- BCL-2:
-
B Cell Lymphoma 2
- FGF2:
-
Fibroblast Growth Factor 2
- CD31 / PECAM-1:
-
Cluster of Differentiation 31 / Platelet Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule
- BAX:
-
Bcl-2-Associated X protein 4
- SSTR2 / 5:
-
Somatostatin Receptor 2 / 5
- TP53 / p53:
-
Tumor Protein 53
- FGFR1-4:
-
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 / 2 / 3 / 4
- STAT3:
-
Signal transducer and activators of transcription type 3
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian Target Of Rapamycin
- IGF-1:
-
Insulin like Growth Factor-1
- PTTG-1:
-
Pituitary Tumor Transforming Gene protein-1
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen Activated Protein Kinases
- ETNK2:
-
Ethanolamine Kinase 2
- MERTK:
-
Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase MER
- PIP5K1B:
-
Phosphatidylinositol-4-Phosphate 5-Kinase Type 1 Beta
- CDK:
-
Cyclin-dependent Kinases
- CDKN1A / 2A / 1B / 2C:
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A / 2A / 1B / 2C
- GADD45:
-
Growth Arrest and DNA Damage-inducible protein 45
- CABLES1:
-
Cdk5 And Abl Enzyme Substrate 1
- TERT:
-
Telomerase reverse transcriptase
- TERC:
-
Telomerase RNA Component
- CD27 / 28 / 37:
-
Cluster of Differentiation 27 / 28 / 37
- ICOS:
-
Inducible T cell co-stimulator
- OX40:
-
Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily 4
- CTLA-4:
-
Cytotoxic T lymphocyte associated protein 4
- PD1:
-
Programmed Death 1
- PD-L1:
-
PD Ligand 1
- IL8 / 6 / 1ß:
-
Interlukin 8 / 6 / 1ß
- CCL2 / 3 / 4 / 10 / 22:
-
C-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 2 / 3 / 4 / 10 / 22
- CX3CL1:
-
C-X3-C motif Chemokine Ligand 1
- CXCL1:
-
C-X-C motif Chemokine Ligand 1
- CD8 + T Lymphocytes:
-
Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes
- CD4 + T Lymphocytes:
-
T-helper cells
- NK cells:
-
Natural Killer cells
- M2 macrophages:
-
Alternative activated macrophages
- LDHA:
-
Lactate Dehydrogenase A
- NAD:
-
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide
- GLUT-1:
-
Glucose Transporter 1
- MMP2 / 9 :
-
Matrix Metalloproteinase 2 / 9
- FASN:
-
Fatty Acid Synthase
- p21:
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1
- p16:
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A
- pRB:
-
Retinoblastoma protein
- E2F:
-
E2 Factor
- TGFß:
-
Transforming Growth Factor ß
- p19:
-
Teratocarcinoma cell line P19
- E-CAD:
-
E-cadherin
- EMT:
-
Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition
- N-CAD:
-
N-cadherin / Cadherin-2 / Neural Cadherin
- EPCAM:
-
Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule
- SMAD3:
-
Mothers Against Decapentaplegic homolog 3
- SNAI2:
-
Snail Family Transcriptional Repressor 2
- PITX2:
-
Paired Like Homeodomain 2
- ECM:
-
Extracellular Matrix
- PKC:
-
Protein Kinase C
References
Hanahan D, Weinberg R. Hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100:57–70.
Hanahan D, Weinberg R. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–74.
Lazebnik Y. What are the hallmark of cancer? Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10:232–3.
Sonnenschein C, Soto AM. The aging of the 2000 and 2011 Hallmarks of cancer reviews: A critique. J Bio Sci. 2013;38:651–63.
Ahmed-Fouad Y, Aanei C. Revisiting the hallmarks of cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 2017;7:1016–36.
Hanahan D. Hallmarks of cancer: New dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022;12:31–46.
Melmed S, Kaiser UB, Lopes MB, Bertherat J, Syro LV, Raverot G, et al. Clinical biology of the pituitary adenoma. Endocr Rev. 2022;43:1003–37.
Patel A. Bening vs malignant tumors. JAMA Oncol. 2020;6:1488.
Marino-Enriquez A, Fletcher C. Shouldn’t we care about the biology of benign tumours? Nat Rev Cancer. 2014;14:701–2.
Molitch ME. Diagnosis and treatment of pituitary adenomas: A review. JAMA. 2017;317:516–24.
Mercado M, Melgar V, Salame L, Cuenca D. Clinicly non funcioning pituitary adenomas: Pathogenic, diagnostic and therapeutic aspects. Endocrinol Diabetes Nutr. 2017;64:384–95.
Ramirez C, Cheng S, Vargas G, Asa SL, Ezzat S, Gonzalez B, Cabrera L, Guinto G, Mercado M. Expression of Ki-67, PTTG1, FGFR4, and SSTR2,3 and 5 in nonfunctioning pituitary adenomas: A high throughput TMA, immunohistochemical study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97:1745–51.
Vargas G, Gonzalez B, Ramirez C, Ferreira A, Espinosa E, Mendoza V, Guinto G, Lopez-Felix B, Zepeda E, Mercado M. Clinical characteristics and treatment outcome of 485 patients with nonfunctioning pituitary macroadenomas. Int J Endocrinol. 2015;2015:756069.
Yoo F, Kuan EC, Heaney AP, Bergsneider M, Wang MB. Corticotrophic pituitary carcinoma with cervical metastases: case series and literature review. Pituitary. 2018;21:290–301.
Andonegui-Elguera S, Silva-Roman G, Peña-Martinez E, Taniguchi-Ponciano K, Vela-Patiño S, et al. The genomic landscape of corticotroph tumors: from silent adenomas to ACTH-secreting carcinomas. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:4861.
Aguilera A, Gomez-Gonzalez B. Genome instability: a mechanistic view of its causes and consequences. Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:204–17.
Garcia-Guzman B, Portocarrero-Ortiz L, Dorantes-Argandar AA, Mercado M. Hereditary pituitary tumor syndomes: Genetic and clinical aspects. Rev Invest Clin. 2020;72:8–18.
Barry S, Korbonits M. Update on the genetics of pituitary tumors. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2020;49:433–52.
Trivellin G, Daly AF, Faucz FR, Yuan B, Rostomyan L, Larco DO, et al. Gigantism and acromegaly due to Xq26 microduplications and GPR101 mutation. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:2363-2374.G.
Wanichi I, Mariani B, Frassetto F, Siqueira SA, Musolino N, Cunha-Neto MB, et al. Cushing’s disease due to somatic USP8 mutations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pituitary. 2019;22:435–42.
Perez-Rivas LG, Theodoropoulou M, Ferrau F, Nusser C, Kawaguchi K, Stratakis CA, et al. The gene of the ubiquitin-specific protease 8 is frequently mutated in adenomas causing cushing’s disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100:E997-1004.
Reincke M, Sbiera S, Hayakawa A, Theodoropoulou M, Osswald A, Beuschlein F, et al. Mutations in the deubiquitinase gene USP8 cause Cushing’s disease. Nat Genet. 2015;47:31–8.
Landis CA, Masters SB, Spada A, Pace AM, Bourne HR, Vallar L. GTPase inhibiting mutations activate the α chain of Gs and stimulate adenylyl cyclase in human pituitary tumours. Nature. 1989;340:692–6.
Landis CA, Harsh G, Lyons J, Davis RL, McCormick F, Bourne HR. Clinical characteristics of acromegalic patients whose pituitary tumors contain mutant Gs protein. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990;71:1416–20.
Mendoza V, Sosa E, Espinosa-de-Los-Monteros AL, Salcedo M, Guinto G, Cheng S, Sandoval C, Mercado M. GSPalpha mutations in Mexican patients with acromegaly: potential impact on long term prognosis. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2005;15:28–32.
Albani A, Perez-Rivas LG, Dimopoulou C, Zoop S, Colon-Bolea P, Roeber S, et al. The USP8 mutational status may predict long-term remission in patients with Cushing´s disease. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2018. https://doi.org/10.1111/cen.13802.
Cui Y, Li C, Jiang Z, Zhang S, Li Q, Liu X, Zhou Li R, et al. Single-cell transcriptome and genome analyses of pituitary neuroendocrine tumors. Neuro Oncol. 2021;23:1859–71.
Neou M, Villa C, Armignacco R, Jouinot A, Raffin-Sanson ML, Septier A, Letourneur F, et al. Pangenomic classification of pituitary neuroendocrine tumors. Cancer Cell. 2020;37:123-134.e5.
Wierinckx A, Roche M, Raverot G, Legras-Lechuer C, Croze S, Nazaret N, et al. Integrated genomic profiling identifies loss of chromosome 11p impacting transcriptomic activity in aggressive pituitary PRL tumors. Brain Pathol. 2011;21:533–43.
Lasolle H, Elsensohn MH, Wierimckx A, Alix E, Bonnefille C, Vasiljevic A, et al. Chromosomal instability in the prediction of pituitary neuroendocrine tumors prognosis. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2020;8:190.
Chang M, Yang C, Bao X, Wang R. Genetic and epigenetic causes of pituitary adenomas. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;11:596554.
Taniguchi-Ponciano K, Andonegui-Elguera S, Peña-Martinez E, Silva-Roman G, Vela-Patiño S, et al. Transcriptome and methylome analysis reveals three cellular origins of pituitary tumors. Sci Rep. 2020;10:19373.
Ghafouri-Fard S, Abak A, Hussen BM, Taheri M, Sharifi G. The emerging role of non-coding RNAs in pituitary gland tumors and meningioma. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13:5987.
Li J, Qian Y, Zhang C, Wang W, Qiao Y, Song H, et al. LncRNA LINC00473 is involved in the progression of invasive pituitary adenoma by upregulating KMT5A via ceRNA-mediated miR-502-3p evasion. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12:580.
Cristina C. Angiogenesis in pituitary adenomas: human studies and new mutant mouse models. Int J Endocrinol. 2014;2014:608497.
Dai C, Liang S, Sun B, Li Y, Kang J. Anti-VEGF therapy in refractory pituitary adenomas and pituitary carcinomas: A review. Front Oncol. 2021;11:773905.
Wang Y, Li J, Hu Z, Tohti M, Hu Y, Wang S, Li W, Lu Z, Ma C. The expression profile of Dopamine D2 receptor, MGMT and VEGF in different histological subtypes of pituitary adenomas: a study of 197 cases and indications for medical therapy. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2014;33:56.
Sanchez-Ortiga R, Sanchez-Tejada L, Moreno-Perez O, Riesgo P, Niveiro M, Pico Alfonso AM. Over-expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in pituitary adenomas is associated with extracellular grpwth and recurrence. Pituitary. 2013;16:370–7.
Arita K. Relationship between intratumoral hemorrhage and overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in pituitary adenoma. Hiroshima J Med Sci. 2004;53:23–7.
Mallea-Gil MS, Cristina C, Perez-Millan MI, Rodriguez-Villafane AM, Ballarino C, et al. Invasive giant prolactinoma with loss of therapeutic response to cabergoline: expression of angiogenic markers. Endocr Pathol. 2009;20:35–40.
Zimering MB, Katsumata N, Sato Y, Brandu ML, Aurbach GD, et al. Increased basic fibroblast growth factor in plasma from multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1: relation to pituitary tumor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993;76:1182–7.
Turner HE, Nagy Z, Gatter KC, Esiri MM, Harris AL, Wass JA. Angiogenesis in pituitary adenomas and the normal pituitary gland. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85:1159–62.
Itoh J, Serizawa A, Kawai K, Ishii Y, Teramoto A, Yoshiyuki R, et al. Vascular networks and endothelial cells in the rat experimental pituitary glands and in the human pituitary adenomas. Microsc Res Tech. 2003;60:231–5.
Perez-Millan MI, Berner SI, Luque GM, De Bonis C, Sevlever G, Besu-Villalobos D, Cristina C. Enhanced nestin expression and small blood vessels in human pituitary adenomas. Pituitary. 2013;16:303–10.
Singh R, Letai A, Sarosiek K. Regulation of apoptosis in health and disease: the balancing act of BCL-2 family proteins. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20:175–93.
Saraga-Babic M, Bazina M, Vukojevic K, Bocina I, Stefanovic V. Involvement of pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic factors in the early development of the human pituitary gland. Histol Histopathol. 2008;23:1259–68.
Kontogeorgos G, Sambaziotis D, Piaditis G, Karameris A. Apoptosis in human pituitary adenomas: a morphologic and in situ end-labeling study. Mod Pathol. 1997;10:921–6.
Guzzo MF, Carvalho LRS, Bronstein MD. Apoptosis: its role in pituitary development and neoplastic pituitary tissue. Pituitary. 2014;17:157–62.
Xin M, Li R, Xie M, Park D, Owonikoko TK, Sica GL, et al. Small-molecule Bax agonists for cancer therapy. Nat Commun. 2014;5:4935.
Hafezi S, Rahmani M. Targeting BCL-2 in cancer: advances, challenges, and perspectives. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13:1292.
Sambaziotis D, Kapranos N, Kontogeorgos G. Correlation of bcl-2 and bax with apoptosis in human pituitary adenomas. Pituitary. 2003;6:127–33.
Kulig E, Jin L, Qian X, Horvath E, Kovacs K, et al. Apoptosis in nontumorous and neoplastic human pituitaries: expression of the Bcl-2 family of proteins. Am J Pathol. 1999;154:767–74.
Mercado M, Espinosa E, Ramirez C. Current status and future directions of pharmacological therapy for acromegaly. Minerva Endocrinol. 2016;41:351–65.
Fleuren EDG, Zhang L, Wu J, Daly RJ. The kinome “at large” in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2016;16:83–98.
Xie Y, Su N, Yang J, Tan Q, Huang S, Jin M, et al. FGF/FGFR signaling in health and disease. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5:181.
Durcan E, Keskin FE, Ozkaya HM, Sirolu S, Sahin S, Korkmaz OP, Gazioglu N, Tanriover N, et al. Fibroblast growth factor Receptor-4 expression in pituitary adenomas is associated with aggressive tumor features. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2022;130:125–33.
Quian ZR, Sano T, Asa SL, Yamada S, Horiguchi H, Tashiro T, et al. Cytoplasmic expression of Fibroblast growth factor receptor-4 in human pituitary adenomas: relation to tumor type, size, proliferation, and invassiveness. J clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89:1904–11.
Nakano-Tateno T, Tateno T, Hlaing MM, Zheng L, Yoshimoto K, Yamada S, Asa SL, Ezzat S. FGFR4 polymorphic variants modulate phenotypic features of Cushing disease. Mol Endocrinol. 2014;28:525–33.
Jalali S, Monsalves E, Tateno T, Zadeh G. Role of mTOR inhibitors in Growth Hormone-Producing pituitary adenomas harboring different FGFR4 genotypes. Endocrinology. 2016;157:3577–87.
Chen R, Duan J, Li L, Ma Q, Sun Q, Ma J, Li C, et al. mTOR promotes pituitary tumor development through activation of PTTG1. Oncogene. 2017;36:979–88.
Liu C, Nakano-Tateno T, Satou M, Chik C, Tateno T. Emerging role of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) in pituitary adenomas. Endocr J. 2021;68:1143.
Zhou C, Jiao Y, Wang R, Ren SG, Wawrowsky K, Melmed A. STAT3 upregulation in pituitary somatotroph adenomas induces growth hormone hypersecretion. J Clin Invest. 2015;125:1692–702.
Braicu C, Buse M, Busuioc C, Drula R, Gulei D, Raduly L, et al. A comprehensive review of MAPK: A promising therapeutic target in cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2019;11:1618.
Taniguchi-Ponciano K, Portocarrero-Ortiz LA, Guinto G, Moreno-Jimenez S, Gomez-Apo E, Chavez-Macias L, et al. The kinome, cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases of pituitary adenomas, a look into the gene expression profile among tumors from different lineages. BMC Med Genomics. 2022;15:52.
Hibberts NA, Simpson DJ, Bicknell JE, Broome JC, Hoban PR, Clayton RN, Farrell WE. Analysis of cyclin D1 (CCND1) allelic imbalance and overexpression in sporadic human pituitary tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 1999;5:2133–9.
Simpson DJ, Frost SJ, Bicknell JE, Broome JC, McNicol AM, Clayton RN, Farrell WE. Aberrant expression of G(1)/S regulators is a frequent event in sporadic pituitary adenomas. Carcinogenesis. 2001;22:1149–54.
Jordan S, Lidhar K, Korbonits M, Lowe DG, Grossman AB. Cyclin D and cyclin E expression in normal and adenomatous pituitary. Eur J Endocrinol. 2000;143:R1-6.
Roussel-Gervais A, Bilodeau S, Vallette S, Berthelet F, Lacroix A, Figarella-Branger D, Brue T, Drouin J. Cooperation between cyclin E and p27(Kip1) in pituitary tumorigenesis. Mol Endocrinol. 2010;24:1835–45.
Hossain MG, Iwata T, Mizysawa N, Qian ZR, Shima SWN, Okutsu T, Yamada S, Sano T, Yoshimoto K. Expression of p18 (INK4C) is down-regulated in human pituitary adenomas. Endocr Pathol. 2009;20:114–21.
Simpson DJ, McNicol AM, Murray D, Bahar A, Turner HE, Wass JAH, Esiri MM, Clayton RN, Farrell WE. Molecular pathology shows p16 methylation in nonadenomatous pituitaries from patients with Cushing’s disease. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:1780–8.
Aubrey BJ, Strasser A, Kelly GL. Tumor-supressor functions of the TP53 pathway. Cold Spring Harb Prespect Med. 2016;6:a026062.
Thapar K, Scheithauer BW, Kovacs K, Pernicone PJ, Laws ER. P53 expression in pituitary adenomas and carcinomas: correlation with invasiveness and tumor growth fractions. Neurosurgery. 1996;38:765–70.
Saeger W, Ludecke B, Ludecke DK. Clinical tumor growth and comparison with proliferation markers in non-functioning (inactive) pituitary adenomas. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2008;116:80–5.
Yagnik G, Jahangiri A, Chen R, Wagner JR, Aghi MK. Role of a p53 polymorphism in the development of nonfunctional pituitary adenomas. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017;446:81–90.
Michaelis KA, Knox AJ, Xu M, Kiseljak-Vassiliades K, Edwards MG, et al. Identification of growth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible gene beta (GADD45beta) as a novel tumor suppressor in pituitary gonadotrope tumors. Endocrinology. 2011;152:3603–13.
Hernandez-Ramirez LC, Gam R, Valdes N, Lodish MB, Pankratz N, Balsalobre A, Gauthier Y, et al. Loss-of-function mutations in the CABLES1 gene are a novel cause of Cushing’s disease. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2017;24:379–92.
Martins CS, Santana-Lemos BA, Saggioro FP, Neder L, Machado HR, et al. Telomere length and telomerase expression in pituitary tumors. J Endocrinol Invest. 2015;38:1243–6.
Can N, Celik M, Bulbul BY, Sut N, Ozyilmaz F, Ayturk S, et al. TERT expression in pituitary adenomas. Turk Patoloji Derg. 2017;33:103–11.
Yoshino A, Katayama Y, Fukushima T, Watanabe T, Komine C, Yokoyama T, et al. Telomerase activity in pituitary adenomas: significance of telomerase expression in predicting pituitary adenoma recurrence. J Neurooncol. 2003;63:155–62.
Miyake Y, Adachi J, Suzuki T, Mishima K, Araki R, Mizuno R, Nishikawa R. TERT promoter methylation is significantly associated with TERT upregulation and disease progression in pituitary adenomas. J Neurooncol. 2019;141:131–8.
Heaphy CM, Bi WL, Coy S, Davis C, Gallia GL, Santagata S, Rodriguez FJ. Telomere length alterations and ATRX/DAXX loss in pituitary adenomas. Mod Pathol. 2020;33:1475–81.
Matsumoto R, Fukuoka H, Iguchi G, Odake Y, Yoshida K, Bando H, et al. Accelerated telomere shortening in acromegaly; IGF-I induces telomere shortening and cellular senescence. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0140189.
Chew V, Toh HC, Abastado JP. Immune microenviroment in tumor proegression: characteristics and challenges for therapy. J Oncol. 2012;2012:608406.
Mei Y, Bi WL, Greenwald NF, Du Z, Agar NYR, Kaiser UB, et al. Increased expression of programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) in human pituitary tumors. Oncotarget. 2016;7:76565–76.
Dai C, Liang S, Sun B, Kang J. The progress of immunotherapy in refractory pituitary adenomas and pituitary carcinomas. Front endocrinol. 2020;11:608422.
Marques P, Barry S, Carlsen E, Collier D, Ronaldson A, et al. Chemokines modulate the tumour microenvironment in pituitary neuroendocrine tumours. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2019;7:172.
Heshmati H, Casanova S, Racadot J, Van Effenterre R, et al. Prevalence of lymphocytic infiltrate in 1400 pituitary adenomas. Endocrine J. 1998;45:357–61.
Lupi I, Manetti L, Caturegli P, Menicagli M, Cosottini M, Iannelli A, et al. Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes but not serum pituitary antibodies are associated with poor clinical outcome after surgery in patients with pituitary adenoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95:289–96.
Lu JQ, Adam B, Jack AS, Lam A, Broad RW, Chik CL. Immune cell infiltrate in pituitary adenomas: more macrophages in larger adenomas and More T cells in growth hormone adenomas. Endocri Pathol. 2015;26:263–72.
Zhan X, Deciderio DM. Editorial: Molecular network study of Pituitary Adenomas. Front Endocrinol. 2020;11:26.
Wang Z, Guo X, Gao L, Deng K, Lian W, Bao X, et al. The immune profile of Pituitary Adenomas and a novel immune classification for predicting immunotherapy responsiveness. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020;105:e3207–e3223.
Vela-Patiño S, Salazar MI, Remba-Shapiro I, Peña-Martinez E, Silva-Roman G, Andonegui-Elguera S, et al. Neuroendocrine-immune interface: interactions of two complex systems in health and disease. Arch Med Res. 2022;53:240–51.
Han C, Lin S, Lu X, Xue L, Wu ZB. Tumor-associated macrophages: new horizons for pituitary adenoma researches. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:785050.
Van der Heiden MG, Cantley LC, Thompson CB. Understanding the Warburg effect: the metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science. 2009;324(5930):1029–33.
Miao P, Sheng S, Sun X, Liu J, Huang G. Lactate dehydrogenase A in cancer: a promising target for diagnosis and therapy. IUBMB Life. 2013;65:904–10.
An J, Zhan Y, He J, Zang Z, Zhou Z, Pei X, et al. Lactate dehydrogenase A promotes the invasion and proliferation of pituitary adenoma. Sci Rep. 2017;7:4734.
Feng J, Zhang Q, Zhou Y, Yu S, Hong L, Zhao S, Yang J, et al. Integration of proteomics and metabolomics revealed metabolite-protein networks in ACTH-Secreting pituitary adenoma. Frent Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018;9:678.
Zhan X, Desiderio DM. Signaling pathway networks mined from human pituitary adenoma proteomics data. BMC Med Genomics. 2010;3:13.
Mooi WJ, Peeper DS. Oncogene-induced cells senescence-halting on the road to cancer. N Eng J Med. 2006;355:1037–46.
Mooi WJ. Oncogene-induce cellular senescence: causal factor in the growth arrest of pituitary microadenomas? Horm Res. 2009;71(supp2):78–81.
Liu XL, Ding J, Meng LH. Oncogene-induced senescence: a double edged sword in cancer. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018;39:1553–8.
Alexsandraki K, Khan MM, Chahal HS, Dalantaeva NS, Trivellin G, Berney DM, Caron P, et al. Oncogene-induced senescence in pituitary adenomas and carcinomas. Hormones (Athens). 2012;11:297–307.
Sabatino ME, Petiti JP, del Valle-Sosa L, Perez PA, Gutierrez S, Leimgruber C, Latini A, et al. Evidence of celular senescence during the development of estrogen-induced pituitary tumors. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2015;22:299–317.
Arzt E, Chesnokova V, Stalla G, Melmed S. Pituitary adenoma growth: a model for cellular senescence and cytokine action. Cell Cycle. 2009;8:677–8.
Chesnokova V, Melmed S. Pituitary senescence: the evolving role of Pttg. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010;326:55–9.
Manojlovic-Gacic E, Skender-Gazibara M, Popovic V, Soldatovic I, Boricic N, Raicevic S, et al. Endocrine Pathol. 2016;27:1–11.
Chen K, Li G, Kang X, Liu P, Qian L, Shi Y, Osman RA, Tang Z, Zhang G. EMT-related markers in serum exosomes are potential diagnostic biomarkers for invasive pituitary adenomas. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2021;17:3769–80.
Shen X, Liu Q, Xu J, Wang Y. Correlation between the expression of Interleukin-6, STAT3, E-Cadherin and N-Cadherin protein and invasiveness in nonfunctional pituitary adenomas. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2021;82(Suppl 3):e59–69.
Jia W, Zhu J, Martin TA, Jiang A, Sanders AJ, Jiang WG. Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition (EMT) markers in human pituitary adenomas indicate a clinical course. Anticancer Res. 2015;35:2635–43.
Tamura R, Ohara K, Morimoto Y, Kosugi K, Oishi Y, Sato M, Yoshida K, Toda M. PITX2 expression in non-functional pituitary neuroendocrine tumor with cavernous sinus invasion. Endocr Pathol. 2019;30:81–9.
Yang C, Bao X, Wang R. Role of matrix metalloproteinases in pituitary adenoma invasion. Chin Neurosurg J. 2018;4:2–7.
Gonzalez-del Pliego M, Aguirre-Benitez E, Paisano-Ceron K, Valdovinos-Ramirez I, Rangel-Morales C, Rodriguez-Mata V, et al. Expression of Eag1 K+ channel and ErbBs in human pituitary adenomas: cytoskeleton arrangement patterns in cultured cells. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013;6:458–68.
Laporte E, Vennekens A, Vankelecom H. Pituitary remodeling throughout life: are resident stem cells involved? Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;11:604519.
Chen L, Ye H, Wang X, Tang X, Mao Y, Zhao Y, et al. Evidence of brain tumor stem progenitor-like cells with low proliferative capacity in human benign pituitary adenoma. Cancer Lett. 2014;349:61–6.
Mertens F, Gremeaux L, Chen J, Fu Q, Willems C, Roose H, Govaere O, et al. Pituitary tumors contain a side population with tumor stem cell-associated characteristics. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2015;22:481–504.
Peverelli E, Giardino E, Treppiedi D, Meregalli M, Belicchi M, Vaira V, Corbetta S, et al. Dopamine receptor type 2 (DRD2) and somatostatin receptor type 2 (SSTR2) agonists are effective in inhibiting proliferation of progenitor/stem-like cells isolated from nonfunctioning pituitary tumors. Int J Cancer. 2017;140:1870–80.
Budan RM, Georgescu CE. Multiple pituitary adenomas: a systematic review. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2016;7:1.
Jastania RA, Alsaad KO, Al-Shraim M, Kovacs K, Asa SL. Double adenomas of the pituitary: transcription factors Pit-1, T-pit, and SF-1 identify cytogenesis and differentiation. Endocr Pathol. 2005;16:187–94.
Acknowledgements
All figure except Fig. 1 was created with BioRender.com.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the writing. KTP and MM performed the literature search and revised the work. DMR, JK, ACZ, IRS, GSR, SVP, AES, AVP performed the literature search. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Marrero-Rodríguez, D., Taniguchi-Ponciano, K., Kerbel, J. et al. The hallmarks of cancer… in pituitary tumors?. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 24, 177–190 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11154-022-09777-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11154-022-09777-y