Abstract
Background and aims
Proline and glycinebetaine are osmolytes playing a role in resistance to salt and water stress but their involvement in plant adaptation to heavy metals remain unclear.
Methods
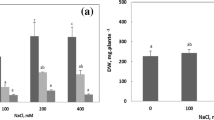
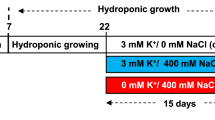
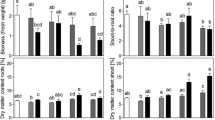
Young plants of the halophyte Kosteletzkya pentacarpos were grown in nutrient solution in the presence of Cd (20 or 40 μM) or Zn (200 or 400 μM), or a combination of both heavy metals and in the presence or absence of NaCl 50 mM for 48 h. Osmolytes concentrations, enzyme activities involved in their metabolism and expression of corresponding genes were determined in roots and leaves.
Results
Cadmium but not zinc increased proline and glycinebetaine in the leaves. Salinity reduced proline content in Cd-treated plants but increased it in plants exposed to Cd + Zn. Proline was produced through both glutamate and ornithine pathways while proline dehydrogenase was inhibited in response to heavy metals. Correlation between enzyme activities and corresponding gene expression was significant in the leaves but not in the roots. Gene coding for proline transport (KvProT) was upregulated in response to heavy metals.
Conclusion
Low NaCl dose (50 mM) afford protection to heavy metal stress in K. pentacarpos and its effect on osmolyte synthesis depends on considered metal and plant organ.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aamer M, Muhammad UH, Abid A, Su Q, Liu Y, Adnan R, Muhammad AUK, Tahir AK, Huang G (2018) Foliar application of glycinebetaine (GB) alleviates the cadmium (Cd) toxicity in spinach through reducing Cd uptake and improving the activity of antioxidant systems. Appl Ecol Environ Res 16:7575–7583
Bai J, Zhao Q, Wang W, Wang W, Jia J, Cui B, Liu W (2019) Arsenic and heavy metals pollution along a salinity gradient in drained coastal wetland soils: depth distribution, sources and toxic risks. Ecol Indic 96:91–98
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207
Ben Hassine A, Ghanem M, Bouzid S, Lutts S (2008) An inland and a coastal population of the Mediterranean xero-halophyte species Atriplex halimus differ in their ability to accumulate proline and glycinebetaine in response to salinity and water stress. J Exp Bot 59:1315–1326
Ben Rejeb K, Abdelly C, Savouré A (2014) How reactive oxygen species and proline face stress together. Plant Physiol Biochem 80:278–284
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chen THH, Murata N (2008) Glycinebetaine: an effective protectant against abiotic stress in plants. Trends Plant Sci 23:9
Chen J, Wu J, Lu Y, Cao Y, Zeng Y, Zhang Z, Wang L, Wang S (2016) Molecular cloning and characterization of a gene encoding the proline transporter protein in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Crop J 4:384–390
Farooq MA, Ali S, Hameed A, Bharwana SA, Rizwan M, Ishaque W, Farid M, Mahmood K, Iqbal Z (2016) Cadmium stress in cotton seedlings: physiological, photosynthesis and oxidative damages alleviated by glycinebetaine. S Afr J Bot 104:61–68
Figuerora-Soto CG, Valenzuela-Soto EM (2018) Glycine betaine rather than acting only as osmolyte also plays a role as regulator in cellular metabolism. Biochimie 147:89–97
Fugiwara T, Mitsuya S, Miyake H, Hattori T, Takabe T (2010) Characterization of a novel glycinebetain/proline transporter gene expressed in the mestome sheath and latteral root cap cells in barley. Planta 232:133–143
Grieve CM, Grattan SR (1983) Rapid assay for determination of water soluble quaternary ammonium componds. Plant Soil 70:303–307
Guan C, Huang YH, Cui X, Liu SJ, Zhou YZ, Zhang YW (2018) Overexpression of gene encoding the key enzyme involved in proline-biosynthesis (PuP5CS) to improve salt tolerance in switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.). Plant Cell Rep 37:1187–1199
Han RM (2013) Sodium chloride improves heavy metal tolerance in the halophyte species Kosteleyzkya virginica independently of growth stimulation. PhD Thesis, Université catholique de Louvain, 309 p
Han RM, Lefèvre I, Ruan C-J, Beukelaers N, Qin P, Lutts S (2012a) Effects of salinity on the response of the wetland halophyte Kosteletzkya virginica (L.) Presl. to copper toxicity. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:1137–1150
Han RM, Lefèvre I, Ruan CJ, Qin P, Lutts S (2012b) NaCl differently interferes with Cd and Zn toxicities in the wetland halophyte species Kosteletzkya virginica (L.) Presl. Plant Growth Regul 68:97–109
Han RM, Lefevre I, Albacete A, Pérez-Alfocea F, Barba-Espín G, Díaz-Vivancos P, Quinet M, Ryan CJ, Hernández JA, Cantero-Navarro E, Lutts S (2013a) Antioxidant enzyme activities and hormonal status in response to Cd in the wetland halophyte Kosteletzkya virginica (L.) Presl. under saline conditions. Physiol Plant 147:352–368
Han RM, Quinet M, André E, van Elteren J, Destrebecq F, Vogel-Mikuš K, Cui G, Debeljak M, Lefèvre I, Lutts S (2013b) Accumulation and distribution of Zn in the shoots and reproductive structures of the halophyte plant species Kosteletzkya virginica as a function of salinity. Planta 238:441–457
Hossain MA, Hasanuzzaman M, Fujita M (2010) Up-regulation of antioxidant and glyoxylase systems by exogenous glycinebetaine and proline in mung bean confer tolerance to cadmium stress. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 16:259–272
Kaur G, Asthir B (2015) Proline: a key player in plant abiotic stress tolerance. Biol Plant 59:609–619
Kavi Kishor PB, Sreenivasulu N (2014) Is proline accumulation per se correlated with stress tolerance or is proline homeostasis a more critical issue? Plant Cell Environ 37:300–311
Kavi Kishor PB, Kumari PH, Sunita MSL, Sreenivasulu N (2015) Role of proline in cell wall synthesis and plant development and its implication in plant ontogeny. Front Plant Sci 6:544
Kubala S, Wojtyla L, Quinet M, Lechowska K, Lutts S, Garnczarska M (2015) Enhanced expression of the proline synthesis gene P5CSA in relation to seed osmopriming improvement of Brassica napus germination under salinity stress. J Plant Physiol 183:1–12
Kumar V, Sharma A, Kaur P, Sidhu GPS, Bali AS, Bhardwaj R, Thukral AK, Cerda A (2019) Pollution assessment of heavy metals in soils of India and ecological risk assessment: a state of the art. Chemosphere 216:449–462
Kurepin LV, Ivanov AG, Zaman M, Pharis RP, Allakherdiev SI, Hurry V, Hüner NPA (2015) Stress-related hormones and glycinebetaine interplay in protection of photosynthesis under abiotic stress conditions. Photosynth Res 126:221–235
Lefèvre I, Marchal G, Meerts P, Corréal E, Lutts S (2009) Chloride salinity reduces cadmium accumulation by the Mediterranean halophyte species Atriplex halimus L. Environ Exp Bot 65:142–152
Lin W, Wu K, Lao Z, Hu W, Lin B, Li Y, Fan H, Hu J (2019) Assessment of trace metal contamination and ecological risk in the forest ecosystem of Dexing mining area in Northeast Jiangxi Province, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 167:76–82
Lutts S (2000) Exogenous glycinebetaine reduces sodium accumulation in salt-stressed rice plants. Int Rice Res Notes 25:39–40
Lutts S, Lefèvre I (2015) How can we take advantage of halophyte properties to cope with heavy metal toxicity in salt-affected areas? Ann Bot 115:509–528
Lutts S, Bouharmont J, Kinet JM (1999a) Physiological characterization of salt-resistant rice somaclones. Aust J Bot 47:835–849
Lutts S, Majerus V, Kinet JM (1999b) NaCl effects on proline metabolism in rice (Oryza sativa) seedlings. Physiol Plant 105:450–458
Mansour MMF, Ali EF (2017) Gluycinebetaine in saline conditions: an assessment of the current state of knowledge. Acta Physiol Plant 39:56
Paradisone V, Barrameda-Medina Y, Monteisinos-Pereira D, Romero L, Esposito S, Ruiz JM (2015) Roles of some nitrogenous compounds protectors in the resistance to zinc toxicity in Lactuca sativa cv. Phillipus and Brassica oleracea cv. Bronco. Acta Physiol Plant 37:137
Patar A, Giri A, Boro F, Bhuyan K, Singha U, Giri S (2016) Cadmium pollution and amphibians: studies in tadpoles of Rana limnocharis. Chemosphere 144:1043–1049
Sdouga D, Ben Amor F, Ghribi S, Kabtni S, Tebini M, Branca F, Trifi-Farah N, Marghali S (2019) An insight from tolerance to salinity stress in halophyte Portulaca oleracea L.: physio-morphological, biochemical and molecular responses. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 172:45–52
Silva-Ortega CO, Ochoa-Alfaro AE, Reyes-Aguero JA, Aguado-Santacruz GA, Jimenez-Bremont JF (2008) Salt stress increases the expression of P5CS gene and induces proline accumulation in cactus pear. Plant Physiol Biochem 46:82–92
Singh V, Tripathi BN, Sharma V (2016) Interaction of Mg with heavy metals (Cu, Cd) in Triticum aestivum with special reference to oxidative and proline metabolism. J Plant Res 129:487–497
Skopelitis DS, Paranychianakis NV, Paschalidis KA, Pliakonis ED, Delis ID, Yakoumakis DI, Kouvarakis A, Papadakis AK, Stephanou EG, Roubelakis-Angelakis KA (2006) Abiotic stress generates ROS that signal expression of anionic glutamate dehydrogenases to form glutamate for proline synthesis in tobacco and grapevine. Plant Cell 18:2767–2781
Szabados L, Savouré A (2010) Proline: a multifunctional amino acid. Trends Plant Sci 15:89–97
Tang X, Wang H, Shao C, Shao H (2015) Global gene expression of Kosteletzkya virginica seedling responding to salt stress. PLoS One 10:e0124421
Wang H, Tang X, Wang H, Shao HB (2015) Proline accumulation and metabolism-related genes expression profiles in Kosteletzkya virginica seedlings under salt stress. Front Plant Sci 6:792
Weretilnyk EA, Hanson AD (1986) Betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase from spinach leaves: purification, in vitro translation of the mRNA and regulation by salinity. Arch Biochem Biophys 271:56–63
Yang Q, Li Z, Lu X, Duan Q, Huang L, Bi J (2018) A review of soil heavy metal pollution from industrial and agricultural regions in China: pollution and risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 642:690–700
Yao WQ, Lei YK, Yang P, Li QS, Wang LL, He BY, Xu ZM, Zhou C, Ye HJ (2018) Exogenous glycinebetaine promotes soil cadmium uptaker by edible amaranth grown during subtropical hot season. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15:1794
Zegaoui Z, Planchais S, Cabassa C, Djebbar R, Belbachir OA, Carol P (2017) Variation in relative water content, proline accumulation and stress gene expression in two cowpea landraces under drought. J Plant Physiol 218:26–34
Zhang L, Becker DF (2015) Connecting proline metabolism and signaling pathways in plant senescence. Front Plant Sci 6:552
Zhang C, Shi S, Liu Z, Yang F, Yin G (2019) Drought tolerance in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) varieties is associated with enhanced antioxidative protection and declined lipid peroxidation. J Plant Physiol 232:226–240
Zhou MX, Dailly H, Renard ME, Han RM, Lutts S (2018a) NaCl impact on Kosteletzkya pentacarpos seedlings simultaneously exposed to cadmium and zinc toxicities. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:17444–17456
Zhou MX, Han RM, Ghnaya T, Lutts S (2018b) Salinity influences the interactive effects of cadmium and zinc on ethylene and polyamine synthesis in Kosteletzkya pentacarpos. Chemosphere 209:892–900
Zhou MX, Ghnaya T, Dailly H, Cui G, Vanpee B, Han R, Lutts S (2019) The cytokinin trans-zeatine riboside increased resistance to heavy metals in the halophyte plant species Kosteletzkya pentacarpos in the absence but not in the presence of NaCl. Under review in Chemosphere
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Dr. P. Qin (University of Nanjing) for providing the seeds. Mingxi ZHOU is grateful to the CSC (China scholarship council) for the award of a research fellowship. This article is devoted to the memory of Professor Gilles Guerrier (Université d’Orléans, France).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Juan Barcelo.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 76 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, MX., Renard, ME., Quinet, M. et al. Effect of NaCl on proline and glycinebetaine metabolism in Kosteletzkya pentacarpos exposed to Cd and Zn toxicities. Plant Soil 441, 525–542 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-019-04143-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-019-04143-5